Pertussis vaccination plays a crucial role in combating whooping cough, a highly contagious disease caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Recently, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) has emphasized the urgent need for enhanced vaccination coverage in response to rising infections across the Americas, including instances of antibiotic-resistant strains. This upward trend highlights the important intersection of public health and responsible antibiotic use, particularly as certain antibiotic treatments have become less effective due to resistance. With cases of whooping cough increasing, now more than ever, it is vital for communities to prioritize immunization efforts to protect individuals from this serious health threat. Ensuring robust vaccination rates is essential not only to shield the vulnerable but also to strengthen our collective defense against the looming risk of heightened antibiotic resistance.
The promotion of immunizations against whooping cough, also known as pertussis, reflects a broad strategy in public health to prevent outbreaks of this infectious disease. Recent reports from the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) spotlight the alarming trend of increased infections, along with the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of Bordetella pertussis. This situation calls for a renewed commitment to vaccination programs to bolster protective measures within communities. Additionally, addressing the decline in vaccination coverage, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, is essential to safeguarding the population. Strengthening efforts in vaccination and surveillance not only combats whooping cough but also fosters a healthier environment for all.
The Importance of Pertussis Vaccination in Public Health
Pertussis vaccination plays a crucial role in public health by preventing outbreaks of whooping cough, a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Vaccination coverage is pivotal for achieving herd immunity, which protects those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. Recent decreases in vaccination rates, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, have led to a resurgence of pertussis cases in various regions, including the Americas. Health organizations, including the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), emphasize that maintaining and improving vaccination coverage is essential to avert significant outbreaks and safeguard community health.
Vaccination serves not only to protect individuals but also to prevent the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of Bordetella pertussis. As antibiotic resistance becomes a pressing public health concern, effective vaccination programs can mitigate the risk of treatments failing due to genetic mutations in the bacteria. By promoting early and complete vaccination against pertussis, health authorities can reduce the number of infections and consequently lower the need for antibiotics, thereby helping to combat antibiotic resistance on a larger scale.
Challenges in Achieving High Vaccination Coverage
Despite the proven effectiveness of pertussis vaccines, achieving high vaccination coverage remains a significant challenge for many countries, particularly in the Americas. During the pandemic, many health systems struggled to maintain routine immunization services, resulting in decreased coverage rates for the diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTP) vaccine. This decline raises concerns about the potential for outbreaks of whooping cough, especially in populations with lower immunization rates. Countries reported a concerning rise in cases, with thousands of infections documented in recent years, emphasizing an urgent need to address gaps in vaccination coverage.
Furthermore, disparities in vaccination rates within countries pose additional challenges to public health efforts. Some regions exhibit low immunization rates, leaving communities vulnerable to outbreaks of pertussis. PAHO’s recommendations, including targeting immunization programs at pregnant women and health workers, aim to bolster vaccination coverage and protect newborns at risk of severe pertussis complications. Strengthening these programs requires collaboration between healthcare providers and communities to ensure widespread awareness and access to vaccinations.
The Risk of Antibiotic-Resistant Pertussis Strains
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of Bordetella pertussis presents a serious threat to treatment efficacy and public health safety. Recent findings have indicated that mutations in the bacteria have rendered common antibiotics such as macrolides less effective, complicating treatment for those infected. With the detection of resistant strains in multiple countries across the Americas, it is vital that health authorities adapt their strategies to manage these evolving challenges effectively. PAHO has issued urgent calls for enhanced surveillance and responsible antibiotic use to prevent further escalation of this issue.
Investing in robust vaccination programs is critical not only to prevent cases of pertussis but also to minimize the need for antibiotic interventions that could contribute to resistance. As seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, inappropriate antibiotic use has been linked to the emergence of resistant strains, highlighting the need for education regarding responsible prescribing practices. Combining vaccination efforts with a strong emphasis on mitigating antibiotic resistance can create a comprehensive approach to safeguarding public health against the threats posed by pertussis.
Surveillance and Response Strategies for Pertussis
Enhancing surveillance capabilities is essential for effectively tracking pertussis cases and responding promptly to outbreaks. PAHO has underscored the importance of monitoring infection trends and vaccine coverage to inform public health strategies and interventions. An effective surveillance system enables authorities to identify outbreaks early, implement control measures, and allocate resources where they are most needed, ultimately reducing the risk of widespread transmission.
Additionally, a coordinated outbreak response plan is vital in mitigating the impact of pertussis in affected communities. This includes providing timely vaccinations, ensuring access to healthcare services, and disseminating accurate information about the disease. Healthcare providers play a critical role in these responses, especially in educating patients about the importance of vaccination for themselves and their children. By fostering a collaborative approach between various health agencies and communities, the incidence of pertussis can be significantly reduced.
