Pediatric Tamiflu guidelines are crucial for effectively managing the flu in young patients. However, a recent analysis reveals a concerning trend: many clinicians are not adhering to these national recommendations for prescribing oseltamivir to children, particularly those hospitalized with influenza. The study published in Pediatrics highlights that less than half of pediatricians followed the proper protocol, leading to questions about the consistency of pediatric influenza treatment across the U.S. Hospitals are places where timely and appropriate use of antiviral medications can significantly impact patient outcomes. With the support for further randomized trials of Tamiflu in children, there is an urgent need to align clinical practice with established guidelines to enhance the treatment of hospitalized children with flu.
An examination of the prescribing patterns for antiviral agents in pediatrics reveals a significant gap in treatment compliance. Recent findings illustrate that adherence to oseltamivir prescription guidelines for children facing influenza is alarmingly low among healthcare providers. Despite clear recommendations from the American Academy of Pediatrics, many practitioners struggle with the implementation of pediatric influenza treatment protocols. Factors such as awareness of existing guidelines and the severity of symptoms appear to influence prescribing decisions. This situation underscores the importance of addressing barriers to the appropriate use of Tamiflu in children, especially in hospital settings.
Understanding Pediatric Tamiflu Guidelines
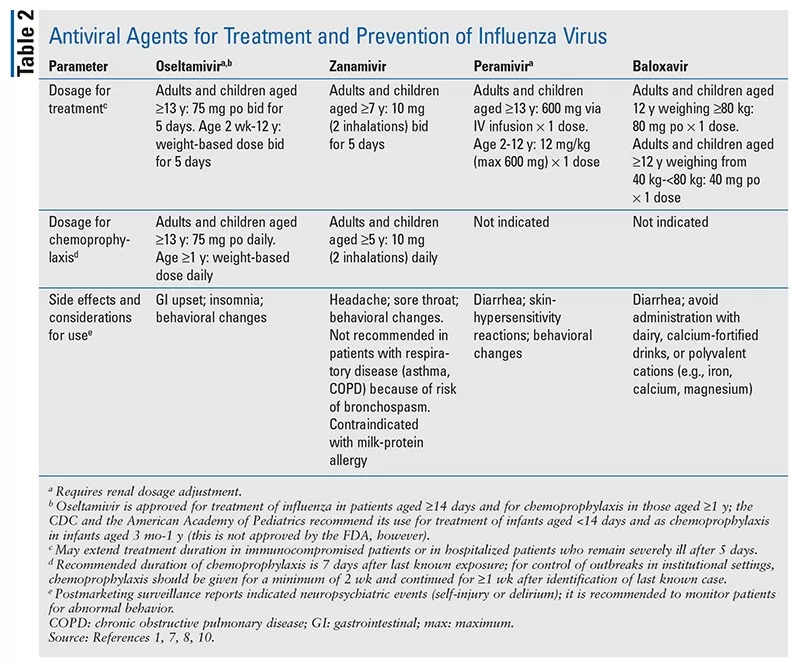
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) lays down essential guidelines for the administration of oseltamivir, commonly known as Tamiflu, to children hospitalized with influenza. According to these guidelines, it is crucial for all U.S. children diagnosed with the flu and requiring hospitalization to receive this antiviral medication. Despite the clarity of these recommendations, a significant number of clinicians fail to adhere to them, raising concerns about the treatment choices made in acute care settings. With inadequate compliance, the potential for optimal recovery may diminish, emphasizing the need for better adherence to established pediatric Tamiflu guidelines.
Understanding these guidelines is imperative for pediatricians and healthcare providers as they navigate treatment strategies for pediatric patients afflicted with influenza. Studies indicate that when clinicians follow these protocols, the overall outcomes for children hospitalized with flu improve markedly. The barriers to adherence among physicians can include misconceptions about the efficacy of Tamiflu, lack of updated knowledge on guidelines, or varying levels of familiarity with medication protocols. Promoting awareness and education surrounding pediatric Tamiflu guidelines could facilitate necessary changes in practice and enhance patient care.
The Importance of Prescribing Oseltamivir for Hospitalized Children
Prescribing oseltamivir to hospitalized children is not just a routine protocol; it plays a pivotal role in mitigating the severity of influenza. Randomized trials have shown its effectiveness in reducing hospital stay length and hastening recovery. Yet surprisingly, the survey reveals less than half of the clinicians surveyed recommended this antiviral drug, even when it was indicated. This not only compromises individual patient care but also poses a risk of increased morbidity associated with viral infections in pediatric patients.
In particular, clinicians often exhibit hesitancy in prescribing oseltamivir to patients exhibiting protracted illnesses or those with symptoms not primarily respiratory. This apprehension can stem from a mix of personal clinical experiences and interpretation of guidelines. The need for comprehensive education on the rationale behind pediatric influenza treatment protocols becomes evident. By fostering an environment where treatment guidelines are regularly communicated and reinforced, healthcare professionals can feel more confident in prescribing oseltamivir, ensuring that hospitalized children receive the care they need promptly.
