Pandemic preparedness has become an urgent priority for global health security in the wake of COVID-19, the world’s most profound health crisis in recent history. A recent report advocates for a significant transformation in how nations prepare for future pandemics, emphasizing that the vulnerabilities exposed by the pandemic must drive proactive change. As we face persistent inequalities and gaps in primary healthcare, the importance of enhancing pandemic risk monitoring cannot be overstated. The World Health Organization’s ongoing efforts, including the newly formed WHO Pandemic Agreement, aim to ensure that nations collaborate more effectively to fortify health systems against infectious disease threats. By adopting a comprehensive approach to pandemic preparedness, we can mitigate risks and protect populations worldwide against future outbreaks.
In light of the lessons learned from the COVID-19 crisis, the discourse around readiness for infectious disease outbreaks has gained momentum. The global community is increasingly recognizing the need for effective strategies to ensure health system resilience amidst the uncertainty of emerging health threats. Future epidemic readiness demands a focus not only on immediate medical responses but also on strengthening the overall structure of healthcare services. By integrating advanced monitoring systems and fostering international collaboration, we can build a more robust foundation for addressing public health emergencies. This evolving dialogue emphasizes the necessity of holistic approaches that prioritize cooperation, equitable healthcare distribution, and comprehensive monitoring to safeguard populations worldwide.
The Urgency of Pandemic Preparedness
In light of the recent exhaustive experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic, the urgency for comprehensive pandemic preparedness has never been more pronounced. A report by the Global Preparedness Monitoring Board emphasizes that despite technological advancements, the global community is still vulnerable to future pandemics. The key takeaway is that preparedness is not simply about developing vaccines or medical treatments; rather, it encompasses a broad spectrum of strategies designed to mitigate risks and manage crises effectively. Through proactive measures, such as investing in robust healthcare infrastructure and establishing effective communication systems, nations can significantly enhance their readiness for any potential disease outbreak.
As we look towards the future, the concept of global health security becomes essential in fortifying our defenses against pandemics. Enhanced surveillance, coupled with strategies to address social inequities, are critical to deflecting the multifaceted threats posed by emerging infectious diseases. To prevent the costly lessons learned from COVID-19 from being forgotten, a paradigm shift in how we approach health crises is required, as recommended by the GPMB. Strengthened global frameworks aimed at pandemic preparedness can empower nations, making them less susceptible to the potentially devastating impacts of future health emergencies.
Strengthening Primary Healthcare Systems
The GPMB highlights that one of the most vital lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic is the critical importance of strengthening primary healthcare systems. A resilient primary healthcare infrastructure not only aids in the timely detection of diseases but also helps mitigate the broader societal and economic effects of pandemics. By focusing on this foundational aspect of health systems, countries can prepare effectively to maintain essential health services while addressing emergent health crises. Robust primary healthcare will enable professionals to respond swiftly to outbreaks, thereby reducing reliance on severe lockdowns and amplifying preventative efforts.
Moreover, a strong primary healthcare system cultivates public trust, which is paramount during health emergencies. In times of crisis, the public relies heavily on transparent and effective communication from healthcare providers. As health systems grow stronger, they can foster relationships that empower communities and increase adherence to health guidelines. This trust and cooperation become pivotal in the aftermath of pandemics, which can otherwise erode social cohesion and worsen health disparities. Hence, the emphasis on primary healthcare as a linchpin in pandemic preparedness cannot be overstated.
Implementing Pandemic Risk Monitoring
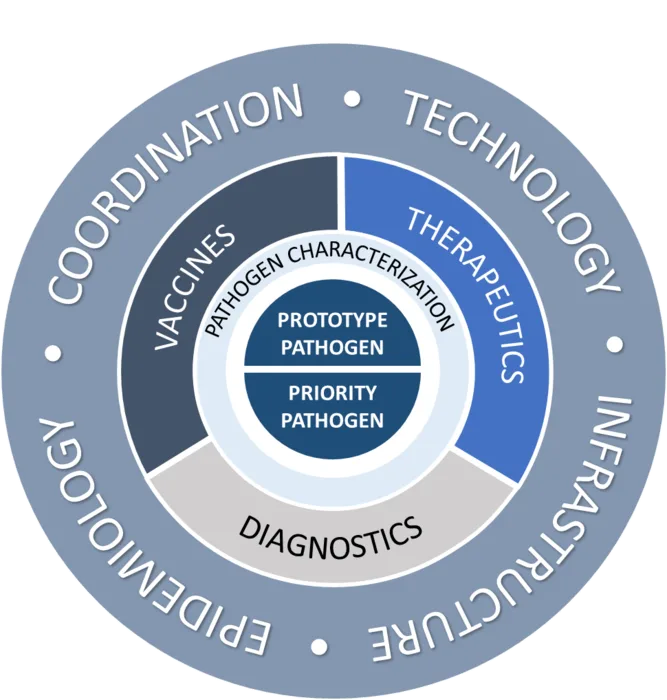
The establishment of a pandemic risk monitoring system is a forward-thinking strategy recommended by the GPMB that underscores the need for real-time health surveillance. Such a system would integrate diverse data—epidemiological, economic, social, and environmental—into a unified platform capable of monitoring emerging threats and vulnerabilities. By harnessing cutting-edge technologies, including artificial intelligence, this observatory could transform decision-making, allowing leaders to assess risks effectively and allocate resources appropriately during a crisis. This proactive stance could prove essential in preventing the exponential spread of diseases and minimizing their impacts on societies.
