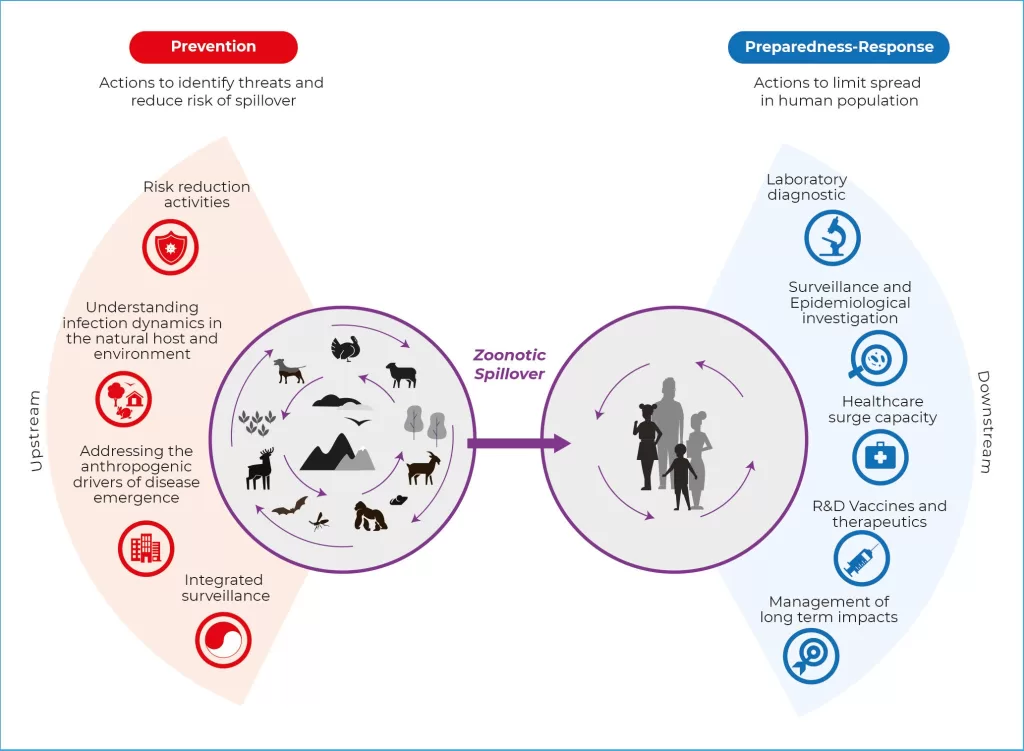
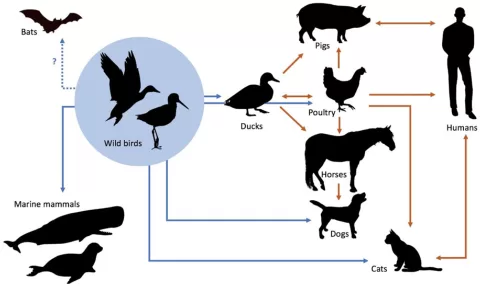
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the concept of spillover prevention has gained unprecedented importance as public health officials recognize the need to protect human populations from emerging infectious diseases. Spillover events, where pathogens jump from animals to humans, are often the first step in the chain of zoonotic transmissions that can trigger global health crises. To enhance pandemic preparedness, it is crucial to focus on innovative strategies that reduce the risk of these spillover incidents, especially with pathogens like Hendra and Nipah viruses haunting us with their potential for severe outbreaks. By investing in One Health investigations, we can gain valuable insights into the ecological dynamics that facilitate spillover and implement effective interventions. Ultimately, prioritizing spillover prevention is not merely a reactive measure; it’s an essential proactive approach towards safeguarding lives and enhancing global health security.
As we delve deeper into the realm of preventing infectious disease transmission, it becomes essential to explore various mechanisms that lead to the encroachment of zoonotic pathogens into human populations. The proactive strategies for mitigating spillover risks include interdisciplinary approaches that align veterinary, environmental, and human health perspectives, often referred to collectively as One Health initiatives. By understanding the intricate relationships between wildlife, livestock, and human activities, researchers can identify critical intervention points that may avert potential outbreaks. Recognizing how pathogens like the Nipah virus interact with their reservoirs illustrates the delicate balance within ecosystems that can either facilitate or hinder pathogen transmission. This nuanced understanding of spillover dynamics not only enhances our readiness for future pandemics but also ensures a more comprehensive strategy in global health preparedness.
Understanding Spillover Prevention in Pandemic Preparedness
Spillover prevention plays a pivotal role in enhancing pandemic preparedness. This concept revolves around the proactive measures that aim to stop zoonotic diseases from crossing over from animals to humans. The significance of spillover prevention has been spotlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic, where the transmission of zoonotic viruses led to widespread global health crises. By focusing on early detection and intervention strategies, we can drastically reduce the chances of viral spillovers, which are often the initial step toward a pandemic. Surveillance of wildlife and their interactions with humans is crucial for identifying potential spillover events before they happen.