The Role of Community Awareness in Pertussis Vaccination
Community awareness is a key factor in improving vaccination rates against pertussis. Education plays a pivotal role in dispelling myths and misconceptions surrounding the DTP vaccine, leading to increased acceptance among parents and caregivers. Campaigns to inform the community about the dangers of whooping cough and the importance of timely vaccinations are crucial for fostering trust in vaccination efforts. Such initiatives can guide families in making informed decisions that prioritize the health of their children and the larger community.
Local collaboration between healthcare providers, schools, and community organizations is essential to promote vaccination and provide resources to families. Outreach programs that engage directly with communities can help ensure that families understand the necessity of vaccinations and are aware of local vaccination clinics. As part of a comprehensive public health strategy, building community awareness not only increases vaccination rates but also enhances herd immunity, ultimately protecting vulnerable populations who are unable to receive vaccines.
Pregnant Women and Pertussis Vaccination: Safeguarding Newborns
Immunizing pregnant women against pertussis is a crucial strategy to protect newborns, who are particularly vulnerable to severe complications from whooping cough. Health authorities recommend that expectant mothers receive the DTP vaccine during their third trimester, ensuring that antibodies are passed to the baby and providing initial protection until they can receive their own vaccinations. This preventive measure is especially vital during times of increased pertussis activity, as it significantly lowers the risk of infection in newborns.
In addition to protecting newborns, vaccinating pregnant women contributes to broader community immunity. Since newborns cannot be vaccinated immediately after birth, protecting their mothers through vaccination helps create a shield against the disease. Encouraging healthcare providers to discuss the importance of pertussis vaccination with expectant mothers is a critical component of prenatal care, helping to ensure that both mothers and their babies remain healthy and safe from whooping cough.
Addressing Disparities in Vaccination Coverage
Disparities in vaccination coverage underscore the unequal access to healthcare services and resources, which can significantly affect public health outcomes. In the context of pertussis, certain communities experience lower rates of vaccination due to socioeconomic factors, lack of information, or healthcare access barriers. Public health campaigns must focus on these vulnerable populations to ensure equitable access to the pertussis vaccine, aiming to eliminate gaps in coverage that can lead to outbreaks.
To effectively bridge these disparities, tailored interventions that address the specific needs of different communities are essential. Engaging community leaders and stakeholders can help design programs that resonate with local populations, encouraging higher vaccination participation. Furthermore, ensuring that information is accessible in multiple languages and formats can enhance understanding and acceptance of the importance of vaccination, ultimately contributing to a more robust public health response to pertussis.
The Global Resurgence of Pertussis and Its Implications
The global resurgence of pertussis has raised alarms among public health officials, as the rates of infection continue to rise in many regions. Factors contributing to this resurgence include declining vaccination rates, the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare delivery systems. As communities grapple with these challenges, it is evident that a multifaceted approach is necessary to tackle the pertussis crisis effectively.
Strengthening global and regional vaccination initiatives, improving surveillance systems, and promoting responsible antibiotic use are key strategies to stem the tide of rising pertussis cases. Emphasizing the need for consistent vaccination schedules and reinforcing community education efforts can lead to a more informed populace, ultimately resulting in more effective management of whooping cough outbreaks and enhancing overall public health safety.
Future Directions for Pertussis Vaccination Programs
To improve pertussis vaccination programs, future directions must focus on innovative strategies to engage communities and boost vaccine adherence. Utilizing technology, such as mobile applications and online platforms, can facilitate appointment scheduling and send reminders for vaccinations. This approach can help address barriers to timely immunization and ensure that families stay informed about vaccination schedules and local clinics.
Additionally, investing in research to develop new vaccine formulations that offer longer-lasting protection against pertussis is critical. Advancements in vaccine technology and understanding the biology of Bordetella pertussis may provide new tools for controlling outbreaks, especially in the face of antibiotic resistance. By prioritizing these efforts, health authorities can create a more resilient vaccination framework capable of responding to current and future public health challenges regarding pertussis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of pertussis vaccination in preventing whooping cough?
