Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak modeling has emerged as a crucial tool in understanding the dynamics of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) transmission, particularly in the context of the recent Uganda Sudan Ebola outbreak in 2022. By leveraging advanced individual-based modeling techniques, researchers have been able to estimate the potential case burden and duration of the outbreak, providing valuable insights for public health officials. The case burden of the Sudan Ebola virus emphasizes the need for effective interventions, as the disease has been linked to high mortality rates, contributing to a significant death toll during previous EVD outbreaks. This modeling approach not only aids in predicting the outbreak’s trajectory but also highlights the importance of timely and efficient response strategies in mitigating the spread of infection. As the threat of Ebola persists, robust outbreak modeling is essential for informed decision-making in managing Ebola Virus Disease in Uganda and beyond.
The modeling of disease outbreaks, particularly those involving the Sudan Ebola virus, plays a vital role in assessing public health impacts and crafting responsive strategies. In the event of a viral outbreak, such as the EVD outbreak seen in Uganda, researchers deploy sophisticated computational frameworks to anticipate case loads and the duration of the crisis. These forecasts are instrumental in understanding the disease’s progression and inform necessary interventions to contain transmission. By utilizing models that account for factors such as population interactions and demographic diversity, health authorities can better strategize their responses to mitigate the health impacts of Ebola virus disease. Thus, modeling the Sudan Ebola case burden not only serves as a predictive measure but also underscores the urgency and importance of swift public health responses.
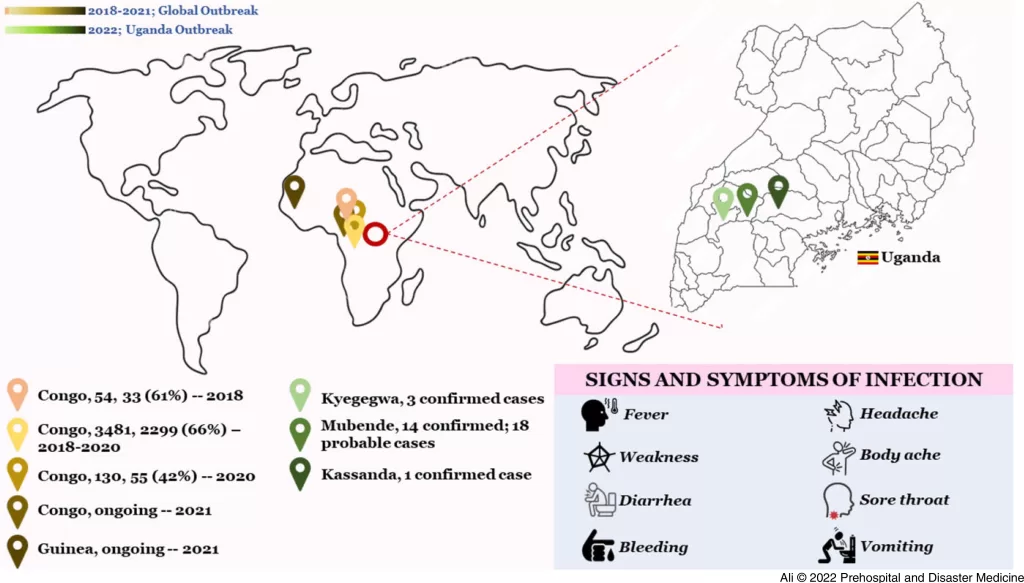
Understanding the 2022 Sudan Ebola Virus Outbreak in Uganda
In September 2022, an outbreak of Sudan Ebola virus was confirmed in the Mubende District of Uganda, marking a critical public health concern. The rapid escalation of cases, with spread to eight other districts, raised alarms among health officials and the community alike. Initial reports indicated a significant burden from the outbreak, with international scrutiny over the effectiveness of Uganda’s health responses. Efforts were directed towards controlling the disease, yet the nature of the Sudan Ebola case burden highlighted the complexities involved in managing such outbreaks.
The outbreak posed not only an immediate threat to public health but also raised questions about the preparedness of healthcare systems in Uganda and neighboring regions. With historical context showing a pattern of Ebola Virus Disease outbreaks in Africa, including the recognized Uganda Sudan Ebola outbreak occurrences, this incident urged health authorities to implement stringent measures effectively. Understanding the dynamics of the EVD burden, especially in densely populated cities, proved paramount in formulating effective interventions to mitigate the impact of this deadly virus.
Modeling Disease Outbreaks: Insights from the Sudan Ebola Virus Case
The development of the individual-based modeling (IBM) framework for the Sudan Ebola virus outbreak was instrumental in predicting the spread and potential impact of the disease. This innovative approach utilized detailed demographic data and incorporated varying community interactions, crucial for accurately estimating the outbreak’s trajectory. Past EVD outbreak modeling in Uganda provided essential lessons, enabling more tailored responses, particularly in regions with rapid case inflations.
