Shigella sonnei is a significant pathogen that has been increasingly implicated in Shigella outbreaks, particularly within sexual networks. This bacterium not only causes enteric illness but has also gained attention for its capability to be transmitted sexually, notably among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men (GBMSM). Recent genomic surveillance studies have revealed a worrying trend of antimicrobial resistance, particularly involving strains carrying the bla CTX-M-15 gene variant. As Shigella sonnei continues to spread within these populations, the urgency for effective public health interventions becomes clear. The rising incidence of this sexually transmitted infection underscores the importance of monitoring these strains to combat the growing threat posed by drug-resistant bacteria in our communities.
Shigella sonnei, responsible for an array of gastrointestinal infections, represents a serious public health concern, particularly throughout certain demographic groups. This pathogen has not only shown resilience but has also adapted to sexually transmitted avenues, making it critical for health surveillance efforts. Among populations like gay and bisexual men, conditions have allowed for the proliferation of multidrug-resistant strains, thus intensifying the risk of Shigella-related illnesses. As researchers delve into genomic surveillance, they uncover patterns of resistance that highlight the importance of understanding microbial evolution within these transmission networks. Recognizing how Shigella sonnei spreads and mutates is vital for formulating effective health policies and interventions.
Understanding Shigella Outbreaks: The Case of S. sonnei
Shigella outbreaks pose significant public health challenges, especially when associated with sexually transmitted infections. Shigella sonnei, a leading cause of shigellosis in the UK, has been particularly notable for its emergence within specific communities, including gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men (GBMSM). The nature of transmission in these networks underscores the importance of targeted public health strategies to prevent and control infections. As a result, understanding the epidemiology of Shigella outbreaks is crucial for effective intervention.
Recent genomic surveillance has revealed alarming trends regarding antimicrobial resistance in Shigella sonnei, with multiple variants of resistance genes documented. These insights highlight how outbreaks can evolve rapidly, with instances of extensively drug-resistant strains appearing in GBMSM populations. Public health authorities need to be vigilant and responsive to these changes, ensuring that screening and treatment protocols are adapted to mitigate the risks associated with Shigella outbreaks.
The Impact of Antimicrobial Resistance on GBMSM Health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a formidable challenge for managing the health of populations at risk, particularly within the GBMSM community. The emergence of Shigella sonnei strains that are resistant to standard treatments complicates the landscape of shigellosis management. Increased incidences of strains carrying resistance genes like bla CTX-M-15 highlight how selective pressures in sexual networks can accelerate the spread of resistant infections, threatening public health and individual wellbeing.
Addressing antimicrobial resistance within GBMSM networks requires a multifaceted approach, including improved education, screening, and treatment strategies tailored to these populations. Enhancing genomic surveillance can play a key role in tracking the emergence of resistant strains, enabling healthcare providers to implement targeted interventions that preserve the effectiveness of existing antibiotics and protect vulnerable individuals from severe health outcomes.
Genomic Surveillance: Unraveling Shigella sonnei Dynamics
Genomic surveillance serves as a critical tool in understanding the dynamics of Shigella sonnei transmission within affected communities. In recent studies, whole-genome sequencing has identified specific SNP linkage clusters, like t10.1814, providing insights into how infections are spreading among GBMSM populations. This level of detail can inform public health responses, allowing for more effective tracking of outbreaks and identification of potential hotspots for transmission.
The ability to harness genomic data to guide public health strategies is essential in an era of rising antimicrobial resistance. Continuous monitoring and analysis of Shigella sonnei genomes help elucidate patterns of resistance and transmission, leading to more informed interventions. This proactive approach not only aids immediate response efforts but also contributes to long-term strategies aimed at mitigating future outbreaks and improving overall health outcomes.
Addressing Trends Following COVID-19 Lockdowns
The impact of COVID-19 lockdowns has been profound, influencing various health behavior patterns, including the transmission dynamics of Shigella sonnei. As restrictions lifted, an increase in shigellosis cases among GBMSM was observed, raising concerns about heightened sexual activity contributing to a resurgence of infections. These post-lockdown trends underscore the necessity for heightened awareness and vigilance among at-risk populations, particularly in the context of sexually transmitted infections.
Healthcare providers and public health officials must adapt their strategies to the evolving landscape of STIs as society transitions back to pre-pandemic norms. Tailored educational campaigns and accessible screening options will be crucial in reducing the incident rates of Shigella sonnei infections and managing antimicrobial resistance effectively. By addressing these emerging patterns, public health systems can better protect vulnerable populations and mitigate the risks associated with sexually transmitted infections.
