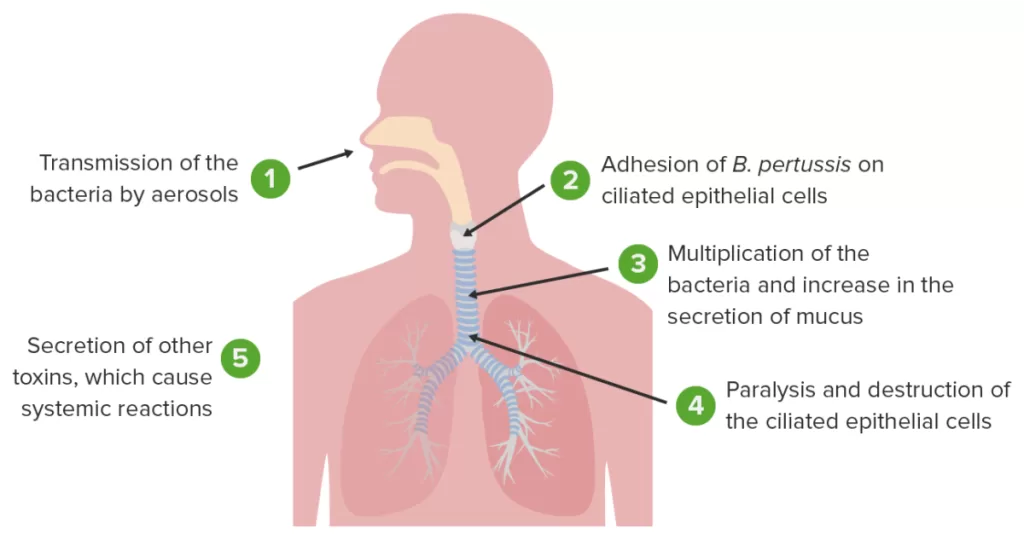
Pertussis transmission dynamics play a crucial role in understanding the spread of whooping cough, especially during outbreaks such as the one observed in South Korea in 2024. This highly contagious respiratory infection, caused by *Bordetella pertussis*, has shown surprising resilience even in populations with high vaccination coverage. During this outbreak, a significant proportion of cases were detected among vaccinated children, raising concerns about the effectiveness of current public health interventions. Notably, super spreading events contributed to the rapid transmission, with just a small percentage of infected individuals responsible for the majority of cases. As pertussis epidemiology continues to evolve, it is imperative for health authorities to adapt strategies to mitigate the impact of future outbreaks.
Understanding the patterns of transmission for whooping cough, known scientifically as pertussis, is essential for effective public health management. Recent occurrences of this illness, particularly in vaccinated demographics, have rekindled interest in its transmission pathways and dynamics. Infection outbreaks, marked by significant instances of super spreading, bring to light critical factors impacting pertussis spread among school-aged children. The significance of public health measures and the implications of vaccination on community health are vital areas of study in pertussis epidemiology. Addressing these dynamics helps produce informed interventions aimed at containing potential outbreaks.
Understanding Pertussis Transmission Dynamics
Pertussis transmission dynamics are crucial for understanding how this highly contagious disease spreads, particularly in populations with high vaccination coverage. Analysis of recent school-based outbreaks, such as the one observed in South Korea in 2024, reveals that even vaccinated children can serve as vectors for the infection. This phenomenon underscores the importance of studying transmission parameters, including serial intervals and the risk of superspreading events. The outbreak highlighted that 15% of cases contributed to 80% of the transmissions, demonstrating the necessity of effective public health interventions.
Moreover, recent research has shown that although vaccination programs have significantly reduced the overall incidence of whooping cough, the bacterium responsible for pertussis, *Bordetella pertussis*, still poses a significant threat in communities. This study in the vaccinated school population evidenced the complex dynamics involved in pertussis transmission, necessitating further investigations into protective immunity and its waning effects over time. Public health responses must adapt to these dynamics, incorporating rapid contact tracing and enhanced vaccination strategies.
Impact of Vaccination on Pertussis Outbreaks
Vaccination has played a critical role in reducing the incidence of whooping cough worldwide, yet outbreaks continue to occur, particularly in vaccinated cohorts. The recent 2024 outbreak in South Korea is a striking example, indicating that vaccinated children can still transmit *Bordetella pertussis*. Notably, a significant percentage of infected individuals had received multiple doses of the pertussis vaccine, suggesting that the immunity conferred may diminish over time. This phenomenon can lead to increased susceptibility among adolescents and adults, raising concerns about herd immunity.