Furthermore, the envisioned monitoring framework expands upon existing structures to support local and global health initiatives. By utilizing a comprehensive approach to pandemic risk monitoring, countries can establish early-warning systems that inform public health responses before a crisis escalates. This capability is vital in a world where future pandemics are not just likely but inevitable. As the GPMB notes, countries need to invest in these monitoring systems to ensure preparedness, making the leap from reactive to proactive health management part of their sustainable health strategies.
International Collaboration for Effective Pandemic Responses
To establish a cohesive and resilient global response to future pandemics, international cooperation is indispensable. The GPMB advocates for the ratification of the WHO Pandemic Agreement, which aims to facilitate better collaboration among nations. Such an agreement represents a collective commitment to overcoming the gaps highlighted by COVID-19 and encourages the implementation of more structured and equitable mechanisms for sharing resources and knowledge. When countries work together, pooling their strengths and resources, the global health landscape becomes considerably more secure and prepared for unforeseen health challenges.
Furthermore, addressing the geopolitical disparities that defined the COVID-19 response is crucial for equitable international cooperation. The GPMB believes that the WHO Pandemic Agreement can serve as a foundation for bridging these gaps. By creating systems that prioritize shared interests and cooperative mechanisms, nations can effectively navigate their differences and address common threats. Ultimately, enhanced collaboration can lead to a collective strategy that mitigates risks associated with future pandemics, ensuring that every nation is better equipped to handle the unexpected, thus fostering a healthier global community.
Leveraging Technology for Pandemic Preparedness
As advancements in technology reshape the landscape of healthcare, leveraging these innovations for pandemic preparedness becomes increasingly vital. Technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and machine learning can significantly enhance our capabilities to predict, monitor, and respond to health crises. For instance, advanced analytics can facilitate the integration of diverse health data, enabling timely insights into disease patterns and outbreaks. Furthermore, digital platforms can support communication strategies that ensure public adherence to health advisories during emergencies.
Additionally, technology-driven solutions can streamline the processes for vaccine development and distribution during outbreaks. By enhancing the efficiency of logistics and operations, technology reduces time frames and increases the reach of health interventions. Investing in digital health tools that support surveillance and reporting mechanisms can directly contribute to a country’s preparedness for future pandemics, ultimately leading to improved public health outcomes. Hence, integrating technology into the core of pandemic preparedness strategies is essential for building resilient health systems.
Equity and Access in Pandemic Preparedness
As underscored by the GPMB report, addressing systemic inequities is a fundamental component of effective pandemic preparedness. Marginalized communities often bear the brunt of health crises, exacerbating existing disparities and hindering effective public health responses. Ensuring equitable access to healthcare resources during pandemics is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic necessity for safeguarding global health security. Countries must prioritize efforts to dismantle barriers that limit healthcare access for vulnerable populations, creating inclusive systems that can address their unique needs.
Furthermore, the importance of equity extends beyond access to healthcare; it encompasses ensuring that resources, such as vaccines and medical supplies, are equitably distributed. During the COVID-19 pandemic, disparities in vaccine distribution were evident, highlighting a need for systematic reforms. By fostering collaboration amongst nations to develop fair distribution frameworks, the focus can shift towards creating fairer global health systems. Implementing a collaborative approach to pandemic preparedness will thus not only enhance response efforts but will also build greater trust among communities, facilitating a shared commitment to public health.
The Role of Government in Pandemic Preparedness
Governments play a critical role in shaping the framework for pandemic preparedness and response. As the GPMB report advocates, decisive governmental action is vital to address the shortcomings exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. This includes investing in public health infrastructure, ensuring that health systems are robust enough to respond to crises, and facilitating collaboration across sectors. By prioritizing international agreements like the WHO Pandemic Agreement, governments can establish a unified front to tackle global health threats effectively.
Moreover, governance mechanisms that promote transparency, collaboration, and accountability are essential for fostering public trust during health emergencies. By engaging with communities and incorporating their input into preparedness strategies, governments can create more responsive frameworks that truly reflect the needs of the populace. This collaborative governance is key to enhancing preparedness and ensuring that health policies are not only effective but also equitable, thus paving the way for a stronger, more resilient global health landscape.
Lessons Learned from Past Pandemics
Reflecting on the lessons learned from past pandemics, such as the Ebola outbreak and COVID-19, is crucial for shaping future preparedness strategies. The insights gleaned from these experiences illuminate the essential components required for an effective response to health crises. Key lessons include the importance of rapid implementation of public health measures, robust communication strategies, and establishing flexible healthcare systems that can adapt to changing circumstances. By analyzing previous pandemics’ successes and failures, we can enhance our approach to future health threats.