By adapting an IBM previously used for other diseases, researchers could estimate key metrics such as case numbers, deaths, and the outbreak’s duration. Projected outcomes indicated that immediate intervention could significantly reduce the case burden, emphasizing the necessity of prompt and effective public health responses during an EVD outbreak. The findings from the Sudan Ebola modeling exercise not only contributed to understanding this specific outbreak but also laid a foundation for future modeling efforts in similar scenarios across Uganda and beyond.
EVD Outbreak Modeling: Lessons Learned from Past Incidents
Ebola Virus Disease outbreaks have historically affected multiple regions of Africa, necessitating extensive studies in outbreak modeling to inform response strategies. Insights derived from previous incidents such as the Uganda Sudan Ebola outbreak emphasized the importance of swift action to curb the spread of the virus. Learning from prior EVD experiences, health authorities and modelers were better equipped to develop robust intervention strategies, encompassing contact tracing, isolation, and public engagement efforts.
Each outbreak has unique characteristics that depict the dynamics of disease transmission; thus, continued refinement of EVD outbreak modeling techniques remains imperative. By analyzing data from past outbreaks, researchers can identify patterns and potential interventions that may effectively reduce morbidity and mortality rates associated with the disease. This proactive approach can significantly inform future public health responses, reducing overall fatalities and ensuring better outcomes during similar crises.
The Role of Nonpharmaceutical Interventions in Containing EVD
In light of the lack of effective treatments or vaccines against the Sudan Ebola virus, health authorities relied heavily on nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) as pivotal strategies to mitigate the outbreak. Such interventions included aggressive case isolation, contact tracing, and community education, creating a multifaceted approach to controlling disease transmission. The efficacy of these strategies was evident during the 2022 outbreak, highlighting how swift implementation of NPIs can drastically affect the outbreak’s trajectory.
Data from the modeling efforts revealed that NPIs could significantly alter the number of predicted cases and deaths in various scenarios. For instance, aggressive interventions kept the outbreak within manageable bounds, preventing far greater numbers of infected individuals. The ongoing need to emphasize NPIs as fundamental components of outbreak management and public health policy becomes clear, especially in regions where diseases like EVD pose a continual threat to health systems.
Impact of Early Response: A Case Study of the SUDV Outbreak
The rapid response by the Ministry of Health (MOH) in Uganda during the Sudan Ebola virus outbreak exemplifies the critical importance of timely intervention in controlling infectious diseases. Modeling predictions indicated that the prompt measures taken by health officials potentially averted thousands of cases and deaths. It underscores the necessity of an immediate and coordinated response, particularly in high-risk scenarios, to prevent exponential increases in case numbers.
Underestimated is often the ripple effect of a swift response, as seen through various models predicting dire outcomes without intervention. The success of the MOH demonstrates that calculated public health strategies can lead to favorable outcomes in even the most challenging situations. By prioritizing immediate action, health authorities can not only save lives but also stabilize community health, allowing for quicker recovery and resilience in future outbreaks.
Evaluating Case Burdens through Predictive Modeling Techniques
The evaluation of case burdens in infectious disease outbreaks like Sudan Ebola virus has greatly benefited from predictive modeling techniques. Utilizing individual-based models allowed researchers to simulate different outbreak scenarios and estimate potential case counts and fatalities accurately. The findings of the Sudan Ebola modeling study revealed significant insights into the expected burden, thus influencing decisions on interventions and public health policies.
The ability to accurately predict case burdens is not only crucial during an outbreak but also serves as a guide for long-term preparedness and response strategies. Through modeling, public health officials can better understand how various factors influence disease spread and subsequently allocate resources more effectively. Such modeling efforts are invaluable for guiding comprehensive planning and response frameworks that can adapt to various outbreak scenarios, helping to mitigate the effects of EVD and other similarly dangerous viral diseases.
Geographic Disparities in the Spread of EVD in Uganda
Geographic factors play a vital role in the spread of the Sudan Ebola virus within Uganda. The individual-based modeling framework utilized for the SUDV outbreak not only accounted for demographic data but also integrated geographic distribution and population movement. Such considerations are crucial for understanding how the virus can spill over from affected areas to densely populated regions, amplifying transmission risks.
EVD outbreaks reveal stark disparities within affected countries, often driven by variations in healthcare accessibility, population density, and local traditions regarding burial practices. Understanding these geographic disparities through modeling helps policymakers create targeted interventions that account for local conditions, ultimately leading to a more effective containment of EVD spread and enhancing the overall response to future outbreaks.
