Recent spikes in parvovirus B19 cases across the United States have raised significant health concerns, particularly among vulnerable populations such as pregnant women and children with sickle cell disease. This virus, known for its association with B19 infection, can lead to serious complications during pregnancy and exacerbate conditions in those with existing blood disorders. Reports indicate a troubling rise in community transmission, suggesting that the increased positivity rates in lab tests reflect a broader outbreak related to parvovirus B19 in 2024. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued alerts, specifically warning healthcare providers to remain vigilant regarding B19 infections among at-risk groups. With the potential for severe complications in pregnant women and children, understanding how parvovirus B19 spreads and affects these populations is crucial for public health management.
In recent months, there has been a notable rise in cases of a viral infection commonly known as parvovirus B19, which poses risks for both pregnant individuals and children suffering from blood disorders such as sickle cell disease. This infectious disease often circulates during seasonal outbreaks and can lead to significant complications, particularly in those with compromised immune systems. The alarming uptick in infections suggests a resurgence of community transmission, which had been mitigated during the pandemic. Public health officials and healthcare providers are now called to pay extra attention to the challenges presented by B19 during these times. As awareness grows, understanding the implications of this respiratory virus becomes increasingly vital for safeguarding at-risk populations.
Understanding Parvovirus B19 and Its Resurgence in the US
Parvovirus B19 has recently been identified as a rising concern in public health, particularly with the increase in documented cases across the United States. In 2024, commercial laboratories reported a significant increase in parvovirus B19 positivity rates, particularly among vulnerable populations such as pregnant women and children with sickle cell disease. Understanding the dynamics of B19 infection is crucial as it highlights the ongoing community transmission and the potential implications for those at risk.
Research indicates that parvovirus B19 infection can lead to serious complications, including anemia in children and complications during pregnancy. Pregnant women infected with B19 face heightened risks, including miscarriages and fetal anemia, while children, especially those with sickle cell disease, are at risk for severe anemia or aplastic crises. Given these risks, it becomes essential for healthcare professionals and the community to be aware of the symptoms and the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.
The Impact of Parvovirus B19 on Pregnant Women
The recent spike in parvovirus B19 cases has raised alarm among healthcare providers regarding the potential complications for pregnant women. Pregnant patients represent a particularly vulnerable group, as B19 infection is associated with serious risks, including miscarriage and fetal complications like hydrops and severe anemia. In a recent report, five pregnant women afflicted with B19 were documented, with varying outcomes, ranging from a miscarriage to healthy full-term deliveries.
Healthcare providers are advised to remain vigilant for symptoms of B19 infection in pregnant patients. Clinical signs such as reduced fetal movement or signs of hydrops should prompt immediate evaluation. The reported 9.9% positivity rate for B19 among clinical specimens suggests a change in transmission dynamics that could mean more pregnant women are at risk. Raising awareness among expecting mothers and healthcare professionals about the potential consequences of parvovirus B19 is essential for improving maternal and fetal outcomes.
Sickle Cell Disease: An Increased Risk of B19 Infection Complications
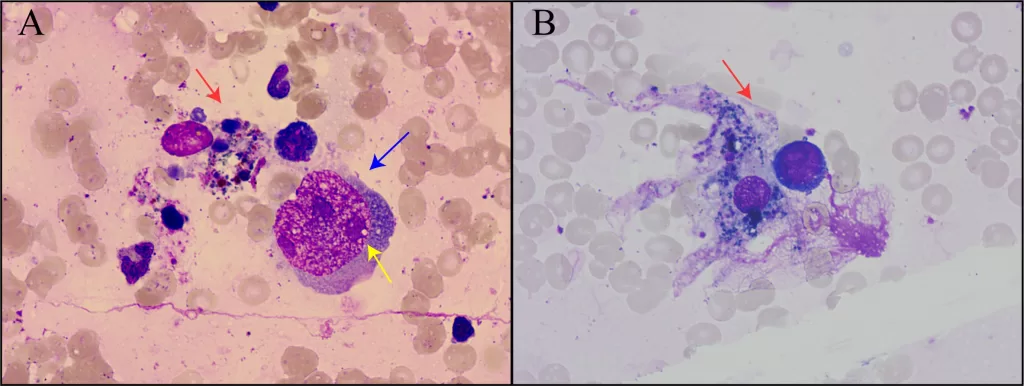
Children with sickle cell disease (SCD) are particularly susceptible to complications arising from parvovirus B19 infections. Recent findings reveal that the incidence of B19-associated aplastic crises in children with SCD has markedly increased, highlighting an alarming trend with significant public health implications. Clinicians should maintain a low threshold for testing for B19 in these patients, especially when symptoms of severe anemia present.
