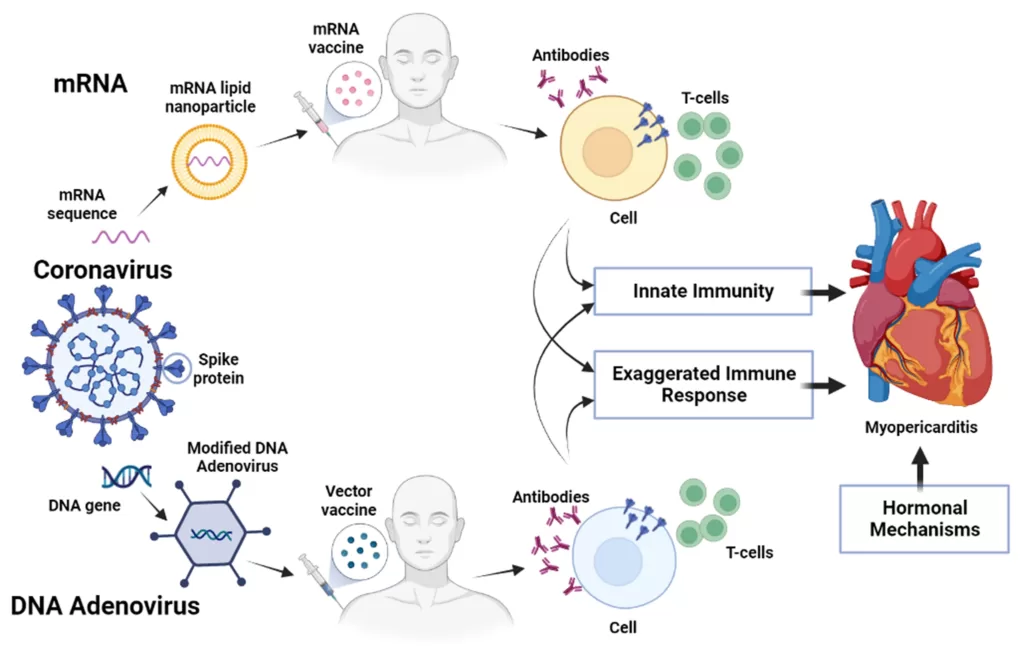
Myocarditis and COVID-19 vaccination have become topics of heightened awareness as millions receive mRNA COVID-19 vaccines worldwide. Following the launch of the vaccination campaign, health authorities identified myocarditis—an inflammation of the heart muscle—as a rare but notable side effect linked primarily to these vaccines. While the overall likelihood of experiencing myocarditis post-vaccination remains low, the myocarditis risk is particularly pronounced in younger males, prompting increased public health scrutiny. It is vital to understand COVID-19 vaccine side effects and their implications, especially given the robust safety measures associated with mRNA vaccines. Ongoing research into myocarditis epidemiology continues to characterize cases, elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms behind this condition following COVID vaccination and ensuring that widespread vaccine deployment upholds safety for all demographic groups.
Inflammation of the heart, known as myocarditis, has drawn significant attention in the context of COVID-19 immunization. This condition reportedly occurs following the administration of various vaccines, particularly mRNA ones designed to combat the coronavirus. Emerging data reveal a correlation between COVID vaccination and an elevated risk of myocarditis, with a stronger incidence noted in younger populations. Understanding the relationship between COVID-19 vaccines and potential adverse effects, including myocarditis, is essential for informed public health messaging. Continued studies into vaccine-associated myocarditis will provide clarity on the epidemiological patterns and contribute to enhancing vaccine safety protocols.
Understanding Myocarditis Risk After COVID-19 Vaccination
Myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle, has been identified as a rare adverse event associated with certain COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. Reports indicate that the myocarditis risk tends to be higher in younger males, primarily following vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines. Despite this concerning correlation, it is crucial to underline that these cases are infrequent and often mild, with most patients recovering without significant intervention. Understanding the myocarditis risk in relation to COVID-19 vaccination is essential, as it informs public health policies and helps mitigate fears surrounding vaccine safety.
Epidemiological data on myocarditis post-vaccination show a much lower incidence than myocarditis linked to COVID-19 infection itself. Studies indicate that while vaccine-associated myocarditis occurs, the risk is significantly outweighed by the benefits of vaccination, particularly in preventing severe COVID-19 outcomes. Ongoing research is vital to establish a clearer picture of the relationship between myocarditis and COVID-19 vaccination, providing assurance to the public regarding vaccine safety while addressing potential health risks.
