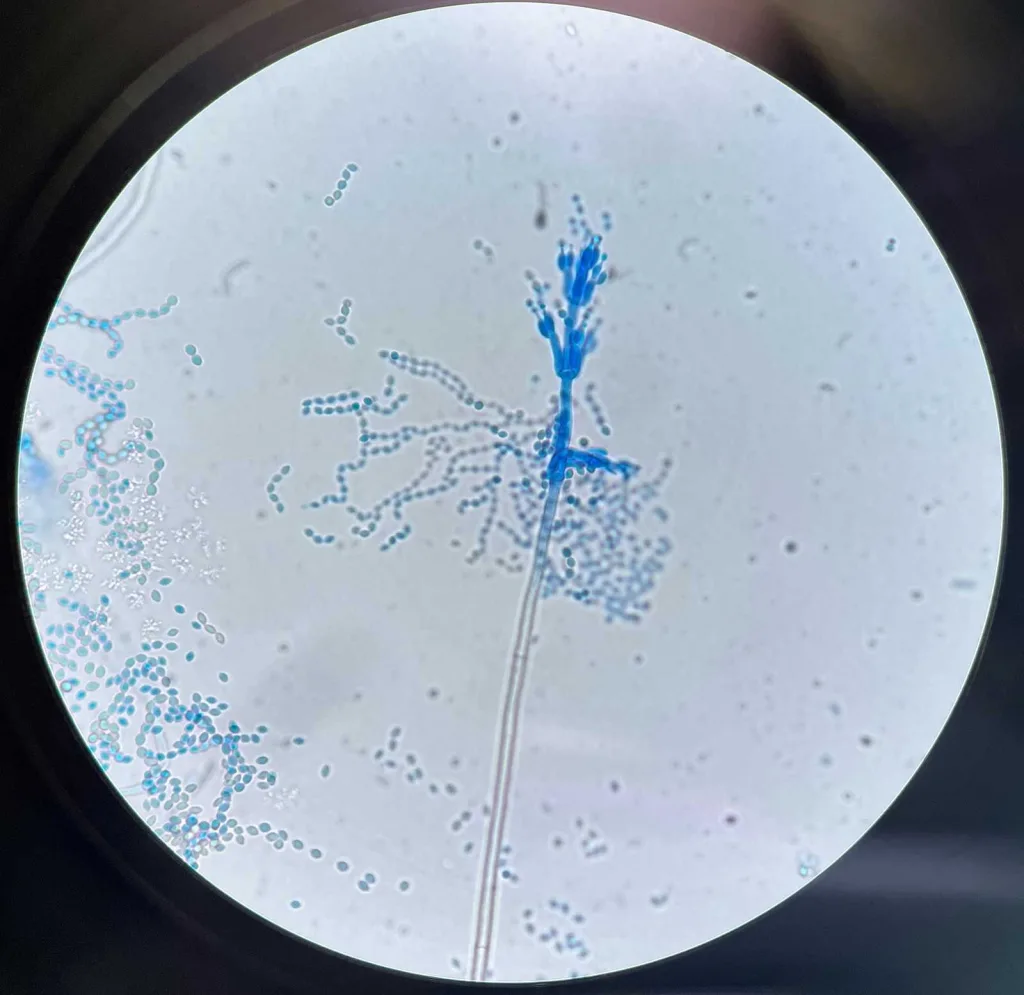
Purpureocillium lilacinum, an intriguing environmental mold and effective bionematicide, has recently garnered attention due to its rising rates of infection in laboratory cultures across the United States. From March 2019 to February 2025, reports indicated a notable surge in P. lilacinum culture rates, particularly prevalent in South Atlantic and Pacific regions. While this fungus primarily thrives in soil and decaying matter, its convergence with human health risks has sparked concern, especially regarding P. lilacinum infection in immunocompromised individuals. Fungal infections, including those caused by this mold, can often be misidentified, complicating timely and accurate treatment—an issue exacerbated by its intrinsic resistance to standard antifungal therapies. With increased mold culture rates and the potential for severe outcomes, understanding the dynamics of P. lilacinum is crucial in the realm of public health and clinical practice.
P. lilacinum, also known as Paecilomyces lilacinus, is a filamentous fungus commonly found in various environments including soil and decomposing organic matter. This organism is recognized for its dual role as a bionematicide in agriculture, combating soil-dwelling nematodes, while also posing a risk for human fungal infections, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. Strains of P. lilacinum have been utilized in agricultural practices since 2005, yet its rising infection rates in clinical settings have prompted significant research to better understand its epidemiology. The challenges in diagnosing infections related to this mold species, which are often confused with other fungal pathogens, underscore the need for awareness and advanced diagnostic techniques in healthcare. As we explore this fascinating mold, we highlight the important intersection between environmental mold dynamics and their clinical implications.