Public Health Strategies in Managing Shigella Outbreaks
Effective public health strategies are necessary to manage the rising cases of shigellosis attributed to Shigella sonnei. These strategies must focus on early detection, widespread screening, and education, particularly among populations at risk such as GBMSM. Engaging community leaders and utilizing existing health networks can facilitate awareness campaigns that educate individuals on symptoms, prevention, and the importance of seeking treatment.
Moreover, integrating genomic surveillance into routine public health practices will allow for a more dynamic response to emerging outbreaks. By continuously monitoring the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in Shigella strains, public health officials can adjust treatment guidelines and allocate resources effectively to contain outbreaks before they escalate. Mobilizing community resources and enhancing access to care are pivotal in controlling the public health threat posed by Shigella sonnei.
The Role of Screening in Shigella Prevention
Screening plays a critical role in preventing the spread of Shigella sonnei, especially in high-risk populations. Regular testing can help identify cases early and ensure that individuals receive prompt treatment, thereby reducing transmission rates. Targeted screening strategies tailored for GBMSM communities can help mitigate the incidence of sexually transmitted shigellosis, addressing a pressing need following the rise in cases post-lockdown.
Public health initiatives should also emphasize the importance of routine screening as part of comprehensive sexual health services. By effectively communicating the benefits of regular testing, health providers can encourage individuals to take proactive measures against infections like Shigella sonnei. Coupled with education on safe sexual practices, screening can significantly reduce the prevalence of shigellosis and its associated health consequences.
Raising Awareness About Shigellosis Risks
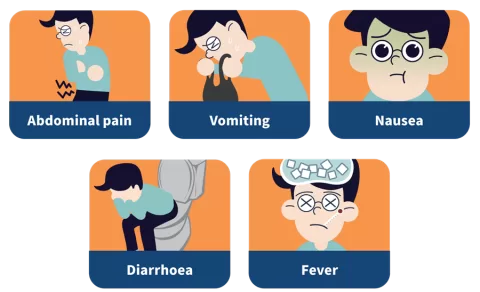
Raising awareness about the risks of Shigella infection within the GBMSM community is paramount in combatting the rising incidence of shigellosis. Misinformation and stigma surrounding STIs can often deter individuals from seeking testing and treatment. Public health campaigns must focus on destigmatizing shigellosis and promoting an understanding of its health implications, including the long-term effects of antimicrobial resistance.
Education should emphasize the signs and symptoms of shigellosis and the importance of seeking medical attention if suspected. Engaging community leaders and influencers in these campaigns can enhance reach and foster a supportive environment that encourages open discussions about sexual health. By proactively addressing these issues, public health efforts can significantly improve health outcomes for at-risk populations.
Future Directions in Shigella Research
Future research directions in Shigella sonnei management should prioritize innovative approaches to combat the rising tide of antimicrobial resistance. Investigating alternative treatment modalities, including phage therapy and novel antibiotics, could provide valuable insights into managing resistant strains effectively. Moreover, continued genomic surveillance will be essential in monitoring the evolution of resistance and transmission pathways.
Collaboration between researchers, public health authorities, and community organizations can facilitate the advancement of strategies aimed at preventing and controlling shigellosis outbreaks. By fostering an interdisciplinary approach to Shigella research, stakeholders can ensure that the most pressing public health challenges are addressed proactively, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for vulnerable populations.
Enhanced Surveillance for Effective Outbreak Control
Enhanced surveillance systems are critical for effectively controlling Shigella outbreaks, especially in light of the evolving resistance patterns seen in Shigella sonnei. Implementing real-time data collection and analysis can provide immediate insights into outbreak dynamics, allowing for swift intervention strategies tailored to specific communities. Public health agencies must invest in strengthening these systems to ensure they can respond promptly to emerging threats.
Additionally, integrating multidisciplinary approaches within surveillance frameworks can enhance data sharing and collaboration among various public health entities. By fostering partnerships between genomic research teams and epidemiological investigators, more comprehensive strategies can be developed that address both the biological and social determinants of health that influence Shigella transmission among GBMSM.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Shigella sonnei and why is it significant in sexually transmitted infections among GBMSM?