Additionally, the importance of global partnerships during health emergencies cannot be overstated. The collaborative efforts witnessed during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the value of international cooperation and knowledge-sharing. However, these lessons also highlighted the disruptions caused by inequities between nations. Going forward, the global community must prioritize establishing strong partnerships that transcend borders. By fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous learning, countries can collectively fortify their defenses against the inevitable challenge of future pandemics.
Adapting to Future Health Crises
Adapting to future health crises requires a proactive approach that goes beyond reactive measures. The GPMB emphasizes the necessity to evolve pandemic preparedness in response to changing landscapes, acknowledging that emerging infectious diseases will differ from those encountered in the past. This adaptive paradigm calls for innovative strategies and forward-thinking policies that embrace both technological advancements and a comprehensive understanding of social determinants of health. By recognizing the dynamic nature of health challenges, we can effectively shield populations from potential outbreaks.
Equally important is the commitment to continuous improvement of health systems based on lessons learned from previous pandemics. Countries must engage in constant assessments, refining their strategies to meet emerging threats effectively. Importantly, this evolution should not happen in isolation; it requires global participation and shared understanding. By promoting collaboration across borders, Nations can shape a resilient future that anticipates change, embraces adaptability, and prioritizes health security on a global scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key recommendations for pandemic preparedness in future pandemics?
The key recommendations for pandemic preparedness focus on strengthening primary healthcare systems, establishing a pandemic risk monitoring framework, and enhancing international cooperation. These elements are vital for effectively addressing health crises and mitigating the extensive social and economic impacts of future pandemics.
How does primary healthcare contribute to pandemic preparedness?
Robust primary healthcare is crucial for pandemic preparedness as it enables early detection, response to emerging diseases, and continues essential services. A resilient primary healthcare system helps reduce reliance on drastic measures, enhances communication, fosters trust, and minimizes initial damages during a pandemic.
What is the role of the WHO Pandemic Agreement in global health security?
The WHO Pandemic Agreement plays a significant role in global health security by establishing structured, equitable mechanisms for international cooperation during health crises. This agreement aims to address gaps that undermined previous pandemic responses, ensuring nations collaborate more effectively against future pandemics.
What is a pandemic risk monitoring system and how does it work?
A pandemic risk monitoring system integrates diverse data sources—epidemiological, economic, social, and environmental—into a single platform for real-time analysis. It aims to track threats and vulnerabilities, enhancing leaders’ ability to assess risks, improve forecasting, and allocate resources effectively.
Why is international cooperation essential for pandemic preparedness?
International cooperation is essential for pandemic preparedness as it ensures that countries work together to address shared threats, share vital information, and implement coordinated responses. Effective collaboration can significantly mitigate the impact of pandemics on global health and security.
What lessons from COVID-19 should inform future pandemic preparedness strategies?
Lessons from COVID-19 highlight the importance of investing in primary healthcare, establishing effective communication networks, and being prepared for the socio-economic shocks of pandemics. Understanding pandemics as multifaceted challenges requires a comprehensive approach to preparedness that goes beyond health.
How can technologies improve pandemic risk monitoring and preparedness?
Technologies, including artificial intelligence, can enhance pandemic risk monitoring by facilitating near-real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making. By integrating various data sources, technology improves forecasting and ensures timely responses to emerging health threats.
What impact do pandemics have on social cohesion and inequality?
Pandemics can exacerbate existing inequalities and disrupt social cohesion, leading to severe economic and emotional repercussions. Addressing these impacts is a critical aspect of pandemic preparedness, as it ensures that responses are equitable and supportive of all community members.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Report’s Purpose | Advocate for a paradigm shift in pandemic preparedness. |
| GPMB Background | Established by WHO and World Bank in 2018 to monitor global pandemic readiness. |
| Key Lessons from COVID-19 | Pandemics require coordinated, multisectoral responses beyond immediate health measures. |
| Core Approach | Care, measure, and cooperate to enhance preparedness. |
| Stronger Healthcare Systems | Develop robust primary healthcare systems to withstand pandemics. |
| Risk Monitoring | Establish near-real-time pandemic risk monitoring systems utilizing AI. |
| International Cooperation | Countries must ratify the WHO Pandemic Agreement for better collaboration. |
| Future Preparedness Strategy | Prepare for pandemics that differ from past ones by adapting strategies. |
Summary
Pandemic preparedness is crucial for ensuring that the world can effectively respond to future health crises. The recent report from the Global Preparedness Monitoring Board highlights the urgent need for a paradigm shift in how countries approach this issue. By addressing inequities, enhancing collaboration, and building robust healthcare systems, nations can better protect themselves against the profound social and economic shocks that pandemics bring. Increasing international cooperation through agreements such as the WHO Pandemic Agreement is essential for fostering a unified global response. As we move forward, embracing these strategies will improve our ability to navigate future pandemics.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.