Moreover, lessons learned from past zoonotic spills, particularly with viruses like Hendra and Nipah, illustrate the importance of immediate response mechanisms. Effective spillover prevention requires a holistic approach that integrates veterinary health, environmental science, and human medicine. Implementing this One Health strategy allows for a more comprehensive understanding of how pathogens function across different species and environments, fostering a preventive culture within public health policy.
The Role of One Health Investigations in Containing Zoonotic Diseases
One Health investigations are essential to understanding the complexities of zoonotic diseases, as they promote collaboration among diverse fields such as wildlife biology, public health, and veterinary medicine. This interdisciplinary approach enables experts to analyze how pathogens can jump from animals to humans. When researchers conduct spillover investigations, they focus not only on the pathogens themselves but also on the ecological and social factors that contribute to the risk of transmission. This comprehensive understanding is vital for developing effective prevention and control measures.
Through thorough surveillance and investigation of zoonotic diseases, we gain insight into transmission pathways, such as those seen with Hendra and Nipah viruses. This information can lead to practical interventions, such as altering human-animal interactions or implementing environmental management strategies that minimize disease risk. Ultimately, investing in One Health investigations equips us to create a robust framework for future pandemic prevention and ensures a well-prepared response strategy.
Case Studies: Lessons from Hendra and Nipah Virus Spillovers
The spillover investigations of the Hendra virus highlight the link between ecological changes and increased pandemic risk. In Australia, changing environmental conditions and food shortages altered bat behaviors, leading them to closer contact with human populations. By closely monitoring these interactions and understanding the ecological triggers for spillover, public health officials can implement targeted measures to mitigate these risks, such as habitat management and public awareness campaigns about the risks of zoonotic diseases.
Similarly, the Nipah virus case study emphasizes the importance of practical interventions at the community level. Simple methods, like using pot covers to protect date palm sap from bat contamination, have proven effective in preventing transmission. These low-tech solutions demonstrate that community engagement and education are crucial elements in spillover prevention strategies. By integrating local knowledge with scientific research, we can create a roadmap for comprehensive pandemic preparedness that emphasizes prevention and preparedness through evidenced-based community practices.
The Importance of Interdisciplinary Approaches in Pandemic Preparedness
Successful pandemic preparedness hinges on interdisciplinary approaches that encompass veterinary, ecological, and public health sectors. These intersections are where the One Health framework truly shines, as different fields contribute unique perspectives on zoonotic diseases. By fostering collaboration among various sectors, we can develop comprehensive strategies to not only detect potential spillover events but also to understand the broader environmental influences that contribute to them. Interdisciplinary dialogues promote innovation in disease prevention methodologies and lead to better outcomes in managing public health crises.
Furthermore, the integration of diverse expertise enhances our ability to respond to emerging infectious diseases. For instance, veterinary epidemiologists can work alongside wildlife biologists to monitor animal populations and behaviors that pose a spillover risk. Additionally, involving local communities in these investigations helps translate scientific data into actionable public health measures that resonate with affected populations. By uniting these various disciplines under a collaborative umbrella, we create a stronger front in the fight against pandemics.
The Challenges of Detecting Zoonotic Spillovers Early
Despite advancements in technology and methodology, detecting zoonotic spillovers early remains a complex challenge. One of the primary hurdles is the often asymptomatic nature of many zoonotic pathogens, which means transmission can occur undetected before a significant outbreak arises. Moreover, the environmental conditions that facilitate spillovers are constantly changing due to factors such as climate change, urbanization, and agricultural practices. These dynamics complicate surveillance efforts and necessitate ongoing adaptations in our approaches to monitoring potential zoonotic threats.
To overcome these challenges, it is essential to enhance surveillance systems that incorporate real-time data from various ecosystems and zoonotic reservoirs. Digital tracking tools can improve monitoring effectiveness, while community-based reporting can heighten awareness about potential spillover incidents in local contexts. Addressing the gaps in early detection not only requires technological advancements but also a commitment to fostering partnerships between researchers, policymakers, and communities, ensuring that we remain vigilant in our efforts to prevent pandemics at their source.
Implementing Effective Surveillance Systems for Early Detection
Creating effective surveillance systems is key to early detection of zoonotic diseases and preventing spillover events. These systems should incorporate data from diverse sources, including wildlife health monitoring, environmental assessments, and human health reports. By analyzing this pooled data, health authorities can identify emerging hotspots where zoonotic transmission is likely to occur, guiding targeted intervention measures. Enhanced surveillance strategies that integrate technological advancements, such as GIS mapping and machine learning models, can significantly increase our ability to predict and respond to potential spillover risks.
Furthermore, collaboration with local communities plays a vital role in the success of surveillance initiatives. Engaging local stakeholders—such as farmers, wildlife workers, and healthcare providers—allows for a more comprehensive understanding of zoonotic dynamics in specific regions. Training these community members in recognizing signs of disease and reporting unusual animal behaviors can transform local knowledge into a valuable resource for broader public health efforts. This grassroots approach not only strengthens surveillance systems but also fosters a culture of shared responsibility in pandemic prevention.
