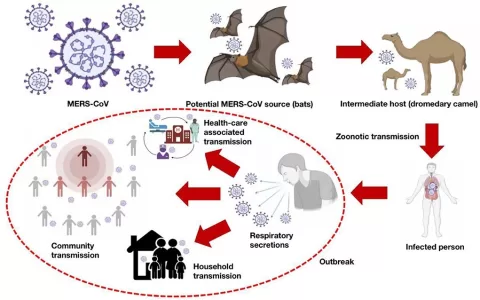
Pathogen genomics is revolutionizing public health by enhancing our ability to understand and combat infectious diseases. Through cutting-edge genomic sequencing technologies, the complex genetic makeup of pathogens can be decoded, providing invaluable insights for tracking their spread and evolution. This surge in knowledge is not only transforming disease prevention strategies but is also integral to improving response efforts during global health crises. With support from organizations such as the CDC Advanced Molecular Detection program, bioinformatics tools have become essential for analyzing vast amounts of genomic data. As we delve deeper into pathogen genomics, public health officials are better equipped to safeguard communities against infectious threats.
The study of pathogen genomes is reshaping the landscape of infectious disease management, utilizing advanced molecular technologies to offer critical insights into microbial behaviors. By exploring the intricate genetic structures of viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens, researchers can better forecast disease outbreaks and tailor public health strategies. This genomic approach, paired with robust bioinformatics, supports informed decision-making and enhances surveillance programs across the globe. As we navigate the complexities of public health in an age marked by emerging threats, the role of genetic sequencing and comprehensive data analysis is becoming increasingly vital. Ultimately, this synergy of science and technology is paving the way for a more proactive and responsive health system.
The Evolution of Pathogen Genomics in Public Health
Over the past decade, pathogen genomics has seen remarkable advancements and has become a cornerstone in public health practice. The ability to sequence the genomes of various pathogens—including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites—enables health officials to understand the genetic makeup of these organisms. This genomic data allows for a more refined analysis of pathogen evolution, transmission dynamics, and resistance patterns, ultimately facilitating better disease control strategies. By utilizing genomic sequencing technologies, public health professionals can pinpoint outbreak sources and track their spread more effectively, thus enhancing their response capabilities when faced with infectious diseases.
Moreover, the integration of genomics with traditional public health epidemiology has opened up new avenues for disease surveillance. This synthesis of methods aids in deciphering epidemiological trends and behaviors that were previously difficult to assess. As such, pathogen genomics acts not only as a diagnostic tool but also as a powerful instrument for forecasting public health needs. The ongoing challenges posed by infectious diseases highlight the necessity of continuously refining these genomic approaches to ensure a robust public health framework.
The Role of Bioinformatics in Pathogen Genomics
Bioinformatics plays a vital role in transforming raw genomic data into useful public health intelligence. As pathogen sequencing generates enormous volumes of data, efficient bioinformatics tools and platforms are essential for analyzing this information. They allow scientists to interpret sequence data, identify mutations, track lineage variations, and even predict potential public health threats posed by emerging pathogens. Investments in bioinformatics not only enhance data management and analysis capabilities but also foster collaboration across laboratories, providing a more comprehensive understanding of infectious diseases.
Additionally, the application of bioinformatics is critical for ensuring data standardization and accessibility, which are paramount for facilitating global collaboration during health crises. Initiatives such as the CDC Advanced Molecular Detection program have emphasized bioinformatics as a cornerstone of public health genomics infrastructure. By equipping public health practitioners with the necessary bioinformatics skills, the field can better adapt to the ever-changing landscape of infectious diseases, leading to more timely public health interventions and streamlined communication within the global health community.
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Genomic Surveillance
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of genomic sequencing at unprecedented levels, underscoring its importance in the realm of public health. With the rapid emergence of variants, timely genomic surveillance became essential for tracking changes in the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Over 17 million viral genomes were sequenced and shared globally, providing invaluable insights into viral transmission patterns and mutation rates. This collective effort to gather and analyze genomic data facilitated a proactive public health response, allowing authorities to adjust vaccination strategies and implement targeted control measures.
Furthermore, the success of genomic surveillance during the pandemic has solidified its role as a critical component of public health strategy. It has also highlighted the importance of international cooperation in data sharing and has spurred discussions around ethical considerations in genomic research. By leveraging the lessons learned from the pandemic, public health organizations are now better equipped to enhance their genomic surveillance capabilities for future outbreaks, ensuring a quicker and more effective response to emerging public health threats.