Understanding Purpureocillium lilacinum and Its Environmental Impact
Purpureocillium lilacinum, recognized for its significant role as an environmental mold, often thrives in conditions rich in organic material, such as soil and decaying plant matter. Its presence in various ecological niches highlights its adaptability and resilience. Notably, this fungus has transitioned from being predominantly an environmental organism to a bioproduct, serving as an effective bionematicide in agricultural practices. The duality of its existence reflects both the benefits and potential hazards it poses, especially in human health contexts.
The environmental mold is not just limited to agricultural settings; it plays multifaceted roles across diverse ecosystems. P. lilacinum is frequently isolated in studies assessing soil health and microbial diversity. However, with increasing incidences of P. lilacinum infection in clinical settings, researchers are compelled to delve deeper into its ecological distributions. The implications of its robust environmental presence necessitate a balanced understanding of mold culture rates as they relate to public health.
The Rise of P. lilacinum Infection Cases in the United States
Recent analytics from laboratory culture data reveal a concerning increase in Purpureocillium lilacinum infection cases within the United States. Fungal culture results from a prominent national laboratory network indicate that culture rates surged significantly from 2019 to 2024, with the highest rates observed among males and older individuals. These findings align with epidemiological patterns associated with other fungal infections, reinforcing the urgent need for clinicians to be aware of rising P. lilacinum cases.
The observed uptick in P. lilacinum infections poses critical challenges for healthcare professionals. Given its indistinguishability from other mold infections during clinical assessments, accurate diagnosis becomes imperative. Delayed recognition can lead to inappropriate treatment, particularly as P. lilacinum exhibits intrinsic resistance to standard antifungal therapies like amphotericin B. Therefore, diagnostic innovations, including microscopy and quick-turnaround tests, may be crucial in managing these fungal infections effectively and mitigating their impact.
Factors Influencing P. lilacinum Culture Rates
Several factors contribute to the rising culture rates of Purpureocillium lilacinum, particularly its geographic distribution across the United States. Data from the CDC emphasizes that regions such as the South Atlantic and Pacific are witnessing notably higher occurrences of P. lilacinum cultures, often correlated with demographic variables such as age and gender. Understanding the economic and environmental contexts within these areas can provide insights into why these trends persist, shedding light on the complexity of fungal ecology.
Additionally, the specimen types yielding high culture results are predominantly respiratory samples, suggesting a respiratory significance that cannot be overlooked. This trend indicates a possible linkage between environmental exposure to P. lilacinum mold and an increased likelihood of respiratory infections, particularly among the immunocompromised and older populations. Continuous monitoring and research are essential to further elucidate these relationships and inform public health strategies.
The Clinical Implications of P. lilacinum Infections
The clinical implications of arising P. lilacinum infections are profound, particularly given their potential to mimic other mycological infections. While this mold rarely causes disease, when it does, it can lead to serious health issues, including hyalohyphomycosis. The variance in clinical manifestations underscores the necessity for heightened awareness among healthcare providers to facilitate early diagnosis and appropriate treatment strategies.
Moreover, with reported mortality rates reaching up to 20%, clinicians must remain vigilant when managing cases that involve P. lilacinum. Effective management will depend on interdisciplinary approaches that integrate infectious disease protocols and microbiological insights. Rapid identification techniques and education about the nature of this environmental mold are critical for improving patient outcomes.
Strategies for Diagnosing P. lilacinum Infections
As P. lilacinum infections become more prevalent, practitioners are urged to reassess traditional diagnostic approaches. The long culture identification process, which can exceed three weeks, not only delays treatment but may also exacerbate patient morbidity. Incorporating advanced methodologies such as rapid molecular diagnostics and fungal PCR assays could immensely enhance early detection and ensure timely interventions.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals should prioritize training and awareness regarding the clinical features and risk factors associated with P. lilacinum infection. Improved recognition skills will enable quicker decisions in patient triage and management. Exploring the utility of nonculture-based methods, such as microscopy, could play a pivotal role in the timely identification of these infections, ultimately improving clinical outcomes.
Public Health Considerations for P. lilacinum
The public health implications surrounding Purpureocillium lilacinum extend beyond clinical settings into environmental monitoring. With rising cultivation rates, understanding the ecological roles of this mold and its potential as a human pathogen is essential for public health organizations. Surveillance programs can benefit from incorporating data regarding P. lilacinum, particularly in regions where environmental mold exposure is rampant.
Moreover, educational outreach targeting healthcare providers and the general public could foster greater awareness of risk factors associated with P. lilacinum. By promoting preventive measures and understanding environmental mold, stakeholders can effectively lessen the risk of infection and inform interventional strategies that may preemptively address escalating culture rates.
The Role of Bionematicides in Agriculture
Purpureocillium lilacinum has gained recognition as a bionematicide, an environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides in agriculture. Its application in controlling nematode populations illustrates the beneficial use of this mold while also presenting challenges in managing its impact on human health. Farmers increasingly rely on such biopesticides to reduce dependency on synthetic chemicals, highlighting a shift towards more sustainable agricultural practices.
However, the dual-use of P. lilacinum as both an agricultural ally and a potential pathogen necessitates careful consideration in its deployment. Continuous research into the ecological consequences of deploying P. lilacinum in agricultural systems is pivotal to balance its beneficial aspects as a bionematicide against potential health risks. Policymakers must oversee the integration of these practices to ensure safety for both crops and human populations.
