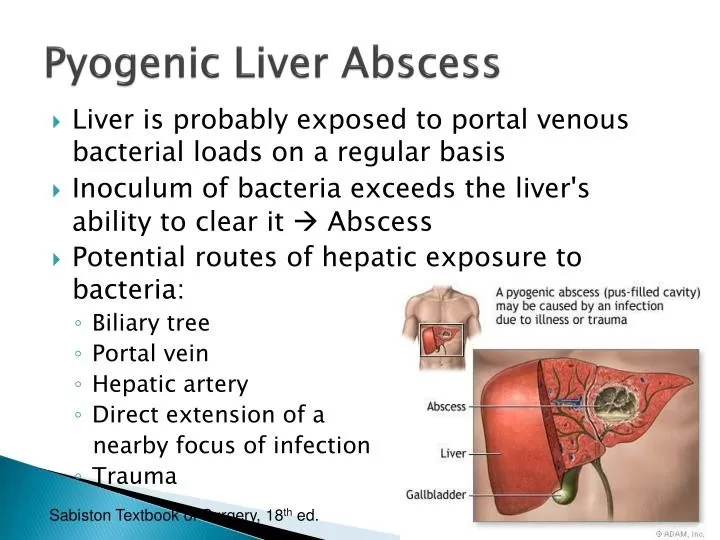
Syphilis and pyogenic liver abscess are two medical conditions that, while seemingly unrelated, can intersect in rare and clinically significant ways. Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium *Treponema pallidum*, is notorious for its wide-ranging symptoms, complicating diagnosis and treatment. In rare instances, it can lead to severe complications such as a pyogenic liver abscess, which is an accumulation of pus within the liver due to infection. This case illustrates the importance of recognizing syphilis symptoms and understanding liver abscess causes, particularly in populations at risk for sexually transmitted infections. Timely syphilis diagnosis can be crucial for preventing such life-threatening conditions, underscoring the need for vigilant screening and awareness.
The intersection of syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection, and pyogenic liver abscess, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by bacterial infection in the liver, may not be immediately obvious. In this context, it’s vital to explore the symptoms of syphilis and the subsequent complications that can arise, such as the formation of liver abscesses. Often overlooked, syphilis diagnosis plays a significant role in managing health risks, especially for individuals with compromised immune systems or those engaging in high-risk behaviors. Understanding the potential liver abscess causes, such as infections that stem from untreated syphilis, can enhance the approach to clinical care. Addressing these interconnected health issues can lead to better patient outcomes and highlight the importance of infection control measures.
Understanding Syphilis: Symptoms and Stages
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by *Treponema pallidum*, a spirochete bacterium known for its complex and varied symptoms that challenge accurate diagnosis. The disease progresses through four significant stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. In the primary stage, a chancre or sore appears at the site of infection, often going unnoticed. As the infection advances to secondary syphilis, patients may experience a widespread rash and systemic symptoms such as fever and swollen lymph nodes. The subtlety and diversity of syphilis symptoms demand high suspicion and effective screening measures to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
Each stage of syphilis presents unique challenges for healthcare practitioners. The secondary stage, for instance, may be characterized by systemic signs that can mimic other conditions, complicating the diagnostic process. Tertiary syphilis poses even greater risks, as it can lead to severe complications involving multiple organ systems, including the liver. Although uncommon, syphilitic hepatitis can occur and may present as an elevated alkaline phosphatase level, thereby prompting further investigation into possible liver abscess causes.
The Rare Connection between Syphilis and Pyogenic Liver Abscess
The case of syphilis manifesting as a pyogenic liver abscess, as reported by Meyer and Granada, highlights a rarely documented clinical presentation of this sexually transmitted infection. Although rare, the liver can be involved in syphilis, leading to complications like hepatic gummas or syphilitic hepatitis. In the case discussed, a 52-year-old man presented with significant liver enzyme elevations and an abdominal mass, ultimately diagnosed as a benign abscess associated with secondary syphilis. This connection between syphilis and liver pathology underscores the need for thorough diagnostic strategies when patients exhibit atypical liver dysfunction.
Pyogenic liver abscesses are often caused by a variety of infectious agents, but the identification of *Treponema pallidum* as a causal factor presents a unique challenge. The patient’s history of well-controlled HIV further complicates the clinical picture, as immunocompromised individuals may experience atypical presentations of common infections. This case serves as a potent reminder of the importance of considering sexually transmitted infections in differential diagnoses, particularly when evaluating patients for unexplained liver abnormalities and elevated liver enzymes.