The findings from this outbreak call for a reassessment of vaccination protocols to address potentially waning immunity among adolescents and young adults. This data suggests that booster vaccinations should be emphasized, particularly for children transitioning into high school, to maintain collective immunity in schools. Public health officials can leverage these insights to design more effective vaccination campaigns that target older age groups, ultimately reducing the incidence of pertussis and the risk of future outbreaks.
Epidemiology of Pertussis in Vaccinated Populations
The epidemiology of pertussis within vaccinated populations presents unique challenges to public health. Despite widespread immunization efforts since the 1940s, outbreaks continue to surface, often in clusters within communities with high vaccination rates. The 2024 incident in South Korea not only sheds light on these outbreaks but also emphasizes the changing landscape of pertussis epidemiology, where vaccinated individuals can experience and transmit the infection. Understanding the epidemiological patterns, including seasonal trends and demographic influences, is pivotal for designing effective health interventions.
Additionally, the comprehensive assessment of transmission patterns in vaccinated populations reveals critical insights into the pathogen’s behavior. With data showing a notable attack rate and significant cases attributable to superspreaders, health authorities are prompted to consider novel strategies for monitoring and controlling pertussis outbreaks. The reliance on traditional immunity models must be supplemented with real-time data analytics to better inform public health responses and improve vaccination coverage.
Super Spreading Events in Pertussis Transmission
Super spreading events are a crucial aspect of pertussis transmission dynamics, where a small fraction of infected individuals contribute disproportionately to new infections. The South Korea outbreak demonstrated that 15% of active cases were responsible for 80% of the total transmissions. This information is vital for public health officials as it highlights the need for targeted interventions aimed at limiting these high-risk individuals. Recognizing the characteristics of superspreaders can facilitate quicker containment strategies, reducing the overall burden of disease in the community.
In order to mitigate the impact of super spreading events, public health initiatives must incorporate strategies that include enhanced surveillance and early identification of potential high-risk cases. The outbreaks illustrate the importance of contact tracing and vaccination compliance among individuals exposed to identified cases. By focusing on these key areas, health authorities can effectively interrupt transmission chains and protect both vaccinated and unvaccinated populations from the resurgence of pertussis.
Public Health Interventions for Controlling Pertussis
Public health interventions are fundamental in managing the spread of pertussis, particularly in light of recent outbreaks among vaccinated populations. Health authorities must prioritize strategies such as rapid case identification and extensive contact tracing to curb transmission rates effectively. The South Korean outbreak elucidates the importance of timely reporting and collaboration between educational institutions and health agencies, which can enhance response effectiveness in schools and communities.
Moreover, reinforcing vaccination programs through educational campaigns about the importance of booster shots can improve community immunity. By ensuring that parents are informed about the need for ongoing immunizations, public health officials can foster higher vaccination rates, particularly among adolescents who may be at greater risk of contracting and spreading the disease. Enhanced communication strategies will help in addressing vaccine hesitancy, ultimately protecting vulnerable populations from pertussis outbreaks.
The Role of Immunity in Pertussis Resurgence
The resurgence of pertussis cases in recent years has prompted an examination of immunity’s role in disease transmission dynamics, particularly in populations with high vaccination coverage. While initial immunization provides substantial protection against *Bordetella pertussis*, studies have shown that immunity wanes over time, leading to increased susceptibility in older populations. This aspect was starkly highlighted during the 2024 outbreak in South Korea, where a majority of infected individuals had been vaccinated, indicating a critical gap in long-term immunity.
As such, understanding the interplay between natural and vaccine-induced immunity is essential for formulating effective public health responses. Prioritizing research on the length and quality of vaccine-induced immunity will assist in shaping public health policies that encourage booster vaccinations at appropriate intervals. In doing so, we can mitigate the risks associated with pertussis resurgence and protect future generations.
Strategies for Enhancing Vaccination Coverage
Enhancing vaccination coverage is a primary strategy for controlling pertussis outbreaks, especially in the face of waning immunity among vaccinated individuals. Public health authorities must develop comprehensive strategies to engage communities and ensure that vaccination programs remain efficient and accessible. This includes improving outreach efforts in schools and using multimedia campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of complete vaccination schedules, particularly for children and adolescents.
Furthermore, leveraging partnerships with local healthcare providers can facilitate better vaccination uptake within communities. By implementing reminder systems and offering flexible vaccination clinics, public health interventions can target populations that may otherwise fall through the cracks of routine immunizations. Ultimately, these strategies can help foster a greater commitment to vaccinations, thus reinforcing community immunity against pertussis.
