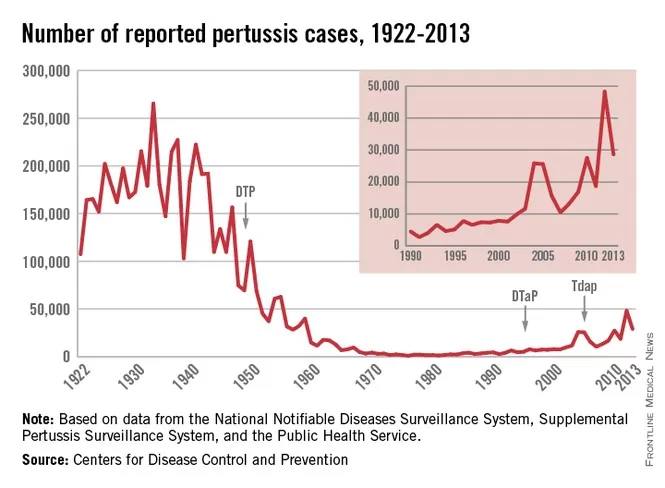
In Louisiana, pertussis deaths have tragically claimed the lives of two infants in the past six months, highlighting the urgent need for attention to whooping cough prevention measures. These vaccine-preventable fatalities are a stark reminder that vaccination rates in the state have declined, potentially ushering in a pertussis outbreak. As of last week, the CDC reported 110 confirmed cases of whooping cough in Louisiana, raising concerns about the effectiveness of childhood vaccines in combating this infectious disease. The upward trend in infections, with over 35,000 cases reported nationwide last year, emphasizes the importance of maintaining robust vaccination rates to protect our most vulnerable populations. In light of these alarming CDC pertussis statistics, public health officials are urging communities to prioritize vaccination to prevent further tragedies in the future.
The recent surge in fatalities due to whooping cough has highlighted a pressing public health issue in Louisiana. Known medically as pertussis, this contagious disease can be deadly, particularly among infants and young children. With vaccination rates declining, there is an increasing risk of outbreaks, which can lead to severe complications and even death. Public health experts emphasize the necessity of childhood immunizations to build herd immunity and prevent the spread of this preventable illness. As communities grapple with misinformation surrounding vaccines, the implications of these declines raise concerns about the overall effectiveness of public health strategies.
The Recent Pertussis Deaths in Louisiana
The tragic news of two infants dying from pertussis in Louisiana underscores a daunting public health crisis. Pertussis, commonly known as whooping cough, is a vaccine-preventable disease that poses grave risks, especially to infants and young children. Despite the fact that effective childhood vaccines have existed for decades, the recent surge in cases raises concerns about vaccination rates and public awareness. The fatalities serve as a haunting reminder of the consequences of declining immunization. As evidenced by the reports from the CDC, this rise in infections has been noted nationally, with more than 35,000 confirmed cases last year alone.
In a state where health professionals are abandoning the promotion of vaccinations, the impact can be devastating. The deaths of these children due to pertussis spotlight the critical need for effective vaccination campaigns. State health officials are calling upon the community to prioritize childhood vaccines, as the current environment of skepticism may lead to more outbreaks. Addressing this crisis effectively requires restoring public trust in immunization, particularly in a state where concerns about vaccine safety have been publicly voiced.
Understanding Whooping Cough: Symptoms and Risks
Whooping cough, or pertussis, is an infectious disease that primarily affects the respiratory system. It begins with symptoms similar to the common cold, including a runny nose, sneezing, and mild cough. As the illness progresses, it leads to severe coughing fits that can last for weeks. This disease can be life-threatening, especially for infants who are not fully vaccinated, making education about symptoms and prevention critical. Parents must recognize these early signs to seek timely medical intervention, which can save lives.
The risks associated with whooping cough highlight the importance of maintaining high vaccination rates across communities. Health experts recommend that infants receive their DTaP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis) vaccinations starting at two months of age, followed by several booster doses. This is crucial in creating herd immunity, which protects those who can’t be vaccinated, including newborns and individuals with certain health conditions. Decreasing immunity in the broader population raises the likelihood of pertussis outbreaks, making it essential for everyone eligible to get vaccinated and maintain protection.