Collaborative Approaches to Enhancing Infectious Disease Control
Collaboration across various sectors—including academia, public health agencies, and the private sector—is essential for advancing pathogen genomics and infectious disease control. The CDC Advanced Molecular Detection program exemplifies this collaborative spirit by forging partnerships to expand laboratory capacities and promote the integration of advanced genomic technologies within public health systems. Such partnerships enable the sharing of resources, expertise, and data, resulting in more effective monitoring and controlling of infectious diseases across diverse populations.
Moreover, these collaborations are vital for ensuring that advancements in pathogen genomics translate into practical public health applications. By working together, stakeholders can identify emerging threats and develop comprehensive strategies that incorporate genomic data into existing surveillance and response frameworks. This synergistic approach not only enhances the effectiveness of public health interventions but also fosters a more resilient healthcare infrastructure capable of addressing both current and future infectious disease challenges.
Investments in Genomic Technologies for Public Health Advancement
Strategic investments in genomic technologies are crucial for enhancing public health infrastructures, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. These investments facilitate the establishment of local genomic laboratories, training for health professionals, and the development of bioinformatics capacity that is necessary for effective disease monitoring and control. By creating localized networks of expertise and resources, these efforts empower countries to respond to infectious diseases more autonomously and efficiently.
Furthermore, enhancing genomic capabilities at the local level leads to improved health outcomes and more equitable access to public health resources. As these countries become more self-reliant in their genomic surveillance efforts, they can contribute valuable data to global health databases, enriching the collective understanding of infectious diseases. The ongoing commitment to investing in pathogen genomics not only addresses immediate public health challenges but also builds a platform for sustainable health development that can withstand future pandemics.
The Future of Pathogen Genomics in Public Health
Looking ahead, the future of pathogen genomics is poised to revolutionize public health practices even further. Emerging technologies, such as long-read sequencing and machine learning algorithms, promise to enhance the precision of genomic analyses, allowing for deeper insights into pathogen behavior and interaction with hosts. As genomic technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly play an indispensable role in our ability to respond to both emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases with speed and accuracy.
In addition to technological advancements, public engagement and education around pathogen genomics are essential for gaining support and building trust within communities. As public health initiatives increasingly utilize genomic data, maintaining transparency and involving the community in decision-making processes will be vital. By fostering public understanding of pathogen genomics and its implications for health, future generations can be better prepared to contribute to public health strategies and embrace these innovations as integral tools in maintaining global health security.
Ethical Considerations in Pathogen Genomics Research
As the field of pathogen genomics expands, ethical considerations surrounding data sharing, consent, and potential misuse of genomic information become increasingly pertinent. It is critical for researchers and public health officials to establish clear ethical guidelines that govern how genomic data is collected, analyzed, and utilized, especially in the context of infectious disease surveillance. Ensuring the protection of personal information while promoting transparency will foster trust in scientific research and public health initiatives.
Furthermore, engaging with communities and stakeholders when devising genomic research policies helps to ensure that ethical considerations align with public values and expectations. By making ethical practices a priority, the field of pathogen genomics can advance responsibly, paving the way for innovative public health solutions that respect individual rights while maximizing collective health benefits. A proactive approach to ethics in genomic research is essential for achieving sustainable public health outcomes.
The Contributions of the CDC Advanced Molecular Detection Program
The CDC Advanced Molecular Detection (AMD) program has been instrumental in integrating cutting-edge genomics into routine public health practice. By pioneering research and facilitating collaborations, the AMD program has significantly enhanced the ability of public health agencies to detect and respond to infectious diseases more effectively. This program has played a crucial role in not only identifying pathogens but also in understanding their genetic variations and potential impacts on public health outcomes.
Through targeted training and capacity-building initiatives, the AMD program empowers state and local health departments to adopt advanced genomic techniques, ensuring that public health officials are equipped with the latest tools and knowledge. The ongoing work of AMD serves as a model for how public health agencies can leverage advances in pathogen genomics to bolster their surveillance and response capabilities effectively, helping to protect the health of communities nationwide.
Global Perspectives on Genomic Surveillance Initiatives
Global health initiatives focused on genomic surveillance are vital for strengthening the response to infectious diseases on an international scale. These initiatives encourage collaboration among countries, allowing for collective understanding and management of public health challenges. By sharing genomic data across borders, organizations can improve outbreak response efforts and enhance the overall effectiveness of health interventions globally. This collaborative approach highlights the interconnectivity of public health in our globalized world.
