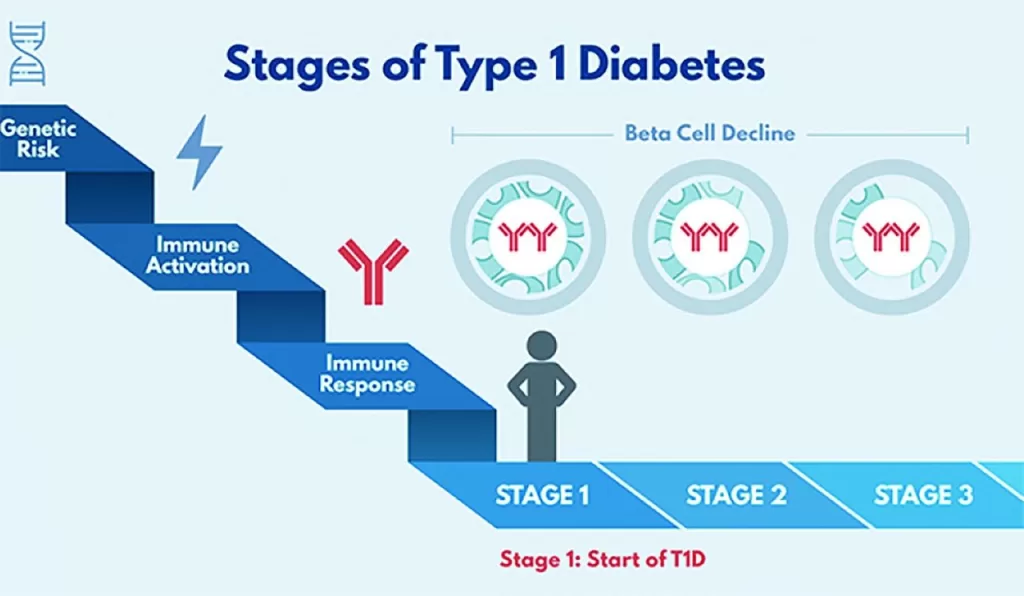
Presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening represents a significant advancement in the early detection of this autoimmune condition, allowing for timely interventions that can alter the disease’s trajectory. With recent developments in T1D screening protocols, healthcare professionals can identify individuals at high risk before the onset of clinical symptoms, providing essential diabetes management support. This proactive approach emphasizes the urgency of screening for diabetes among those with a family history or related autoimmune diseases. Enhanced type 1 diabetes education for both practitioners and patients is critical as we transition towards more effective methods of prevention and treatment. By implementing routine screening practices, we not only help prevent complications but also empower individuals with the knowledge needed to manage their health proactively.
Early identification of type 1 diabetes, especially in at-risk populations, can be facilitated through various screening initiatives aimed at catching the disease before symptoms emerge. This anticipatory healthcare model enables healthcare providers to intervene sooner, improving patient outcomes significantly. As awareness increases surrounding the need for comprehensive T1D screening, barriers to effective implementation must be addressed through education and resources. By focusing on at-risk individuals and adapting healthcare practices, we can promote a culture of vigilance about diabetes risk factors. In essence, developing robust presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening programs will pave the way for better long-term health management strategies and support for affected individuals.
Understanding Presymptomatic Type 1 Diabetes Screening
Presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening has rapidly gained attention due to its potential for early detection and effective management of the disease. By identifying individuals at risk before the onset of symptoms, healthcare professionals can implement interventions that may delay or prevent the full manifestation of type 1 diabetes (T1D). The advent of therapies like teplizumab (Tzield) emphasizes the urgency of recognizing these early risk markers, which often include the presence of specific autoantibodies. Understanding and embracing the T1D screening protocols can drastically improve patient outcomes and reduce long-term complications associated with diabetes.
Effective presymptomatic screening relies on a combination of standardized protocols, clinical awareness, and patient education. As experts emphasize, educating both healthcare providers and patients about the importance of diabetes screening can lead to a more proactive healthcare approach. Providers play a crucial role in identifying high-risk populations, such as first-degree relatives of T1D patients or individuals with other autoimmune conditions. Implementing a structured approach to presymptomatic screening can facilitate timely interventions and comprehensive diabetes management, enhancing the overall quality of care for at-risk individuals.
Challenges and Barriers to T1D Screening Implementation
Despite the clear benefits of presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening, several barriers hinder effective implementation. A significant challenge is the limited awareness among healthcare providers regarding the latest T1D screening protocols. Many providers remain undereducated about the nuances of type 1 diabetes, mistakenly classifying it as type 2 during routine consultations. This misdiagnosis not only affects the treatment plan but also delays necessary interventions that can drastically alter disease progression. Increased educational initiatives for clinical staff on T1D screening are paramount to overcoming this hurdle.