Identifying Factors Influencing Pertussis Transmission
Identifying the factors that influence pertussis transmission is critical for tailoring effective public health interventions. Demographic variables such as age, gender, and vaccination history play a substantial role in the dynamics of pertussis spread, especially in settings like schools where close contact is frequent. The 2024 South Korean outbreak, which had a notably high attack rate among adolescents, indicates that certain age groups may be more susceptible to pertussis, necessitating targeted public health messaging and intervention.
Additionally, environmental factors such as classroom size, ventilation, and overall hygiene practices can significantly impact transmission dynamics. Studies focusing on these aspects can provide valuable insights for developing safer learning environments that minimize the risk of pertussis outbreaks. By thoroughly examining these influencing factors, public health strategies can be more effectively implemented to control transmission and protect community health.
Future Directions in Pertussis Research
Future research directions in pertussis are essential for understanding the evolving challenges posed by *Bordetella pertussis*. As outbreaks continue to occur in vaccinated populations, it is imperative that researchers explore the mechanisms behind waning immunity and its effects on disease dynamics. Ongoing studies should focus on the development of new vaccines that can provide longer-lasting immunity and potentially adapt to the changing landscape of pertussis epidemiology.
Moreover, incorporating advanced modeling techniques to predict outbreak patterns and transmission dynamics will enhance the capacity of public health systems to respond proactively. By investing in research that elucidates the nuances of pertussis, we can adapt vaccination strategies and public health interventions to better manage and control future outbreaks, ensuring community protection against this enduring infectious threat.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do pertussis transmission dynamics influence whooping cough outbreaks in vaccinated populations?
Pertussis transmission dynamics indicate that even in vaccinated populations, the transmission can be significant. As demonstrated in recent outbreaks, including a school-based outbreak in South Korea, pertussis can spread rapidly among vaccinated children. This suggests that while vaccines reduce the severity of the disease, they may not completely prevent transmission, allowing outbreaks to occur.
What role do super spreading events play in the epidemiology of pertussis?
Super spreading events are crucial in the epidemiology of pertussis as they disproportionately contribute to the overall transmission. In the 2024 South Korea outbreak, 15% of cases were responsible for 80% of all transmissions, highlighting the significant impact of super spreaders in spreading whooping cough rapidly, especially within school settings.
Why is it important to conduct studies on pertussis epidemiology in vaccinated children?
Studying pertussis epidemiology in vaccinated children is vital as it helps public health officials understand how vaccination affects disease transmission dynamics. This knowledge is crucial for devising effective public health interventions, such as improving booster vaccine strategies and optimizing response plans during whooping cough outbreaks.
What public health interventions can reduce pertussis transmission in schools?
Effective public health interventions to reduce pertussis transmission in schools include rapid contact tracing, strict adherence to vaccination recommendations, and the timely administration of booster vaccines. Additionally, promoting awareness about the symptoms of pertussis can help in early identification and containment of outbreaks.
How does the serial interval affect our understanding of pertussis transmission dynamics?
The serial interval, which is the time between successive cases of infection, is crucial for understanding pertussis transmission dynamics. In the school-based outbreak analyzed, the mean serial interval was 9.5 days, indicating the potential rapid spread of the disease, emphasizing the need for prompt public health responses to control outbreaks.
What challenges do public health authorities face in managing pertussis outbreaks in vaccinated populations?
Public health authorities face significant challenges in managing pertussis outbreaks in vaccinated populations, largely due to waning immunity levels and the occurrence of super spreading events. The resurgence of whooping cough amongst vaccinated individuals complicates outbreak control efforts, requiring enhanced surveillance and vaccination strategies to maintain community immunity.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Context | Investigated a pertussis outbreak in a school in South Korea, 2024. |
| Transmission Dynamics | Mean serial interval of pertussis was 9.5 days. |
| Superspreading | 15% of cases were responsible for 80% of transmissions. |
| Attack Rate | 10.1% attack rate with a total of 48 confirmed cases. |
| Demographics | 70.8% of cases were male, median age was 15 years with a majority vaccinated. |
| Public Health Implications | Suggests the need for rapid contact tracing and booster vaccinations. |
Summary
Pertussis transmission dynamics have been characterized by a significant resurgence in cases even within vaccinated populations, particularly evidenced by the 2024 school outbreak in South Korea. This outbreak revealed that despite high vaccination coverage, the mean serial interval was 9.5 days, indicating high transmissibility, particularly among vaccinated children. Alarmingly, a small percentage of cases (15%) contributed to the majority (80%) of the transmissions, underscoring the impact of superspreading events. The findings emphasize the critical need for prompt public health measures, enhanced vaccination strategies, and continuous monitoring to mitigate pertussis transmission dynamics effectively.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.