Moreover, engaging in global genomic surveillance initiatives opens doors for knowledge exchange and resource sharing among countries with varying levels of health infrastructure. Such collaborations can lead to tailored solutions that address specific local and regional health issues. As global communication in health sciences continues to improve, leveraging these partnerships will be crucial in ensuring a comprehensive and coordinated approach in addressing infectious diseases worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does pathogen genomics play in public health initiatives?
Pathogen genomics is integral to public health initiatives as it enhances our understanding of infectious diseases by providing detailed insights into pathogen characteristics. This genomic information allows for improved monitoring, surveillance, and response strategies, enabling health organizations to track disease outbreaks effectively and inform public health decisions.
How does genomic sequencing aid in combating infectious diseases?
Genomic sequencing aids in combating infectious diseases by identifying pathogen variants and their transmission dynamics. It allows public health officials to monitor changes in pathogens, assess risks associated with emerging variants, and develop targeted interventions for effective disease prevention and control.
Why is bioinformatics essential in pathogen genomics?
Bioinformatics is essential in pathogen genomics because it facilitates the analysis of vast amounts of sequence data generated during genomic sequencing. It enables researchers to interpret complex genomic information, draw actionable insights from pathogen data, and supports public health efforts in managing infectious diseases.
How did the CDC Advanced Molecular Detection program enhance pathogen genomics applications?
The CDC Advanced Molecular Detection (AMD) program has significantly enhanced pathogen genomics applications by integrating cutting-edge genomic and bioinformatics technologies into routine public health practice, fostering collaboration across organizations, and building the capacity of state and local health departments to utilize these technologies effectively.
What impact did SARS-CoV-2 genomic sequencing have on public health during the pandemic?
The genomic sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 had a profound impact on public health during the pandemic by providing vital data for variant surveillance, informing diagnostics and treatment strategies, and guiding national and local responses to the evolving situation, ultimately contributing to more effective management of the pandemic.
How does pathogen genomics inform outbreak response strategies?
Pathogen genomics informs outbreak response strategies by providing precise data on the genetic makeup of pathogens involved in outbreaks. This genomic insight helps health authorities identify transmission patterns, assess the effectiveness of interventions, and implement tailored strategies for controlling infectious diseases.
What are the challenges of implementing pathogen genomics in low-to-middle-income countries?
The challenges of implementing pathogen genomics in low-to-middle-income countries include limited resources, lack of infrastructure, and inadequate workforce training. However, global partnerships and investments are working to overcome these barriers by establishing sustainable genomic capabilities and enhancing local expertise.
How do advancements in pathogen genomics contribute to global health security?
Advancements in pathogen genomics contribute to global health security by enabling rapid identification and monitoring of emerging infectious diseases. By understanding the genetic determinants of pathogens, countries can prepare for and respond more effectively to health threats, improving overall resilience against pandemics.
What future directions are envisioned for pathogen genomics in public health?
Future directions for pathogen genomics in public health include expanding public engagement with genomic technologies, advancing workforce training, ensuring diverse representation in research, and improving access to genomic data for all communities, thereby enhancing global health responses to infectious diseases.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Advancements in Pathogen Genomics | Significant developments in genomics and epidemiology have transformed public health responses to infectious diseases. |
| Types of Materials Sequenced | Sequencing includes various pathogens (viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic) from different sources like hosts, vectors, and environments. |
| Importance of Bioinformatics | Bioinformatics is essential for analyzing vast amounts of sequence data to create actionable public health insights. |
| Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic | Over 17 million SARS-CoV-2 genomes cataloged, aiding in variant surveillance and informing public health strategies. |
| Role of CDC’s AMD Program | The CDC’s AMD program integrates genomics into public health, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and collaboration. |
| Global Partnerships in Genomics | Partnerships have enhanced genomic sequencing capabilities in low-to-middle-income countries, fostering local expertise. |
| Future Directions | Focus on public engagement, workforce development, and ensuring equitable access to genomic technologies. |
Summary
Pathogen genomics has become a critical aspect of public health, dramatically enhancing our capacity to understand and combat infectious diseases. Innovations in sequencing technology have not only increased the volume of genomic data available but also improved our responses to emerging health threats like the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. The integration of genomic analysis into public health enables timely tracking of pathogen evolution and transmission, ultimately fostering more effective disease control and prevention strategies. As we continue to face public health challenges, the role of pathogen genomics in developing resilient and responsive health systems cannot be overstated.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.