Community Engagement: A Key Element in Pandemic Preparedness
Community engagement is a critical factor in enhancing pandemic preparedness and spillover prevention strategies. By creating awareness among communities about zoonotic diseases and their transmission pathways, we empower individuals to take proactive measures to protect themselves and their neighbors. Education initiatives can focus on promoting safe practices, such as handling animals, food preparation, and recognizing symptoms of zoonotic infections. Furthermore, fostering open channels of communication between health authorities and local populations can lead to timely reporting of unusual disease events.
In the context of spillover prevention, communities play an essential role in monitoring wildlife populations and their interactions with human environments. Training local residents on how to observe and report potential health threats enables a real-time surveillance network fueled by individuals who are most familiar with their local ecosystems. This community-based approach helps bridge the gap between scientific research and practical applications, ensuring that prevention policies are culturally and geographically tailored to the populations they are designed to protect.
The Future of Pandemic Preparedness: Lessons Learned
The COVID-19 pandemic has illuminated critical lessons about the importance of preparedness, particularly regarding the prevention of zoonotic diseases. Moving forward, it is crucial to focus on developing comprehensive frameworks that incorporate the lessons learned from past spillover events. By refining our approaches to pandemic preparedness, we can ensure that our strategies effectively address the identified risk factors, emphasizing spillover prevention as a priority in both research and policy-making.
Additionally, fostering global partnerships is key to creating a unified front against pandemics. Collaborative efforts among nations can enhance information sharing about zoonotic disease outbreaks and the response strategies that are proving effective. This global perspective not only facilitates better resource allocation but also strengthens capacity building in less resourced areas, promoting resilience against potential future pandemics driven by spillover events. The future of pandemic preparedness lies in leveraging our collective knowledge to build robust systems that prioritize prevention and enable swift responses to new threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is spillover prevention and why is it important in pandemic preparedness?
Spillover prevention refers to strategies aimed at stopping pathogens, particularly zoonotic diseases, from transferring from animals to humans. It is crucial in pandemic preparedness because it helps to avert outbreaks before they can spread through human populations, thereby minimizing the risk of future pandemics.
How do One Health investigations contribute to spillover prevention?
One Health investigations integrate expertise from human health, veterinary science, and environmental studies to understand the dynamics of zoonotic diseases. By studying spillover events, such as those involving the Hendra and Nipah viruses, these investigations provide critical insights that inform effective spillover prevention strategies.
What role do zoonotic diseases play in spillover prevention strategies?
Since most pandemics are caused by zoonotic diseases, understanding their origins and transmission pathways is essential for spillover prevention. Identifying potential spillover events allows for targeted interventions that can reduce the risk of zoonotic pathogens reaching human populations.
Can you provide examples of successful spillover prevention related to Hendra and Nipah viruses?
Yes, successful spillover prevention has been observed in the Hendra virus investigations in Australia, where identifying unusual bat behavior led to proactive measures. Similarly, in Bangladesh, the use of pot covers to protect date palm sap from bat contamination significantly lowered Nipah virus transmission to humans.
What are the implications of ignoring spillover prevention in pandemic planning?
Ignoring spillover prevention can lead to a higher risk of pandemics as pathogens continue to emerge from wildlife reservoirs. Effective pandemic planning must prioritize spillover detection and investigation to mitigate future public health threats stemming from zoonotic diseases.
How can communities implement spillover prevention measures?
Communities can implement spillover prevention by engaging in education about zoonotic risks, promoting safe practices for interacting with wildlife, and supporting One Health investigations that monitor disease emergence in local ecosystems.
What is the importance of comprehensive contact tracing in spillover prevention?
Comprehensive contact tracing plays a vital role in spillover prevention as it helps identify how zoonotic pathogens reach humans. By understanding transmission pathways, health authorities can develop interventions that specifically target those routes to prevent future spillover events.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Pandemic Preparedness | Increased focus on pandemic preparedness since COVID-19. |
| Spillover Prevention | Preventing pathogens from entering human populations is crucial. |
| One Health Approach | Involves transdisciplinary expertise to investigate spillovers. |
| Case Studies | Examples include Hendra and Nipah virus spillovers with specific environmental links. |
| Importance of Contact Tracing | Identifying exposures that lead to infection is essential for mitigation. |
| Conclusion | Investigating zoonotic spillovers is critical to mitigate pandemics. |
Summary
Spillover prevention is a crucial aspect of pandemic preparedness, which requires an intensified focus on identifying and investigating zoonotic spillover events. Effective strategies must be developed to prevent pathogens from entering human populations. This proactive approach will not only help in mitigating future pandemic risks but also enhance our understanding of public health threats arising from wildlife. A collaborative, One Health framework that leverages expertise from various fields is essential to achieve these goals, as demonstrated by significant case studies such as Hendra and Nipah viruses.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.