Shigella sonnei is a bacterial pathogen that causes shigellosis, leading to gastrointestinal illness. It is particularly significant among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men (GBMSM) as it can be sexually transmitted. The rising prevalence of Shigella sonnei within these networks highlights the need for targeted public health interventions.
How has antimicrobial resistance impacted Shigella sonnei outbreaks?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has significantly impacted Shigella sonnei outbreaks, with strains like bla CTX-M-15 showing increasing prevalence. The emergence of extensively drug-resistant Shigella strains raises concerns about treatment options, making effective public health surveillance and alternative treatment strategies more crucial.
What role does genomic surveillance play in understanding Shigella sonnei infections?
Genomic surveillance is vital in tracking the evolution and spread of Shigella sonnei, particularly in identifying antimicrobial resistance traits, such as those linked to bla CTX-M variants. This approach helps public health officials monitor outbreaks and implement timely interventions to control the spread.
Why has there been an increase in Shigella sonnei cases among GBMSM since 2022?
The increase in Shigella sonnei cases among GBMSM since 2022 can be attributed to various factors, including changes in sexual behaviors post-COVID-19 lockdowns and the emergence of more transmissible and resistant strains within sexual networks, necessitating a focus on targeted health education.
What is the t10.1814 SNP linkage cluster related to Shigella sonnei infections?
The t10.1814 SNP linkage cluster represents a specific genetic grouping of Shigella sonnei that has been linked to a surge in cases among sexually active individuals. This cluster is significant as it indicates a rise in antibiotic resistance and highlights the need for ongoing genomic surveillance to track its spread.
How can health authorities effectively manage Shigella sonnei outbreaks in GBMSM communities?
To effectively manage Shigella sonnei outbreaks within GBMSM communities, health authorities should enhance screening methods, promote awareness about shigellosis risks, and implement targeted prevention strategies. Ongoing genomic surveillance is also critical in tracking resistant strains and informing public health responses.
What preventive measures can be taken to reduce Shigella sonnei transmission within sexual networks?
Preventive measures to reduce Shigella sonnei transmission in sexual networks include promoting safe sexual practices, increasing testing and screening for sexually transmitted infections, and providing education on hygiene and infection risks related to shigellosis.
What are the implications of the increase in Shigella sonnei cases linked to the bla CTX-M-15 gene?
The increase of Shigella sonnei cases linked to the bla CTX-M-15 gene variant suggests an alarming trend of rising antimicrobial resistance. This situation underscores the urgent need for enhanced public health measures, including improved surveillance and education efforts targeted at high-risk populations.
What impact did COVID-19 lockdowns have on Shigella sonnei infections among GBMSM?
COVID-19 lockdowns have markedly impacted Shigella sonnei infections among GBMSM, leading to a surge in cases post-lockdown. Changes in sexual activities and behaviors during and after this period significantly contributed to the increased transmission of this pathogen.
Why is it important to raise awareness about shigellosis among at-risk populations?
Raising awareness about shigellosis among at-risk populations, particularly GBMSM, is crucial for effective prevention and control of outbreaks. Increased knowledge about transmission, symptoms, and the importance of seeking timely medical care can help reduce incidence rates and inform health interventions.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview of Shigellosis | Bacterial infection leading to enteric illness, transmissible through sexual contact, notably among GBMSM. |
| Emerging Strains | Increase in extensively drug-resistant Shigella strains, particularly those with the bla CTX-M-27 gene variant. |
| Prevalence of bla CTX-M-15 | Surge in prevalence from 10% before 2022 to 33% in 2023 among isolates, indicating rising antimicrobial resistance. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | Diagnosis rates among MSM rose post-lockdowns, highlighting the crisis in Shigellosis due to changing sexual behaviors. |
| Genomic Research | Whole-genome sequencing revealed significant trends and the emergence of the t10.1814 SNP linkage cluster. |
| Public Health Implications | Emphasis on ongoing surveillance, enhanced screening, and awareness in GBMSM communities to combat rising cases. |
Summary
Shigella sonnei has emerged as a significant public health concern, particularly in sexually transmitted contexts among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men (GBMSM). The rise of extensively drug-resistant strains, particularly those carrying the bla CTX-M-15 gene, showcases the urgent need for enhanced surveillance and public health measures. The shifts in epidemiological patterns highlighted by increased case rates post-COVID-19 lockdowns necessitate a proactive approach to managing shigellosis, underscoring the importance of community awareness and effective screening methods.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.