Salmonella Enteritidis South Korea has emerged as a significant public health concern since 2020, particularly in relation to foodborne illnesses linked to poultry products. This specific lineage of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis has shown a troubling rise in outbreaks, leading to severe cases and fatalities. Genomic surveillance efforts have revealed that this lineage clusters within the Global IIa clade, suggesting potential cross-border transmission and emphasizing the need for enhanced monitoring of foodborne pathogens. With poultry safety being a critical issue, vigilance in tracking these Salmonella outbreaks is paramount to safeguard public health. As we analyze the genomic characteristics of these pathogens, we can better understand their spread and develop more effective prevention strategies against Salmonella Enteritidis in South Korea.
The rise of Salmonella Enteritidis in South Korea highlights ongoing challenges with food safety and health management regarding this notorious foodborne pathogen. Since its emergence in 2020, this specific serotype has been associated with alarming rates of transmission linked to poultry products, particularly eggs. The genomic underpinnings of these outbreaks are under close scrutiny to unveil patterns that may protect against future infections. Utilizing advanced genomic surveillance techniques can provide insight into the epidemiology of this enteric pathogen. With concerns mounting over the impacts of poultry safety on public health, understanding the lineage and behavior of Salmonella Enteritidis in South Korea becomes increasingly vital.
Emergence of Salmonella Enteritidis Lineage in South Korea
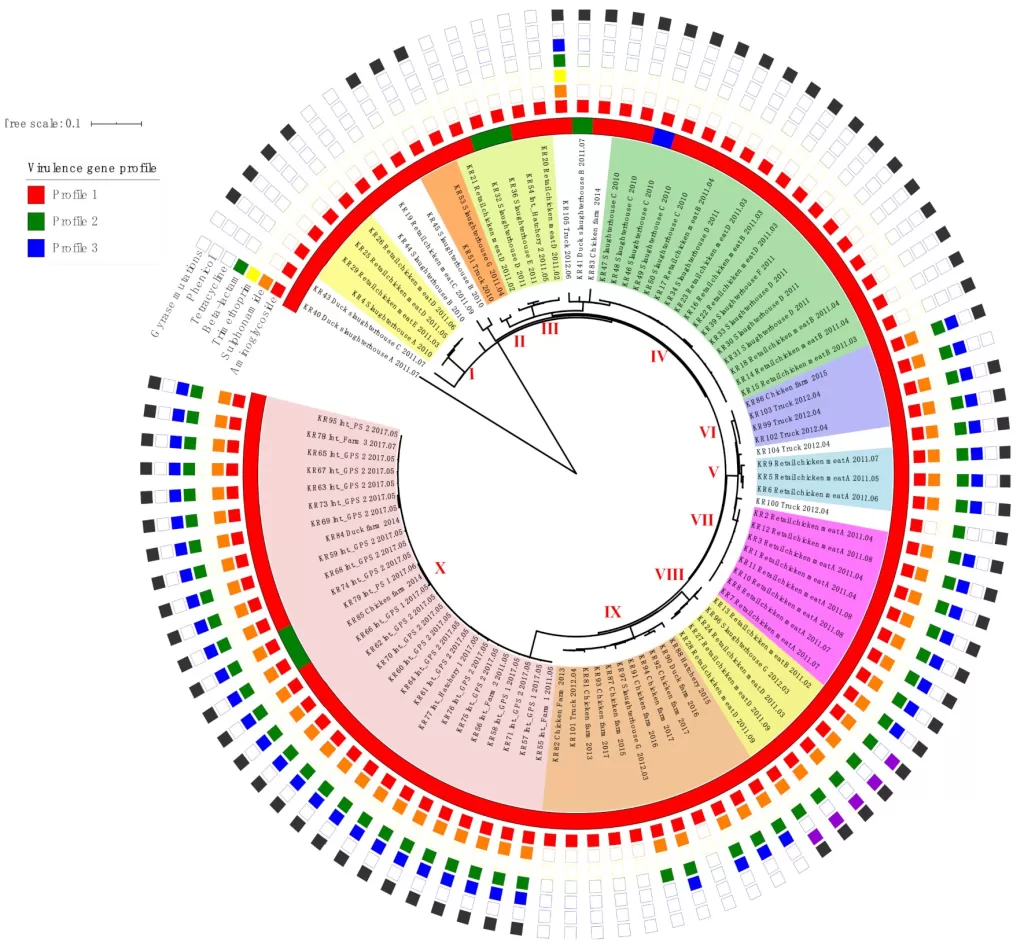
Since 2020, South Korea has witnessed the emergence of a distinct lineage of Salmonella Enteritidis, characterized by the SEGX01.049 pulsed-field gel electrophoresis pattern. This newly identified lineage has led to several significant outbreaks, including two fatal cases, raising alarms about public health implications. The genomic surveillance conducted has revealed that isolates from outbreaks clustered within the Global IIa clade, indicating a concerning trend in contamination sources, primarily linked to poultry products.