Challenges in Adhering to Pediatric Influenza Treatment Protocols
The adherence challenges to pediatric influenza treatment protocols are multifaceted. While a significant number of pediatricians report awareness of oseltamivir prescribing guidelines, a gap remains in consistent application of these guidelines across various clinical settings. Miscommunication, lack of timely access to the latest research, and varying levels of specialty experience can inhibit clinicians’ decisions to prescribe Tamiflu, particularly in urgent care scenarios where rapid decisions are critical for patient stability and recovery.
Moreover, the survey findings indicate a dramatic variance in prescribing behavior among different specialties; infectious disease specialists displayed greater compliance with guidelines compared to pediatric hospitalists. This discrepancy suggests the necessity for tailored educational interventions that address and alleviate specialty-specific barriers to adherence. Implementing ongoing professional development and standardized training sessions can help bridge this gap, promoting an integrated approach to pediatric influenza management that prioritizes prompt and effective antiviral treatment.
Recent Trends in Tamiflu Prescription Practices
Recent trends indicate a concerning decline in the prescription of oseltamivir for children with influenza in hospital settings. Though it remains an effective antiviral treatment, the reluctance to utilize it suggests underlying issues within clinical judgment and understanding of the drug’s benefits. A study highlighted that even among those aware of the current guidelines, a significant cohort still opted against prescribing Tamiflu, hinting at potential misconceptions regarding its role in treatment.
This critical situation calls for an urgent reevaluation of clinical practices surrounding pediatric influenza treatment. Prescribing patterns must be informed by the latest evidence, showcasing randomized trials of Tamiflu and its implications for quicker recovery times and reduced hospital readmission rates. Addressing these trends through collaborative efforts among healthcare providers can lead to improved outcomes for hospitalized children requiring antiviral intervention.
The Need for Further Research on Tamiflu in Children
The pressing call for more research on the use of oseltamivir in hospitalized children cannot be overstated. A significant majority of pediatricians, approximately 87.4%, believe that randomized trials of Tamiflu specifically for this demographic are crucial for enhancing understanding of its effectiveness. Despite existing research, gaps remain in comprehensive data collection that accounts for diverse patient profiles and varying severity of influenza cases.
Further studies are essential not only to bolster guidelines but also to provide a robust framework for clinicians when addressing pediatric influenza treatment. Increasing the volume of evidence-based analysis on Tamiflu in children can empower clinicians to make informed decisions backed by science, thus ensuring that every child receives appropriate antiviral therapy according to clinical guidelines and improves their chances for a swift recovery.
Impact of Knowledge Gaps on Pediatric Treatment Decisions
Knowledge gaps among clinicians can have a profound impact on treatment decisions, especially in the context of pediatric influenza management. The survey’s results show that among those who were well-informed about the guidelines for oseltamivir use, nearly 62% recommended the antiviral therapy, whereas, for those lacking precise knowledge, this number plummeted to 42.4%. This stark contrast underscores the necessity for continuous education and dissemination of updated clinical guidelines to all healthcare providers involved in pediatric care.
By fostering awareness of the importance of adhering to pediatric Tamiflu guidelines, healthcare institutions can equip physicians with the tools needed to make confident and informed prescribing decisions. Addressing knowledge gaps through targeted training initiatives can directly influence clinical behavior and improve adherence rates, ultimately enhancing therapeutic outcomes for young patients suffering from influenza.
The Role of Infectious Disease Specialists in Tamiflu Prescription
Infectious disease specialists are uniquely positioned in the healthcare ecosystem to make informed Tamiflu prescriptions to young patients. Their specialized training allows them to interpret clinical evidence more effectively, guiding their decision-making process when it comes to utilizing oseltamivir for hospitalized children. It’s evident from statistics that these specialists exhibit a higher propensity to recommend Tamiflu compared to their peers in pediatrics, suggesting that their expertise could be leveraged to set standards for best practices in treating pediatric influenza.
Furthermore, the interventions led by infectious disease specialists can drive awareness among other healthcare providers regarding the importance of adherence to pediatric Tamiflu guidelines. By creating interdisciplinary collaborations and fostering relationships between specialties, the entire healthcare team can unite toward common treatment goals, ensuring that antiviral medications are promptly administered when necessary, thus improving patient care quality.
Addressing Resistance to Tamiflu Treatment
Resistance to prescribing oseltamivir, or Tamiflu, among clinicians can stem from various factors, including skepticism about the drug’s efficacy or apprehensions regarding side effects. By understanding these barriers, healthcare systems can develop targeted strategies to alleviate concerns and encourage its appropriate use in pediatric settings. Engaging clinicians through workshops or seminars featuring success stories and evidence from recent studies can help reshape attitudes toward administering preventive antiviral therapy in young patients.