Screening for Syphilis: Importance in High-Risk Populations
Given the potential for rare manifestations of syphilis, such as liver abscesses, appropriate screening is vital, especially in high-risk populations. The case highlighted in the research illustrates the importance of routine syphilis testing in individuals at increased risk due to factors like HIV infection. Early identification and treatment of syphilis not only help to mitigate individual health risks but also contribute to broader public health efforts aimed at reducing transmission rates within communities.
Screening strategies should be enhanced to include comprehensive blood work, especially in patients who report elevated liver enzyme levels or other related symptoms. Regular follow-ups and thorough evaluations of sexual health history can aid practitioners in recognizing trends that may signal underlying syphilis infection. In addition to standard tests like the rapid plasma reagin (RPR), clinicians may consider newer diagnostic methods to ensure appropriate detection of *Treponema pallidum* and its complications.
Clinical Manifestations: Diagnosing Secondary Syphilis
The diagnosis of secondary syphilis demands careful consideration of clinical manifestations and laboratory results. As demonstrated in the reported case, symptoms such as elevated liver enzymes and the presence of abdominal masses should trigger a comprehensive evaluation for syphilis, particularly among populations with a known risk profile. The complexity of diagnosing secondary syphilis lies in its ability to mimic other systemic infections, necessitating clinicians remain vigilant and informed regarding the disease’s diverse presentations.
Additionally, laboratory tests such as serologies for syphilis antibodies are critical in establishing the diagnosis. The combination of positive RPR results and confirmation via PCR testing becomes essential in rare cases where liver abscess is suspected. This thorough diagnostic process not only facilitates appropriate treatment but may also reveal more extensive complications, thereby improving overall management strategies for patients with secondary syphilis.
Implications of Hepatic Involvement in Syphilis
Involvement of the liver in syphilis is a significant clinical concern, given its potential repercussions on patient health. The case of the individual with pyogenic liver abscess underscores the implications of such hepatic involvement, which may necessitate advanced imaging studies and further diagnostic procedures to elucidate the underlying pathology. This highlights the necessity for healthcare providers to remain attentive to the possibility of hepatic abscesses as a sequela of syphilis, particularly in patients with compromised immune systems.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of liver disease associated with syphilis is imperative for ensuring prompt intervention. Given that syphilitic hepatitis can lead to severe liver damage or complications such as liver abscesses, timely diagnosis and treatment may significantly influence patient outcomes. Regular liver function tests in high-risk individuals, coupled with proactive syphilis screening, can lead to improved health management practices and inform strategies to control the spread of infection.
Leverage of Modern Diagnostics in Syphilis Detection
The advent of advanced diagnostic techniques has transformed the landscape of syphilis detection and diagnosis. Traditional laboratory tests are being complemented by molecular techniques such as 16S rDNA and 28S rDNA PCR, which can provide precise identification of *Treponema pallidum* in complex cases like pyogenic liver abscess. These modern approaches enhance the sensitivity and specificity of syphilis testing, allowing healthcare providers to confirm diagnoses even in atypical presentations.
Utilizing a combination of serological and molecular diagnostics not only increases the rates of accurate diagnoses but also supports a comprehensive understanding of the disease’s epidemiology. As healthcare systems seek to optimize their infection control efforts, integrating these advanced diagnostics into routine clinical practice for high-risk populations becomes essential. With the ongoing challenges presented by syphilis resurgence, refining diagnostic capabilities is key to effectively addressing this public health issue.
Empirical Treatment of Liver Abscess: A Case Perspective
The treatment of a liver abscess linked to syphilis requires a nuanced approach, particularly as illustrated by the case of the man who received empirical treatment with antibiotics like ciprofloxacin and metronidazole. Given the complexity of the patient’s clinical picture, including concurrent shigellosis, the choice of empirical therapy reflects a commitment to addressing potential polymicrobial infections while awaiting definitive diagnoses. Understanding the appropriate use of antibiotics in cases where syphilis is a potential underlying cause is crucial, as the treatment regimen may need adjustments based on ongoing diagnostic findings.
Moreover, timely intervention is critical in cases of liver abscess due to the risk of serious complications. The administration of benzathine penicillin for syphilis treatment, as noted in this case, highlights the importance of addressing the underlying infectious process while managing the abscess itself. This comprehensive treatment strategy illustrates the imperative of collaboration between infection specialists and primary healthcare providers in managing such complex cases effectively.
Prevention and Education: Combating Syphilis Spread
Preventing the spread of syphilis, particularly in high-risk populations, is essential to combatting the resurgence of this infection. Awareness and education campaigns focusing on the symptoms of syphilis and the importance of regular screenings can significantly influence health outcomes. Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in disseminating information about safe sex practices, encouraging patients to seek testing and treatment as needed.