The genomic investigation shows that the majority of these isolates are closely related to strains from chicken farms in South Korea and human infections noted in the United Kingdom. This highlights the potential for international transmission of foodborne pathogens, illustrating how Salmonella Enteritidis can be shared across borders. As these outbreaks continue to unfold, understanding the genomic characteristics of this lineage becomes crucial for formulating prevention strategies.
The Importance of Genomic Surveillance
Genomic surveillance plays a pivotal role in tracking and monitoring foodborne pathogens like Salmonella Enteritidis in South Korea. Since the implementation of whole-genome sequencing (WGS) in 2020, the PulseNet Korea network has transitioned from traditional methods like pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to more advanced techniques. This shift allows for detailed analysis of genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships among different strains, which aids in promptly identifying the sources of contamination.
Through advanced genomic tools, researchers can conduct thorough investigations, ensuring that any significant changes or emerging strains are quickly recognized. This capacity for rapid response is vital as it enhances the ability of public health authorities to mitigate risks associated with Salmonella outbreaks. The continuous monitoring provided by genomic surveillance not only protects public health but also ensures that potential sources, particularly poultry, are closely regulated and assessed.
Poultry Safety and Salmonella Enteritidis
Poultry safety has become an increasingly important topic in relation to the recent rise of Salmonella Enteritidis infections in South Korea. The data underscores poultry products, primarily eggs, as major sources of transmission. The increasing prevalence of this pathogen associated with poultry indicates a pressing need for enhanced safety protocols and stringent monitoring systems at farms throughout the country. By addressing poultry safety at its source, public health officials can reduce the risk of Salmonella outbreaks.
Strategies such as training for farmers on biosecurity measures, improved sanitation in poultry processing facilities, and routine testing for Salmonella in poultry are essential. Regulatory bodies also need to collaborate closely with producers to enforce best practices that minimize contamination risks. By combining genomic data with effective food safety measures, South Korea can better control the spread of Salmonella Enteritidis and protect public health.
The Role of PulseNet Korea in Outbreak Response
PulseNet Korea has significantly evolved in its approach to monitoring foodborne illnesses since adopting whole-genome sequencing. Initially relying on pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, the transition to WGS has allowed for a comprehensive method of tracking Salmonella outbreaks and understanding their genetic relationships. This advancement is crucial for responding effectively to emergent strains like the SEGX01.049 lineage, ensuring timely intervention and communication of risks to public health.
Enhanced surveillance through PulseNet Korea enables accurate and rapid identification of outbreak sources, which is vital for effective outbreak response strategies. This network not only tracks local cases but also correlates with global data, allowing scientists to determine potential international links. Coordinated efforts through PulseNet Korea are resulting in improved methods of pathogen surveillance and outbreak management, heralding a future of safer food environments.
Global Context of Salmonella Enteritidis
The emergence of distinct lineages of Salmonella Enteritidis is not just a South Korean issue but part of a global trend affecting various regions. The genomic similarities identified between South Korean isolates and those from the United Kingdom support the notion of shared foodborne pathogens crossing borders. Globalization and changes in food production practices have intensified these trends, as food supply chains now extend beyond local and national boundaries.
In this context, global collaboration among public health agencies is critical in combating the spread of Salmonella Enteritidis. International genomic surveillance networks can facilitate information sharing and expedite response efforts when outbreaks occur. As foodborne pathogens continue to pose threats worldwide, the cooperation between countries is essential for monitoring, predicting, and preventing future outbreaks.
Future Directions in Research on Salmonella Enteritidis
Research into Salmonella Enteritidis must continue to explore the genetic characteristics of emerging lineages and their relationship to food safety. Understanding the mutations and virulence factors associated with these pathogens can provide insights necessary for developing effective vaccines and treatments. Investigating environmental sources and animal reservoirs of Salmonella Enteritidis will also help in preventing outbreaks before they occur.
Furthermore, studies focusing on consumer behaviors and food handling practices will contribute to broader public health initiatives aimed at reducing infections. Combined with advancements in technology and genomic analysis, future research can lead to innovative approaches in controlling Salmonella Enteritidis and ensuring food safety for all.
The Impact of Fatal Outbreaks on Public Health Policy
The occurrences of fatalities linked to Salmonella Enteritidis outbreaks have prompted a reevaluation of public health policies in South Korea. These tragic events often serve as catalysts for change, highlighting gaps in current surveillance systems and food safety regulations. Addressing these issues will require commitment and investment in improving public health infrastructure and response strategies.
Policymakers are now more aware of the implications of foodborne illnesses, which can lead to increased funding for research and public health campaigns. Advocating for consumer education on food safety, coupled with stricter regulations on poultry production, can significantly mitigate the risks of Salmonella Enteritidis outbreaks and protect the community.
Salmonella Enteritidis Surveillance and Prevention Efforts
Continued surveillance of Salmonella Enteritidis is key to preventing foodborne diseases in South Korea. The implementation of whole-genome sequencing has revolutionized how health authorities detect and respond to outbreaks, allowing for more refined tracking of this pathogen. Combining genomic data with epidemiological studies can result in more effective prevention efforts and enhance food safety measures in the poultry industry.