The seriousness of complications due to B19 infections in children with SCD cannot be overstated. Anemia episodes, stroke, and acute chest syndrome are some of the severe issues that can arise in these patients, emphasizing the importance of rapid intervention and management. By understanding the relationship between B19 infection and SCD complications, healthcare professionals can better prepare and protect their patients from potentially life-threatening situations.
Healthcare providers must recognize the risk of B19 complications in children with SCD and aggressively monitor and manage these cases. Awareness of the symptoms of parvovirus B19 and its effects on individuals with underlying conditions like SCD can lead to timely interventions that save lives and improve health outcomes.
Community Transmission Dynamics of Parvovirus B19
The increase in parvovirus B19 cases has been linked to heightened community transmission, particularly following the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Data shows that rates of B19 infections dropped during the pandemic due to social distancing and public health measures aimed at reducing the spread of respiratory viruses. However, as these measures eased, a resurgence in B19 transmission has occurred, showing that large segments of the population remained susceptible to infection.
Monitoring community transmission patterns is vital in controlling outbreaks of parvovirus B19. Public health officials must work collaboratively with healthcare providers to disseminate information about B19, its transmission routes, and prevention strategies. Understanding how B19 spreads can empower communities to take proactive measures to limit further outbreaks and protect those at higher risk.
Public Health Recommendations for Parvovirus B19 Control
In light of the increased parvovirus B19 cases, public health recommendations are essential for mitigating the impact of this viral infection on affected communities. These guidelines emphasize the need for healthcare providers to educate patients, particularly pregnant women and parents of children with sickle cell disease, about the signs and risks associated with B19 infection. Early identification and intervention can significantly improve health outcomes.
Furthermore, implementing preventive measures, such as promoting good hygiene practices and encouraging vaccination where applicable, can aid in reducing the transmission rates of parvovirus B19. By targeting educational initiatives to vulnerable populations, public health officials can play a crucial role in decreasing the incidence of B19 infections and their associated complications.
The Role of Laboratory Testing in Managing B19 Cases
Accurate laboratory testing is fundamental in managing cases of parvovirus B19 infection, particularly as the positivity rates have surged across the US. The testing for immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies and nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) for B19 can help determine recent infections and guide clinical management. Understanding laboratory findings in the context of clinical presentations enables healthcare providers to make more informed decisions regarding treatment and follow-up.
Furthermore, increased laboratory surveillance and reporting of parvovirus B19 cases can help public health agencies track outbreaks more effectively. By fostering collaboration between laboratories and healthcare providers, the integration of testing results with clinical history can enhance the overall response to parvovirus B19, thereby protecting vulnerable populations and ensuring timely care.
Key Symptoms of Parvovirus B19 Infections
Recognizing the symptoms of parvovirus B19 infection is crucial for early diagnosis, especially in high-risk populations like pregnant women and those with sickle cell disease. The classic symptoms include a distinctive “slapped-cheek” rash in children, joint pain in adults, and in more serious cases, significant hematological issues like anemia. Not only are these symptoms important for diagnosing primary infections, but they are also essential for monitoring complications associated with the virus.
Healthcare professionals should educate patients on these symptoms and the potential for serious complications, especially during pregnancy or in children already suffering from blood disorders. Awareness of the symptomatology can lead to prompt medical attention, reducing the risk of severe outcomes like miscarriage or acute anemia crises in vulnerable patients.
Long-term Health Implications of Parvovirus B19 Infection
Long-term health effects following parvovirus B19 infection, although generally mild, can have lasting implications for specific populations. Individuals who experience severe complications may face ongoing health challenges, and parents of children diagnosed with B19 must understand the potential risks associated with their child’s health. Education about the possible recurrence of symptoms and the management of any lingering complications is vital.