Another barrier to effective screening is the lack of standardized workflows within clinical settings. Many healthcare facilities need to establish clear protocols for diabetes screening that include guidelines for obtaining testing and interpreting results. Dr. Schulman-Rosenbaum discusses the role of screening handouts and creating workflows that facilitate easier screening processes. By addressing these barriers systematically, healthcare systems can incorporate T1D screening into routine patient care, ultimately improving diabetes education and management strategies.
Targeted Screening for High-Risk Populations
Targeting high-risk populations for presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening is crucial for early detection and intervention. Research shows that first- and second-degree relatives of individuals diagnosed with T1D are at significantly higher risk. Therefore, it is essential for clinicians to incorporate screening into routine visits for these high-risk individuals. Additionally, patients with other autoimmune disorders, like celiac disease or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, should also be routinely screened for T1D. These targeted strategies ensure that we’re addressing the most vulnerable populations and providing them with the timely care they need to manage their risk effectively.
Implementing targeted screening initiatives involves training healthcare providers to recognize these high-risk groups during consultations. This targeted approach not only aims to identify at-risk individuals earlier but also raises awareness among families affected by type 1 diabetes. By communicating the significance of early detection and integrating screenings into standard medical practice, we can improve diabetes management and enhance the educational resources available to families as they navigate the complexities of T1D.
Essential Steps for Launching Screening Programs
Launching effective presymptomatic T1D screening programs requires strategic planning and collaboration among healthcare providers. One key step is nominating a program champion who is passionate about diabetes health and can drive the implementation process forward. Forming a dedicated implementation team that collaborates to embed screening protocols within existing clinical systems is also essential. This team should focus on creating streamlined workflows that enable seamless screening for diabetes during patient visits, ensuring that coding for insurance coverage is appropriately addressed to alleviate financial barriers.
Integrating T1D screening into existing practices cannot be an afterthought; it requires a systematic approach. The importance of establishing clear referral pathways for diagnostics, such as antibody testing, also comes into play. By utilizing data on at-risk individuals, healthcare systems can optimize their resource allocation, ensuring that those most in need receive appropriate attention. A coordinated approach will facilitate comprehensive diabetes education for patients and empower them to take proactive steps toward managing their health.
Addressing Misdiagnosis Issues in Diabetes
Misdiagnosis is a significant concern in the management of diabetes, especially when it comes to confusing type 1 diabetes with type 2 diabetes. Many adults presenting with hyperglycemia may be misclassified as having type 2, resulting in inadequate treatment and poor health outcomes. Dr. Schulman-Rosenbaum advocates for the use of advanced testing, such as antibody and C-peptide assays, to ensure accurate classification and diagnosis. Implementing these diagnostic best practices can prevent misinterpretation and promote timely intervention for those with presymptomatic T1D.
Addressing misdiagnosis also underscores the need for ongoing education and training in diabetes care. Healthcare providers must stay informed about the latest research regarding autoimmune markers and diabetes classification. Consistent educational initiatives can help mitigate errors in diagnosis, ultimately leading to better management strategies. Effective communication with patients about the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes can also enhance understanding and facilitate patient engagement in their treatment plans.
Monitoring and Follow-Up Strategies for At-Risk Individuals
Once individuals have been identified as at risk for developing type 1 diabetes, it is vital to establish a robust monitoring strategy. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems can play a crucial role in tracking glucose levels and detecting dysglycemia patterns in these patients. Regular follow-ups involving personalized approaches based on individual glucose trends can significantly enhance diabetes management. The goal is to address any signs of progression toward diabetes early to prevent complications and ensure optimal health outcomes.
Moreover, personalized monitoring is not just about tracking blood glucose; it also involves educating patients about their condition and empowering them to take control of their health. Patients should be informed about the implications of their test results and the importance of adhering to prescribed monitoring routines. Providing continuous support and resources can help strengthen their understanding of the disease process, thereby improving their overall diabetes management strategies and promoting better health outcomes.
The Role of Diabetes Education in Prevention and Management
Education is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management and plays a pivotal role in preventing complications associated with type 1 diabetes. By providing comprehensive education on presymptomatic T1D screening and the importance of early detection, healthcare providers can empower individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed health decisions. This education should encompass understanding risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical advice. Moreover, fostering open dialogue between patients and providers about diabetes can enhance education and improve adherence to screening protocols.
Incorporating diabetes education into routine healthcare can lead to a more informed patient population. Educational programs should also focus on lifestyle modifications, nutritional advice, and self-monitoring techniques. By equipping patients with the right tools and knowledge, we can promote proactive diabetes management and potentially reduce the incidence of severe complications associated with T1D. Engaging families and communities in these educational efforts can amplify the impact and facilitate a culture of awareness around diabetes management.