The Future of EVD Research and Modeling
Looking forward, the modeling of the Sudan Ebola virus outbreak has opened new avenues for research and public health responses. As EVD remains a significant threat in several African nations, incorporating advanced data analytics and technology into outbreak modeling will be essential. Future studies should focus on integrating real-time data collection and epidemiological insights to enhance the responsiveness of outbreak responses.
The lessons learned from the Sudan Ebola outbreak and predictive modeling efforts will be instrumental in shaping future public health strategies. Ongoing collaboration between researchers, health authorities, and community stakeholders will be necessary to develop robust frameworks for mitigating the effects of EVD outbreaks. By refining modeling techniques and fostering knowledge exchange among stakeholders, it is possible to build sustainable systems capable of dealing with the complexities of future EVD threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak modeling in understanding Ebola outbreaks?
The Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak modeling plays a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of EVD outbreaks. By employing individual-based modeling platforms, researchers can estimate the case burden, forecast outbreak durations, and evaluate the impact of various intervention strategies. This modeling approach informed effective public health responses during the 2022 outbreak in Uganda, helping to verify the estimated number of cases and deaths along with their respective durations.
How does modeling disease outbreaks like the Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak contribute to public health strategies?
Modeling disease outbreaks, such as the Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak, helps public health authorities make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, intervention timing, and strategies for mitigating the spread of the virus. For instance, during the 2022 outbreak in Uganda, models projected the potential impact of different public health measures, enabling more efficient management of cases and enhancing the effectiveness of nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) like contact tracing and isolation.
What are the key findings related to the Sudan Ebola case burden from outbreak modeling?
Key findings from the Sudan Ebola outbreak modeling indicated that with immediate interventions in place, the median estimated number of cases was 193, with a possible maximum of 13,537 in uncontrolled scenarios. These findings underscore the model’s utility in estimating the case burden and its capacity to predict the epidemic curve, emphasizing the necessity for swift action to prevent massive outbreaks.
How did the model for the Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak account for population dynamics in Uganda?
The Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak model incorporated a geographic distribution of the Ugandan population, reflecting movement and contact patterns among different demographic groups. This consideration of local and regional population interactions was crucial for accurately simulating transmission dynamics, thereby enhancing the reliability of modeled predictions and informing targeted public health responses.
What impact can timely intervention have on the duration of the Sudan Ebola Virus Disease outbreak based on modeling studies?
Timely intervention has a significant impact on the duration of the Sudan Ebola Virus Disease outbreak. The modeling study indicated that effective responses could reduce the outbreak’s median duration to approximately 22 weeks, highlighting that swift action by health authorities can prevent extensive morbidity and mortality associated with delayed responses or uncontrolled scenarios.
What methodologies were used in the Sudan Ebola outbreak modeling to analyze EVD outbreaks?
The methodologies used in Sudan Ebola outbreak modeling involved an individual-based model (IBM) framework, which integrates empirical demographic data and contact networks among population groups. This approach allows for the simulation of transmission and the prediction of case outcomes based on varying intervention scenarios, providing a robust tool for assessing the potential trajectories of outbreaks like EVD.
Why is the Sudan Ebola outbreak modeling relevant for understanding future EVD outbreaks?
The Sudan Ebola outbreak modeling is relevant for understanding future EVD outbreaks as it provides insights into how various factors affect transmission and control measures. Lessons learned from the 2022 outbreak in Uganda can inform strategies for rapid response to similar outbreaks globally, enhancing preparedness and response strategies for potential future cases of Ebola Virus Disease in Uganda and beyond.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Outbreak Confirmation | The Sudan Ebola virus outbreak was confirmed in Uganda on September 20, 2022. |
| Modeling Approach | An individual-based modeling (IBM) platform was developed to estimate cases, deaths, and duration of the outbreak. |
| Case Projections | With NPIs, the baseline scenario estimated 193 cases and 81 deaths; uncontrolled scenario estimated 13,537 cases and 5,279 deaths. |
| Outbreak Duration | Median duration estimated at 22 weeks under intervention; uncontrolled scenario would have extended duration significantly. |
| Intervention Strategies | The Ministry of Health employed NPIs such as isolation, contact tracing, safe burials, and lockdowns. |
| Conclusion | Effective and timely responses by health authorities were critical in averting a potential larger outbreak. |
Summary
Sudan Ebola Virus outbreak modeling played a crucial role in understanding the potential burden and duration of the outbreak in Uganda in 2022. By using an individual-based modeling approach, the study demonstrated that prompt interventions by local health authorities significantly reduced the number of expected cases and deaths. The model provided insights that highlighted the importance of immediate response measures, showcasing how vital they are in controlling outbreaks, particularly when dealing with a highly lethal pathogen like the Sudan Ebola virus.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.