For those with pre-existing health concerns, especially sickle cell disease, the threat of complications from B19 infection necessitates continuous monitoring and supportive care. Understanding the long-term implications of infection reinforces the need for proactive health management and the importance of regular follow-up care to address potential issues stemming from the initial B19 infection.
Conclusion: Increasing Awareness and Prevention Strategies for Parvovirus B19
The resurgence of parvovirus B19 cases presents a critical public health challenge that highlights the need for increased awareness and prevention efforts. Education regarding the signs and symptoms of B19, coupled with outreach to vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women and children with sickle cell disease, can help in prompting timely medical responses. Through collaborative efforts between healthcare providers and public health officials, the community can better manage the risks associated with this infection.
Moreover, emphasizing preventative measures and timely laboratory testing can significantly curtail the transmission rates of parvovirus B19. By fostering a well-informed public and encouraging proactive healthcare behaviors, we can mitigate the impact of this viral infection and safeguard the health of at-risk populations in our communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the complications of parvovirus B19 infection in pregnant women?
Parvovirus B19 infection can lead to serious complications in pregnant women, including an increased risk of miscarriage, especially if contracted during the first trimester. Other potential complications include severe anemia in the fetus, which may necessitate fetal transfusions or could result in hydrops fetalis. Healthcare providers should be vigilant for signs of fetal distress related to B19 infection.
How does parvovirus B19 affect children with sickle cell disease?
Children with sickle cell disease (SCD) are at a heightened risk of complications from parvovirus B19 infections. Infection can trigger an aplastic crisis, a life-threatening condition where the bone marrow stops producing red blood cells. Recent data show an increase in B19-related aplastic crises among SCD patients, warranting prompt testing and monitoring for those affected.
What does the recent spike in parvovirus B19 cases indicate about community transmission?
The recent spike in parvovirus B19 cases, with positivity rates rising significantly in laboratory tests, indicates a concerning increase in community transmission. This surge is attributed to reduced B19 exposure during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in a larger pool of susceptible individuals. Public health officials emphasize the importance of monitoring and implementing prevention measures.
What precautions should pregnant women take regarding parvovirus B19?
Pregnant women should monitor for symptoms of parvovirus B19 infection, such as the characteristic ‘slapped-cheek’ rash and joint pain. It’s crucial for them to consult healthcare providers if exposed to infected individuals, especially children, as infections can lead to serious pregnancy complications. Awareness and education about B19 risks in childcare settings is vital.
How is parvovirus B19 transmitted in communities?
Parvovirus B19 can spread through respiratory droplets and also via blood transmission in certain cases. Enhanced community transmission cycles have been noted, particularly in environments like schools and childcare facilities where children circulate. Awareness campaigns among these groups are essential to curb transmission.
Are there any treatments available for parvovirus B19 infections?
Most parvovirus B19 infections require no specific treatment and resolve on their own, particularly in healthy individuals. However, for at-risk populations like those with sickle cell disease, supportive care including blood transfusions may be necessary to manage severe anemia. Pregnant women should be closely monitored for fetal wellbeing if infected.
What steps can healthcare providers take to manage parvovirus B19 cases?
Healthcare providers should maintain a high index of suspicion for parvovirus B19 infection, particularly in pregnant women and children with conditions like sickle cell disease. Routine screening during outbreaks, patient education on transmission, and prompt intervention for complications are critical steps in managing cases effectively.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase in Cases | Parvovirus B19 infections have spiked in the US, particularly among pregnant women and children with sickle cell disease. |
| CDC Advisory | The CDC has issued an advisory regarding the rise in parvovirus B19 cases and complications. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include a “slapped-cheek” rash in children and joint pain in adults. |
| Pregnant Women Risks | B19 illness can elevate the risk of miscarriage and complications in pregnancy. |
| Sickle Cell Disease | Children with sickle cell disease are at increased risk for life-threatening anemia due to B19 infection. |
| Community Transmission | Increased transmission rates in 2024 are linked to reduced infections during the COVID-19 pandemic. |
Summary
Parvovirus B19 cases have notably increased in the United States, particularly affecting pregnant women and children with sickle cell disease. Health officials are raising awareness to prevent serious complications associated with this viral infection. Pregnant individuals and children with pre-existing conditions should be particularly vigilant and receive appropriate monitoring and care.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.