Exploring COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effects
Like all vaccines, COVID-19 vaccinations come with potential side effects, though most are mild and temporary. Common side effects include soreness at the injection site, fatigue, headache, fever, and muscle pain. However, the appearance of rare adverse effects, such as myocarditis, has been a focus of public concern and scientific scrutiny. Regulatory agencies have embarked on robust monitoring systems and have encouraged transparency about vaccine side effects, thus enhancing public trust while ensuring that individuals can make informed decisions concerning their health.
The emergence of myocarditis as a COVID-19 vaccine side effect has prompted health authorities to delineate these risks clearly. Information campaigns aimed at educating healthcare providers and the public about the nature of these side effects have been implemented. By fostering awareness, authorities can alleviate concerns and emphasize the importance of vaccination in controlling the spread of COVID-19, supporting overall public health goals.
The Safety of mRNA Vaccines in the Context of Myocarditis
mRNA vaccines, which include Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in prompting strong immune responses against COVID-19. However, discussions around the safety of mRNA vaccines, particularly in relation to myocarditis, are critical. Clinical studies and post-vaccination surveillance have shown that while there is a detectable risk of myocarditis following mRNA vaccination, this risk remains quite low when viewed against the backdrop of vaccine benefits, such as greater community immunity and reduced hospitalization rates.
Analyzing the safety profiles of mRNA vaccines enables healthcare professionals to offer informed recommendations. Current guidance emphasizes the importance of weighing the risks of vaccination against the risks associated with contracting the virus itself. In light of defined myocarditis cases linked to vaccination, it remains essential to communicate that the incidence is significantly lower compared to the myocarditis risk posed by COVID-19 infection.
The Role of Public Health in Communicating Risks and Benefits of COVID-19 Vaccination
Effective public health communication plays a pivotal role in informing the population about the risks and benefits associated with COVID-19 vaccination. The identification of myocarditis cases post-vaccination underscores the necessity for transparent dialogue with the community. By clearly outlining the potential side effects, including myocarditis, public health campaigns can arm individuals with knowledge necessary for making informed choices regarding their vaccination.
Moreover, public health agencies are working to ensure that discussions about vaccine risks are balanced with acknowledgment of the immense benefits, such as the drastic reduction in severe disease and hospitalization. This holistic view encourages community trust in vaccination programs and maximizes participation, which is essential for attaining herd immunity and overcoming the pandemic—highlighting the attitude of health agencies focused on transparency and proactive engagement.
Myocarditis Epidemiology in the Context of COVID-19
The epidemiology of myocarditis associated with COVID-19 is becoming a major area of interest in medical research. Data demonstrates that the incidence of myocarditis in the context of COVID-19 infection exceeds that associated with vaccination, particularly among younger populations. These findings underscore the continual need for extensive epidemiological studies focused on understanding the broader implications of myocarditis in these demographics, as well as the long-term impacts of both COVID-19 and vaccination.
Comprehensive epidemiological surveillance is vital to grasp the intricate relations between myocarditis and COVID-19 vaccination. It allows researchers to track and analyze data from various populations continuously, contributing to effective preventive strategies and refined vaccine recommendations. Understanding myocarditis epidemiology helps health officials prioritize resources and inform vaccine policy, ensuring that all public health interventions are evidence-based.
The Pathophysiology of Vaccine-Associated Myocarditis
Investigating the pathophysiology behind vaccine-associated myocarditis is essential for enhancing vaccine safety protocols. Current hypotheses include immune-mediated mechanisms that develop post-vaccination, likely driven by the body’s response to the mRNA. These immune responses, while protective against the virus, may sometimes lead to inadvertent inflammation of the heart muscle, manifesting as myocarditis.
Understanding these mechanisms will better inform researchers and healthcare providers on how to identify at-risk individuals and subsequent strategies to mitigate such risks with future vaccines. Additionally, ongoing research could yield ground-breaking insights, paving the path for refined vaccine formulations that maintain efficacy while minimizing adverse reactions.
Advancing Research on Myocarditis and COVID-19 Vaccines
The ongoing exploration of myocarditis in relation to COVID-19 vaccines highlights the urgency for advanced research and collaboration among scientists, healthcare providers, and public health authorities. Given the recent emergence of case reports, it is paramount to delineate the underlying mechanisms of vaccine-associated myocarditis to formulate better guidelines and risk assessments for vaccination.
Future studies must assess not just the incidence of myocarditis but also long-term outcomes for individuals who experience this adverse effect post-vaccination. Establishing large-scale studies that emphasize diverse populations will provide more comprehensive insights, addressing disparities in vaccine response and aligning with public health initiatives aimed at optimizing COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness.