Moreover, integrating feedback loops within pediatric healthcare settings can promote ongoing discussions regarding treatment options. As resistance diminishes and understanding grows about the importance of utilizing Tamiflu in hospitalized children, there can be significant improvements in patient outcomes and adherence to established pediatrics influenza treatment protocols.
Outcomes of Following Pediatric Tamiflu Guidelines
Adhering to pediatric Tamiflu guidelines has been linked to positive outcomes such as reduced hospitalization duration and lower rates of complications among children suffering from influenza. Research indicates that prompt treatment with oseltamivir can due significantly lessen hospital stays, providing economic benefits as well as improving the quality of health care. Consequently, pediatricians must ensure their prescribing practices align with established recommendations to optimize therapeutic results.
Evaluating clinical outcomes as they relate to guideline adherence can serve as an effective mechanism for assessing the impact of better practices within medical institutions. Findings from various studies advocate for the rigorous application of pediatric influenza treatment protocols that include oseltamivir, ultimately leading to enhanced patient recovery, higher satisfaction rates among families, and a more streamlined healthcare delivery process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the pediatric Tamiflu guidelines for hospitalized children?
The pediatric Tamiflu guidelines recommend that all U.S. children hospitalized due to influenza should receive oseltamivir (Tamiflu) during their hospital stay, as stated by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Adherence to these guidelines is essential for effective pediatric influenza treatment.
Why is there low adherence to pediatric Tamiflu guidelines among clinicians?
A recent survey indicated that only 49.5% of clinicians adhered to pediatric Tamiflu guidelines when prescribing oseltamivir to hospitalized children with the flu. This inconsistency may arise from a lack of awareness of the guidelines or uncertainty about the benefits of Tamiflu in certain cases.
How does oseltamivir compare in effectiveness for pediatric influenza treatment?
Oseltamivir, or Tamiflu, is recommended for pediatric influenza treatment based on established guidelines. However, randomized trials specifically in the pediatric population are necessary to further validate its effectiveness and to increase clinician adherence to using oseltamivir in children hospitalized with the flu.
What are the primary concerns regarding Tamiflu use in children?
Concerns regarding Tamiflu use in children include the variability in prescription practices among clinicians and the management of non-respiratory symptoms or prolonged illnesses in pediatric patients. Understanding pediatric Tamiflu guidelines can alleviate some of these concerns.
What evidence supports the prescribing of oseltamivir for influenza in hospitalized children?
Current pediatric Tamiflu guidelines are supported by clinical evidence suggesting that oseltamivir can reduce the duration of influenza symptoms in hospitalized children. However, more randomized trials in this demographic would strengthen the advocacy for its use among clinicians.
What factors influence clinicians’ decisions to prescribe Tamiflu in children?
Factors influencing the prescription of Tamiflu in children include familiarity with pediatric Tamiflu guidelines, the presence of respiratory versus non-respiratory symptoms, and the clinicians’ specialty area. Infectious disease specialists were most likely to recommend oseltamivir compared to other specialties.
What is the importance of randomized trials for oseltamivir in hospitalized children?
Randomized trials of oseltamivir in hospitalized children are considered crucial by 87.4% of surveyed clinicians, as these studies could provide clearer insights into its efficacy and help to enhance adherence to pediatric Tamiflu guidelines across the medical community.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Adherence to Guidelines | Less than 50% of pediatricians adhere to pediatric Tamiflu guidelines. |
| Survey Data | The study surveyed 787 physicians from March to June 2024 across seven U.S. children’s hospitals. |
| Recommendations by AAP | AAP recommends all hospitalized children with influenza receive oseltamivir. |
| Prescribing Patterns | Oseltamivir was prescribed in only 49.5% of qualifying cases. |
| Awareness of Guidelines | 62.0% of clinicians who knew the guidelines chose oseltamivir vs. 42.4% who did not. |
| Variation by Specialty | Infectious disease specialists prescribed oseltamivir most frequently. |
| Need for Research | 87.4% of respondents think randomized trials in hospitalized children are important. |
| Primary Outcome for Evaluation | Hospital length of stay is the critical outcome to assess. |
Summary
Pediatric Tamiflu guidelines emphasize that all children hospitalized due to influenza should receive oseltamivir; however, adherence to these guidelines remains low among clinicians. A recent survey highlighted that less than half of pediatricians are following these recommendations, indicating a significant gap in practice. The need for further research through randomized control trials is strongly supported by practitioners, which could enhance the understanding and application of these guidelines. It is crucial for healthcare providers to stay informed and ensure compliance with pediatric Tamiflu guidelines to improve the treatment outcomes for hospitalized children with influenza.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.