Innovations in Technology for Diabetes Screening and Management
The integration of technology into diabetes screening and management has revolutionized the way healthcare providers approach presymptomatic type 1 diabetes. Advancements in diagnostic tools, such as online screening platforms and novel testing methods, have made it easier to identify at-risk individuals. Additionally, Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) have transformed diabetes management by providing real-time data, enabling better decision-making for both providers and patients. These technological innovations are crucial in facilitating early detection and intervention for those at risk of T1D.
Moreover, technology can enhance diabetes education by providing individuals with access to digital resources and telehealth services. This can improve patient engagement and adherence to treatment regimens. With easy access to valuable information and virtual consultations, individuals can become more proactive in their healthcare journeys. Embracing these innovations not only enhances diabetes management but also reinforces the importance of timely screening for presymptomatic type 1 diabetes, fostering a comprehensive, patient-centered approach.
The Future of Screening for Presymptomatic Type 1 Diabetes
Looking ahead, the future of presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening is filled with potential. Emerging research continues to shed light on more precise biomarkers and the role of genetics in T1D risk assessment. As our understanding of diabetes evolves, we can expect the development of more refined screening protocols that are tailored to individual risk profiles. This progress will undoubtedly enhance the effectiveness of early detection efforts and promote better patient outcomes through timely interventions and education.
Future screening initiatives must also consider the role of policy changes in healthcare to ensure access to screening and treatments for T1D. Advocating for policies that support diabetes research and the integration of advanced screening technologies in clinical practice can reshape how we approach T1D management. The combined efforts of healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers will be vital in creating a more robust framework for the early detection and management of presymptomatic type 1 diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening and why is it important?
Presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening refers to testing individuals at risk of developing type 1 diabetes (T1D) before any symptoms occur. Early detection through standardized screening protocols is crucial, especially with the availability of treatments like teplizumab (Tzield), which can delay the onset of symptoms in high-risk individuals.
How can healthcare providers implement T1D screening protocols effectively?
To implement T1D screening protocols effectively, healthcare providers should prioritize education on early detection strategies, create workflows that include screening handouts, and integrate these protocols into routine clinical assessments, especially for high-risk populations.
Who should be screened for presymptomatic type 1 diabetes?
Individuals who should be screened for presymptomatic type 1 diabetes include first- and second-degree relatives of those with T1D and patients with autoimmune disorders like Hashimoto’s or celiac disease. Screening is advised during routine care appointments to facilitate early detection.
What are the barriers to presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening in clinical practice?
Barriers to presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening include limited awareness among healthcare providers, inadequate education regarding T1D screening protocols, and the challenge of integrating screening into existing clinical workflows.
How does accurate diagnosis of type 1 diabetes impact diabetes management?
Accurate diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is vital for effective diabetes management, as misclassifying adults as having type 2 diabetes can lead to inappropriate treatment plans. Using antibody and C-peptide testing helps ensure correct diagnosis and tailored management strategies.
What monitoring strategies are recommended for individuals testing positive for T1D autoantibodies?
For individuals testing positive for T1D autoantibodies or those showing mild dysglycemia, personalized monitoring strategies are crucial. These may include regular follow-ups, lifestyle adjustments, and in some cases, the use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems to track glucose patterns.
Why is diabetes education important in presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening?
Diabetes education is critical in presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening, as it increases awareness among healthcare providers about the importance of early detection and improves patient understanding of their risk, leading to more proactive health management.
What role does insurance coverage play in the implementation of T1D screening programs?
Insurance coverage plays a significant role in the implementation of T1D screening programs, as proper coding for screenings can facilitate coverage for patients, thus removing financial barriers that might prevent high-risk individuals from receiving necessary tests.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Presymptomatic T1D Screening | Importance of early detection with standardized protocols, especially with new therapies like teplizumab (Tzield). |
| Barriers to Implementation | Challenges include provider awareness and education gaps on T1D screening protocols; suggested solutions involve screening handouts and workflow improvements. |
| Targeted Screening for High-Risk Groups | Screening is crucial for first- and second-degree relatives of T1D patients and those with related autoimmune conditions during routine appointments. |
| Launching Screening Programs | Key steps include appointing a program champion, forming an implementation team, and integrating screening into existing clinical workflows. |
| Misdiagnosis Issues | Common misclassification of adults as having type 2 diabetes can be mitigated with proper antibody and C-peptide testing. |
| Monitoring Strategies | Recommendations for individuals testing positive for autoantibodies include personalized monitoring, often through continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). |
Summary
Presymptomatic type 1 diabetes screening is vital for early detection and intervention for those at risk. The dialogue with experts emphasizes the need for effective screening protocols and educational efforts to surmount barriers to implementation. By targeting high-risk groups and embedding screening practices into clinical routines, healthcare providers can significantly improve the management of this condition. Embracing new therapies like teplizumab (Tzield) and refining diagnosis strategies further supports timely interventions to prevent the onset of symptomatic type 1 diabetes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.