Trends in Fungal Infections and Their Diagnosis
Fungal infections are on the rise globally, with Purpureocillium lilacinum being one of the many species contributing to this trend. The increase in fungal cultures reported by laboratories signals an urgent need for enhanced diagnostic protocols to effectively manage these infections amidst growing clinical relevance. This trend is often exacerbated by environmental conditions and climatic changes that promote fungal proliferation.
To counteract the rising trend of mold infections, healthcare systems must adapt diagnostic strategies that aim for speed and accuracy. The implementation of improved laboratory practices, including the use of rapid detection techniques, diagnostic algorithms, and the integration of insights from environmental health studies, will collectively bolster efforts to recognize and treat fungal infections effectively. Enhancing clinician awareness regarding the epidemiology of various fungal pathogens like P. lilacinum is also instrumental in improving patient management.
Future Directions for P. lilacinum Research
As research into Purpureocillium lilacinum evolves, scientists are encouraged to explore its diverse implications in both health and environmental contexts. Understanding its genetic makeup, pathogenic mechanisms, and environmental interactions can yield valuable insights into public health. Future studies could focus on developing quicker diagnostic methods and effective treatment protocols while considering the ecological impact of its dual role.
Moreover, longitudinal studies investigating the incidence and outcomes of P. lilacinum infections in varied populations and geographic locations can help clarify epidemiological trends. As the prevalence of fungal infections rises, the integration of interdisciplinary approaches, encompassing clinical, environmental, and agricultural research, will be vital in comprehensively addressing the challenges posed by this mold.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Purpureocillium lilacinum and where is it commonly found?
Purpureocillium lilacinum, commonly known as P. lilacinum, is a filamentous fungus that exists naturally in the environment, especially in soil and decaying organic matter. It is increasingly recognized for its role in environmental mold and as a bionematicide, used in agricultural applications to manage nematode populations.
How does P. lilacinum infection affect human health?
Although P. lilacinum rarely causes infections in healthy individuals, it can lead to hyalohyphomycosis, particularly affecting immunocompromised patients. Symptoms can manifest in various body parts, including soft tissues, eyes, and lungs, with mortality rates reaching up to 20%. The infection is challenging to diagnose due to its similarities with other fungal infections.
What trends have been observed in P. lilacinum mold culture rates in the United States?
Recent analyses of mold culture results from a major commercial laboratory show that P. lilacinum culture rates increased significantly from 56.6 per 100,000 cultures in 2019 to over 90 in 2024, with the highest rates observed in the South Atlantic and Pacific regions. This rising trend suggests a need for heightened awareness among healthcare providers regarding P. lilacinum infections.
Why might P. lilacinum infections be misidentified in clinical settings?
P. lilacinum infections can be misidentified due to their clinical presentation resembling other mold infections. Their cytological and histopathological characteristics are similar, leading to delays in accurate diagnosis and treatment. Furthermore, P. lilacinum displays resistance to certain antifungal treatments, complicating management.
What diagnostic tools can help identify P. lilacinum infections?
Nonculture-based diagnostic tools, particularly microscopy, can aid in the early identification of P. lilacinum infections. These methods can expedite diagnosis and help clinicians differentiate P. lilacinum from other fungal pathogens, which is critical given the organism’s resistance to treatments like amphotericin B.
What demographic factors are associated with increased rates of P. lilacinum infection?
The rise in P. lilacinum culture rates appears to be particularly pronounced among males and individuals over the age of 65. These demographic trends highlight the need for targeted surveillance and improved diagnostic strategies in these high-risk populations.
What implications do rising P. lilacinum mold culture rates have for public health?
The increase in P. lilacinum mold culture rates suggests potential environmental or clinical shifts that require further investigation. Understanding the sources and epidemiology of P. lilacinum infections can inform preventive strategies and improve patient outcomes, particularly for vulnerable populations.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase of Culture Rates | From 56.6 to 74.3 per 100,000 fungal cultures between 2019 and 2024, with a peak of over 90 in Q3 2024. |
| Geographic Distribution | Highest rates observed in South Atlantic (110.6) and Pacific regions (100.3) per 100,000 population. |
| At-Risk Populations | Higher rates among males and individuals over age 65. |
| Types of Specimens | Respiratory specimens comprised the majority of cultures ordered from hospital settings. |
| Impact on Diagnosis | Lengthy identification process (>3 weeks) may lead to delays in treatment and potential misdiagnosis. |
| Clinical Implications | Risk of hyalohyphomycosis especially in immunocompromised patients; intrinsic resistance to amphotericin B. |
Summary
Purpureocillium lilacinum has shown an alarming increase in culture rates among laboratory results in the United States from 2019 to 2024. This rise highlights not only the need for heightened awareness and monitoring of this organism but also the importance of quick and accurate diagnostic methods to mitigate health risks, particularly for immunocompromised populations. Further studies are essential to understand its environmental sources and clinical implications.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.