The Role of Vaccination in Protecting Against Pertussis
Vaccination plays a pivotal role in preventing outbreaks of pertussis, contributing significantly to reducing morbidity and mortality associated with the disease. The CDC’s statistics indicate that vaccination has dramatically lowered incidence rates of whooping cough; however, recent declines in childhood vaccination rates are alarming. Experts stress that failing to vaccinate not only endangers children but can also lead to broader community health challenges as seen with the spreading pertussis outbreaks. Public health campaigns promoting the benefits of childhood vaccines are essential to reverse this trend.
Moreover, experts emphasize the need for ongoing education regarding the safety and efficacy of childhood vaccines. Misinformation can have cascading effects on vaccination projects, leading to skepticism and, ultimately, increased disease prevalence. By reinstating proactive strategies that promote vaccine confidence, health authorities could mitigate the risks posed by environmental conditions that may foster pertussis transmission. It is vital for the community to approach vaccinations with trust and unified action.
Rising Pertussis Cases: National Trends and Statistics
The recent surge in pertussis cases across the nation is raising alarms among public health officials and experts. The CDC has reported that last year marked one of the highest incidences in over a decade, with more than 35,000 confirmed infections. This significant increase not only highlights the vulnerability of public health systems but also demonstrates the need for more vigorous response strategies. As the country navigates a resurgence of whooping cough, a multifaceted approach involving awareness campaigns, transparent communication about vaccine benefits, and community engagement becomes paramount to curb these trends.
In 2025 alone, nearly 6,600 pertussis cases have already been documented, indicating a troubling pattern that mirrors declining immunization rates. This worrying trajectory necessitates a concerted effort among healthcare providers, policymakers, and the community to reinforce the importance of timely vaccinations. By fostering an informed discussion about the impacts of declining vaccination rates, authorities can work towards improving not only the immediate response to pertussis outbreaks but also long-term prevention strategies that safeguard public health.
The Consequences of Declining Vaccination Rates
Declining vaccination rates across the United States are at the heart of the recent pertussis outbreaks, illustrating a direct correlation between immunization practices and disease prevalence. Over the past several years, many parents have become hesitant about vaccines, often fueled by misinformation regarding vaccine safety. This reluctance leads to clusters of unvaccinated individuals, creating fertile ground for diseases like whooping cough to thrive. As evidenced by the deaths of infants in Louisiana, the stakes are real, and communities must act urgently to ensure that widespread immunization continues.
Public health initiatives aimed at addressing the root causes of vaccine hesitancy are essential in reversing these concerning trends. Community outreach and education must focus on dispelling myths and providing transparent information about the effectiveness and safety of childhood vaccines. Only through a dedicated effort to engage with parents and provide credible resources can health authorities hope to restore public confidence in vaccination, thereby protecting vulnerable populations and preventing further outbreaks of pertussis.
Health Officials Urge for Increased Vaccination Against Pertussis
In light of the rising pertussis cases and recent tragedies in Louisiana, health officials are ramping up calls for the public to prioritize pertussis vaccinations. State leaders recognize that persistent public hesitance about vaccines may stem from confusion regarding vaccine safety and efficacy. Health organizations are urging families to consider the overwhelming scientific consensus supporting immunization. The protection provided by vaccines, including DTaP, is crucial in mitigating not just pertussis outbreaks but also enhancing community immunity as a whole.
Experts encourage proactive measures, such as updating vaccinations for children and adolescents, as preventative action against potential outbreaks. Creating awareness campaigns tailored not just to educate but also to listen to community concerns can play an instrumental role in boosting vaccination rates. By taking these steps, the community can change the trajectory of whooping cough incidences and ensure safety for many children who are at risk, thus leading to a healthier population overall.
Pertussis Outbreaks: A Global Perspective
The story of pertussis is not limited to the United States; similar patterns of resurgence have been noted in various countries worldwide. Global vaccination rates, while generally effective, are uneven, and some regions still struggle with low uptake due to cultural resistance, misinformation, and limited healthcare access. This complicates the containment of pertussis, creating cycles of outbreaks that can spread rapidly, especially in areas with low herd immunity. International health organizations emphasize the need for collaborative efforts to address vaccine refusal and improve public education on the benefits of immunization.
These factors highlight the importance of a global approach to vaccination against contagious diseases like pertussis. World initiatives focused on childhood immunization campaigns have shown considerable success in various contexts, leading to lowered infection rates. By establishing solid partnerships between local governments, health organizations, and communities, we can form a robust defense against outbreaks and ultimately work toward eradicating vaccine-preventable diseases on a global scale.