Additionally, community health initiatives targeting populations with elevated syphilis rates can enhance public awareness and promote proactive health behaviors. Engaging in discussions about sexually transmitted infections in a non-stigmatizing environment encourages more individuals to get tested and treated promptly. Through a combination of education, prevention strategies, and enhanced access to healthcare services, it is possible to reduce the incidence of syphilis and its associated complications, such as pyogenic liver abscess.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Syphilis Management
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in managing syphilis and associated conditions, such as pyogenic liver abscess. As frontline responders to public health challenges, it is imperative for providers to remain current with the latest epidemiological data, diagnostic techniques, and treatment guidelines for syphilis. This knowledge enhances their ability to offer informed care and effectively screen at-risk individuals, thereby preventing complications.
Furthermore, cultivating a supportive and open environment for discussing sexually transmitted infections encourages patients to communicate concerns and symptoms without hesitation. Providers’ vigilance in identifying potential syphilis-related complications can lead to early intervention, reducing morbidity associated with untreated infections. By prioritizing patient education and fostering trust, healthcare professionals can significantly contribute to the overall management of syphilis and its complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the link between syphilis and pyogenic liver abscess?
Syphilis, caused by the bacterium *Treponema pallidum*, can rarely lead to pyogenic liver abscess. This condition arises when there is hematogenous spread of the infection, potentially causing lesions in the liver, as seen in cases where secondary syphilis manifests with symptoms like elevated liver enzymes and liver abscess.
What are common syphilis symptoms that may indicate a pyogenic liver abscess?
Common syphilis symptoms include skin lesions, rashes, fever, and systemic signs. In cases where syphilis leads to pyogenic liver abscess, patients may present with abdominal pain, elevated alkaline phosphatase, and other liver function tests abnormalities.
How is syphilis diagnosed when a pyogenic liver abscess is suspected?
Diagnosis of syphilis in patients with suspected pyogenic liver abscess includes serological tests for *Treponema pallidum*, such as rapid plasma reagin (RPR) testing and treponemal antibody tests. Imaging studies can also reveal liver lesions that may prompt further investigation into underlying infections.
What are the liver abscess causes, specifically related to syphilis?
While syphilis is a rare cause of liver abscess, it can develop due to secondary syphilis leading to syphilitic hepatitis. This condition can present as a liver abscess when there is a significant inflammatory response or necrosis, possibly involving a pyogenic process.
What are the signs of syphilitic hepatitis that could lead to a liver abscess?
Signs of syphilitic hepatitis may include jaundice, abdominal pain, fever, and systemic symptoms like weight loss and fatigue. These symptoms can sometimes indicate the presence of a liver abscess or significant liver involvement, necessitating further evaluation.
Can pyogenic liver abscess occur in patients with HIV and syphilis?
Yes, pyogenic liver abscess can occur in patients with HIV, particularly when their immune response is compromised. In some cases, as reported, individuals with well-managed HIV can still develop complicated infections like those linked to syphilis, highlighting the need for thorough screening.
What is the treatment for a pyogenic liver abscess caused by syphilis?
Treatment typically involves broad-spectrum antibiotics to manage the infection, alongside specific treatment for syphilis, often with intramuscular benzathine penicillin. Surgical intervention may be required in cases where the abscess does not resolve with antibiotic therapy.
How rare is it for syphilis to cause a pyogenic liver abscess?
It is quite rare for syphilis to cause a pyogenic liver abscess. The medical literature reports only a few cases, underscoring the importance of considering this atypical presentation in patients with secondary syphilis who exhibit liver-related symptoms.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Syphilis as a Cause of Pyogenic Liver Abscess | This case highlights syphilis as a rare cause of pyogenic liver abscess, emphasizing the need for awareness and screening. |
| Clinical Details | A 52-year-old man with well-controlled HIV presented with abdominal symptoms, leading to the discovery of a liver abscess. |
| Diagnosis Approach | Diagnosis involved elevated liver enzymes, imaging studies (CT and MRI), and PCR testing for *T. pallidum*. |
| Treatment | The patient received benzathine penicillin after positive testing for syphilis, leading to improved liver function. |
| Importance of Screening | The case underscores the importance of screening for syphilis in high-risk populations, especially when presenting with liver lesions. |
Summary
Syphilis and pyogenic liver abscess is an uncommon yet crucial linkage that requires greater awareness in clinical practice. This case illustrates how syphilis can manifest as a liver abscess, particularly in patients with underlying conditions like HIV. It emphasizes the necessity of screening for syphilis, especially among high-risk populations, to ensure prompt diagnosis and treatment. Clinicians should remain vigilant in considering syphilis as a potential cause of unusual symptoms, including liver abscesses, to optimize patient outcomes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.