Conclusion: Balancing Vaccine Risks and Benefits
As the global health community continues to navigate the complexities of COVID-19 vaccination strategies, it is clear that understanding the risks and benefits associated with myocarditis is central to informed public discussions. Though myocarditis may pose a risk, the collective evidence points overwhelmingly to the conclusion that COVID-19 vaccines remain beneficial and vastly safer compared to the risks associated with COVID-19 itself.
Emphasizing a balanced view that acknowledges vaccine risks while highlighting the remarkable protective benefits provided by COVID-19 vaccination is essential for fostering public acceptance. This ongoing dialogue empowers individuals to engage in their health decisions fully, advocating for an evidence-based approach to vaccination that prioritizes community well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between myocarditis and COVID-19 vaccination?
Myocarditis has been identified as a rare adverse event following COVID-19 vaccination, particularly associated with mRNA vaccines like Comirnaty and Spikevax. While the risk of myocarditis post-vaccination exists, studies indicate it is significantly lower than the risk of myocarditis linked to a COVID-19 infection itself.
What are the myocarditis risks associated with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines?
Research shows there is a small increased risk of myocarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccinations, especially among younger males. Despite this risk, the overall incidence is low, emphasizing the importance of the benefit-risk balance of the vaccines in protecting against severe COVID-19 outcomes.
What COVID-19 vaccine side effects should be monitored for myocarditis?
Individuals receiving mRNA COVID-19 vaccines should be monitored for signs of myocarditis, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or feelings of having a fast-beating, fluttering, or pounding heart. Most cases reported are mild and self-limiting, resolving without the need for intensive treatment.
How does COVID vaccination myocarditis compare to myocarditis caused by COVID-19 infection?
COVID vaccination myocarditis occurs at a lower rate compared to myocarditis triggered by COVID-19 infection. Evidence suggests that while COVID-19 vaccination is associated with myocarditis, the risk from the actual virus is significantly higher, reinforcing the vaccine’s safety and efficacy.
What is the epidemiology of myocarditis linked to COVID-19 vaccination?
Epidemiological studies indicate that myocarditis associated with COVID-19 vaccination is a rare event, primarily occurring after mRNA vaccine administration. Efforts to evaluate its incidence across diverse populations are ongoing, focusing on demographic variations and long-term outcomes.
Are mRNA vaccines safe given the risk of myocarditis?
Yes, mRNA vaccines are considered safe overall. The risk of myocarditis following vaccination is low, and the benefits in preventing severe COVID-19 disease greatly outweigh the potential risks of rare side effects like myocarditis.
What steps are necessary for research on myocarditis and COVID-19 vaccination?
Further research is crucial to understand the mechanisms of myocarditis linked with COVID-19 vaccination. This includes gathering more comprehensive data on incidence rates, exploring biological pathways, and refining vaccine strategies to enhance safety and efficacy.
What are the symptoms of myocarditis that may occur after COVID-19 vaccination?
Symptoms of myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination may include chest pain, difficulty breathing, and rapid heartbeats. Most cases are mild and resolve on their own, but individuals are advised to seek medical care if they experience severe symptoms.
How does COVID vaccination improve overall public health despite myocarditis risks?
COVID vaccination, despite its rare association with myocarditis, has been pivotal in reducing hospitalization, mortality, and overall public health disruptions during the pandemic. The benefits significantly surpass the risks, particularly when considering the severe complications related to COVID-19 infection.
What guidelines exist for healthcare providers regarding monitoring post-COVID-19 vaccination myocarditis?
Healthcare providers are recommended to educate patients about the signs of myocarditis after vaccination and to monitor for such symptoms, particularly in younger males, to ensure timely diagnosis and management in the rare event of myocarditis.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Epidemiology of Myocarditis | Myocarditis and pericarditis are rare adverse events linked to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. |
| Risk Assessment | Increased risk of myocarditis observed among younger males post vaccination, particularly with mRNA vaccines. |
| Clinical Manifestations | Most cases of myocarditis are mild, transient, and resolve without serious complications. |
| Comparison with COVID-19 | Vaccination risk is lower than the myocarditis risk from actual COVID-19 infection. |
| Research Needs | Ongoing studies are needed to understand the exact mechanisms of vaccine-associated myocarditis. |
Summary
Myocarditis and COVID-19 vaccination have garnered significant attention due to the rare instances of myocarditis linked with mRNA vaccines. While the risk is present, it is considerably lower than the risk of myocarditis associated with COVID-19 infection itself. The ongoing research aims to clarify the underlying mechanisms of myocarditis post-vaccination, ensuring that future vaccination strategies enhance safety and effectiveness while addressing public health concerns.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.