Preventive measures targeting high-risk foods, such as raw eggs and undercooked poultry, should be prioritized in public health campaigns. Ensuring that food producers adhere to strict hygiene and safety standards will significantly reduce the likelihood of Salmonella Enteritidis infections. Community education focused on food hygiene can empower consumers to protect themselves against foodborne pathogens.
Conclusion: Towards a Safer Food System
As South Korea grapples with the threats posed by Salmonella Enteritidis, it is imperative to foster a robust food safety culture. Comprehensive monitoring systems, including genomic surveillance, must be integrated into everyday practices of food production and handling. The collective efforts of public health officials, food producers, and consumers can create a safer food system.
Collaboration across government agencies and international health organizations will provide the framework necessary for effective responses to Salmonella outbreaks. By proactively addressing the underlying causes of contamination and enhancing food safety measures, South Korea can pave the way for a future with reduced risks of foodborne illnesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of Salmonella Enteritidis in South Korea?
Salmonella Enteritidis is a major foodborne pathogen in South Korea, primarily linked to poultry products such as eggs. Since 2020, a distinct lineage has emerged, causing severe outbreaks and fatalities, highlighting the need for rigorous food safety measures and genomic surveillance.
How has genomic surveillance improved the management of Salmonella Enteritidis outbreaks in South Korea?
Genomic surveillance in South Korea has transitioned to whole-genome sequencing (WGS) since 2020, allowing for enhanced tracking of Salmonella Enteritidis genomic patterns. This technology supports more effective outbreak investigations and the identification of contamination sources, improving public health responses.
What are the potential sources of Salmonella Enteritidis infections in South Korea?
Potential sources of Salmonella Enteritidis infections in South Korea primarily include poultry products, particularly eggs. Recent studies indicate that the SEGX01.049 lineage may have been introduced from the United Kingdom, emphasizing the need for comprehensive monitoring of foodborne pathogens.
What role do poultry safety measures play in controlling Salmonella Enteritidis infections?
Poultry safety measures are crucial in controlling Salmonella Enteritidis infections in South Korea. By implementing rigorous monitoring and biosecurity protocols, the spread of this foodborne pathogen can be mitigated, protecting public health from severe illness associated with salmonellosis.
What is the connection between Salmonella outbreaks and genomic analysis in South Korea?
Genomic analysis has become essential for understanding Salmonella outbreaks in South Korea. It reveals the phylogenetic relationships among bacterial strains, allowing health authorities to trace infection sources and identify potential outbreaks linked to the prevalent Salmonella Enteritidis lineage.
How do surveillance systems like PulseNet Korea contribute to managing Salmonella Enteritidis?
PulseNet Korea contributes significantly to managing Salmonella Enteritidis by facilitating the detection and investigation of foodborne infections using advanced methods like whole-genome sequencing. This enhances the ability to track outbreaks and improve response strategies effectively.
What trends have been observed regarding Salmonella Enteritidis in South Korea since 2020?
Since 2020, a notable increase in Salmonella Enteritidis cases has been observed in South Korea, with the emergence of a specific lineage linked to poultry. This trend underscores the importance of ongoing genomic surveillance and food safety practices to mitigate outbreak risks.
Why is continued genomic surveillance important for public health regarding Salmonella Enteritidis?
Continued genomic surveillance is vital for public health to monitor the evolution and spread of Salmonella Enteritidis. It aids in early detection of outbreaks, understanding transmission pathways, and developing targeted prevention strategies to protect against foodborne illnesses.
What are the implications of Salmonella Enteritidis’s rapid transmission in South Korea?
The rapid transmission of Salmonella Enteritidis in South Korea poses significant public health implications, increasing the risk of foodborne outbreaks. This necessitates an effective response to ensure food safety and reduce the incidence of salmonellosis linked to contaminated poultry products.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Emergence of Lineage | Distinct Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis lineage has circulated in South Korea since 2020. |
| Fatal Infections | Two fatal infection cases linked to this lineage have been reported. |
| Genetic Analysis | Whole-genome sequencing showed significant clustering of isolates in the Global IIa clade. |
| Potential Source | Evidence supports introduction from the United Kingdom, linked to poultry products. |
| Public Health Impact | Salmonella Enteritidis is a leading cause of foodborne illness in South Korea. |
| Surveillance Systems | PulseNet Korea transitioned to using whole-genome sequencing for improved tracking. |
| Need for Monitoring | Ongoing genomic surveillance is crucial for controlling the spread of this pathogen. |
Summary
Salmonella Enteritidis South Korea has become a significant concern since its emergence in 2020, posing serious public health threats due to its rapid transmission through food sources, particularly poultry products. With the identification of this lineage leading to fatal infections and increased outbreak occurrences, the need for robust monitoring and effective food safety measures has never been higher. Enhanced genomic surveillance and tracking via whole-genome sequencing are now critical strategies employed to understand and combat the challenges posed by this pathogen in South Korea.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.