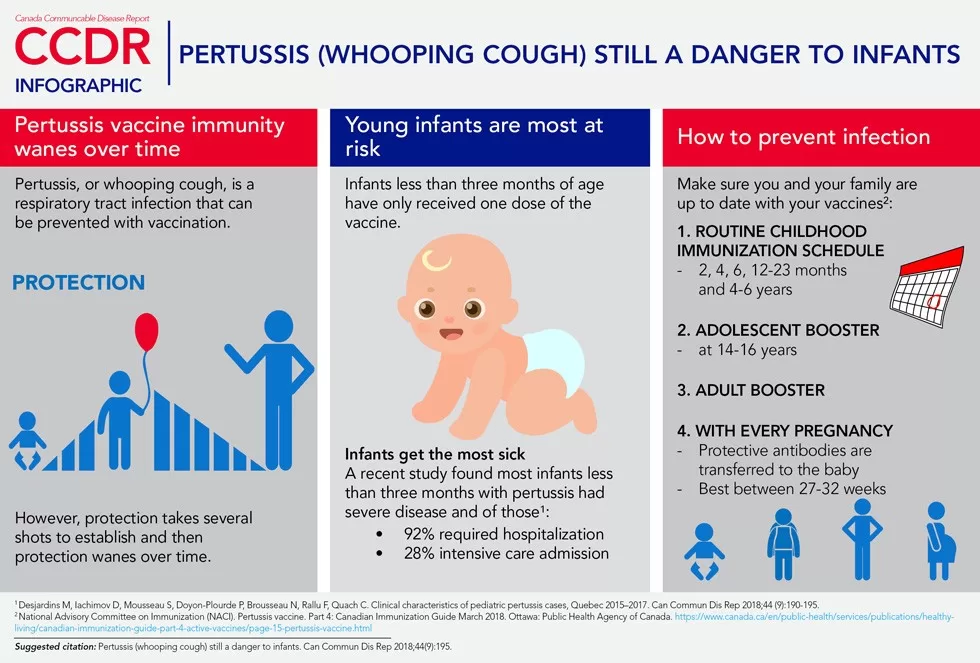
Pertussis vaccination is crucial for preventing whooping cough, a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by Bordetella pertussis. Vaccination helps build immunity in communities, which is essential to achieve herd immunity and prevent outbreaks. Increased vaccination coverage is necessary to protect vulnerable populations, such as infants and pregnant women.
How does antibiotic resistance affect treatment for whooping cough?
Antibiotic resistance poses a significant challenge in treating whooping cough caused by Bordetella pertussis. Genetic mutations in the bacteria have reduced the effectiveness of commonly used macrolide antibiotics, such as azithromycin. Hence, vaccination against pertussis remains the most effective strategy to combat the disease and prevent its spread.
What are the recent trends in vaccination coverage for pertussis in the Americas?
Vaccination coverage for pertussis in the Americas has declined due to the COVID-19 pandemic, reaching historic lows for the DTP vaccine doses. According to PAHO, vaccination rates remain below the recommended 95%, which increases the risk of whooping cough outbreaks and the circulation of antibiotic-resistant strains. Authorities are urging immediate action to enhance vaccination efforts.
How can public health measures increase pertussis vaccination coverage?
Public health measures can effectively increase pertussis vaccination coverage through community awareness campaigns, ensuring access to vaccines, and targeting high-risk groups like pregnant women and healthcare workers. PAHO emphasizes the need for strengthening surveillance systems and outbreak response to manage and reduce the incidence of whooping cough.
What recommendations does PAHO provide regarding pertussis vaccination during outbreaks?
PAHO recommends the immunization of pregnant women during pertussis outbreaks to protect newborns at greatest risk of severe disease. Additionally, vaccination for health workers who come into contact with infants is advised to help contain outbreaks and improve overall vaccination coverage against whooping cough.
Will antibiotics still be effective for treating whooping cough?
While antibiotics like azithromycin are typically used to treat Bordetella pertussis infections, the rise of antibiotic-resistant strains reduces their effectiveness. As pertussis vaccination is the primary prevention method, relying solely on antibiotics for treatment is not sufficient without maintaining robust vaccination coverage.
What is the connection between declining vaccination rates and the resurgence of whooping cough?
The resurgence of whooping cough in recent years is closely linked to declining vaccination rates. As more individuals remain unvaccinated against Bordetella pertussis, herd immunity weakens, allowing the disease to spread and increasing the likelihood of outbreaks and antibiotic-resistant strains.
What role does the community play in increasing pertussis vaccination rates?
Community involvement is vital in advocating for pertussis vaccination, educating others about its importance, and reducing vaccine hesitancy. Local organizations and individuals can help raise awareness and support public health initiatives aimed at increasing vaccination coverage and combating whooping cough effectively.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase in Pertussis Cases | PAHO urges countries in the Americas to enhance surveillance and vaccination due to rising infections and antibiotic-resistant strains. |
| Antibiotic Treatment | Bordetella pertussis infections are treated with macrolide antibiotics; however, genetic mutations are reducing their effectiveness. |
| Resistant Strains Detected | Cases of antibiotic-resistant pertussis have been found in Brazil, Mexico, Peru, and the United States since 2024. |
| Role of Vaccination | Dr. Pilar Ramón-Pardo highlights the importance of vaccination, surveillance, and responsible antibiotic use to prevent public health threats. |
| Historical Vaccination Rates | Vaccination coverage during the pandemic dropped to historic lows, with current rates still below the recommended 95%. |
| Childhood and Maternal Vaccination | PAHO recommends vaccinations for children, pregnant women during outbreaks, and health workers in contact with newborns. |
Summary
Pertussis vaccination is crucial in combating the rising cases of whooping cough, particularly given the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains. The Pan American Health Organization emphasizes the importance of increasing vaccination coverage and improving surveillance to curb the spread of this infectious disease. By addressing gaps in immunization and promoting responsible antibiotic use, public health officials can prevent pertussis from escalating into a significant health threat.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.