The CDC’s Role in Monitoring Pertussis Statistics
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a crucial role in tracking pertussis cases and providing statistics that inform national public health strategies. By analyzing outbreak patterns, vaccine efficacy, and demographic data, the CDC offers insights that can shape policies to improve vaccination coverage and disease prevention. Continuous surveillance by the CDC ensures that any rise in pertussis cases is promptly addressed, and resources are allocated efficiently to affected regions.
In conjunction with local health departments, the CDC also disseminates critical information related to vaccination guidelines and outbreaks. This support is essential, particularly in times of rising case numbers, as seen recently in Louisiana. Public health authorities rely on these statistics to formulate effective communication strategies, encouraging communities to stay informed and proactive regarding childhood vaccines, thus helping to mitigate the resurgence of pertussis and other similar diseases.
Confronting Misinformation Around Child Vaccines
Misinformation surrounding childhood vaccines remains one of the most significant barriers to achieving optimal vaccination rates. Reports of vaccine hesitancy have surged, fueled by anecdotal claims and fearmongering, leading many parents to question the safety of vaccinations, including the DTaP shot for pertussis. These fears can result in lower vaccination rates, which exacerbate the risk of outbreaks, as seen by the recent pertussis cases in Louisiana. Stakeholders in public health must confront this misinformation head-on with comprehensive and clear communication strategies.
Addressing misinformation is critical not only to improve vaccination rates but also to build a more informed citizenry. Health officials and experts are encouraged to collaborate with community leaders and influencers who can effectively reach audiences and explain the benefits of vaccination. Initiatives could include social media campaigns, informative dialogues at local health forums, and transparent discussions with parents. By fostering a culture of understanding around the importance of vaccinations against diseases like pertussis, communities can enhance their overall immunity and health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the recent statistics on pertussis deaths in Louisiana?
Recently, Louisiana reported two infant deaths due to pertussis, also known as whooping cough. This alarming statistic highlights the importance of childhood vaccines, especially as the CDC noted a concerning rise in pertussis cases in the state.
How does declining vaccination rates impact pertussis outbreak occurrences in Louisiana?
Declining vaccination rates in Louisiana have led to increased susceptibility and higher chances of pertussis outbreaks. As immunity drops within communities, the risk of whooping cough infections rises, ultimately contributing to pertussis deaths among infants.
What role does the CDC play in tracking pertussis cases and deaths in Louisiana?
The CDC is instrumental in monitoring pertussis statistics in Louisiana and nationwide. They report on infection rates and mortality, emphasizing the critical need for childhood vaccinations to prevent further deaths from vaccine-preventable diseases like whooping cough.
Why is it important for parents to vaccinate their children against pertussis in Louisiana?
Vaccination against pertussis is crucial in Louisiana to protect infants and young children from a potentially deadly disease. With recent deaths reported, it’s evident that childhood vaccines remain the best defense against whooping cough outbreaks and related fatalities.
What have experts said about the recent rise in pertussis cases and deaths in Louisiana?
Experts have linked the recent rise in pertussis cases and deaths in Louisiana to declining childhood vaccination rates. They warn that as immunization rates fall, communities become more vulnerable to outbreaks, leading to tragic outcomes like infant deaths.
How are public health officials in Louisiana responding to the increase in whooping cough cases?
Public health officials in Louisiana are urging vaccinations and addressing misinformation about childhood vaccines to combat the rise in whooping cough cases. They stress that maintaining high vaccination rates is essential for preventing future pertussis deaths.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Pertussis Deaths in Louisiana | Two Louisiana infants have died of pertussis in the last six months. |
| Rise in Pertussis Cases | As of last week, there are 110 confirmed cases of pertussis in Louisiana. Nationally, there were over 35,000 cases last year, the highest in over a decade. |
| Declining Vaccination Rates | Childhood vaccination rates in the US have dropped over the past five years, leading to increased susceptibility to infections like pertussis. |
| Expert Opinions | Health experts are stressing the importance of vaccinations to prevent outbreaks. |
| Public Health Messaging | Confusion surrounding vaccination safety and efficacy is a challenge for public health advocates. |
Summary
Pertussis deaths in Louisiana have garnered attention as two infants tragically succumbed to this vaccine-preventable disease over the last six months. As cases of pertussis continue to rise, both locally and nationally, health experts are emphasizing the critical need for increased vaccination efforts. The decline in childhood vaccination rates has played a significant role in the resurgence of pertussis, leading to higher susceptibility among populations. To prevent further tragedies, clear and effective messaging about the importance of vaccines is essential in Louisiana and across the United States.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.