Monkeypox Virus Detection has emerged as a crucial focus in public health, particularly in the context of rising cases in recent years. This study highlights the groundbreaking discovery of monkeypox virus (MPXV) clade Ib DNA in wastewater solids from treatment plants throughout the United States. Utilizing an advanced PCR method, researchers analyzed thousands of samples, successfully identifying MPXV clade Ib in an area with a confirmed travel-related case. The ability to monitor potential outbreaks through wastewater surveillance not only aids in infection control but also enhances infectious diseases monitoring across affected regions. As the landscape of infectious diseases evolves, efficiently detecting viruses like monkeypox will be vital in mitigating public health risks.
The detection of the monkeypox virus, often referred to as MPXV, represents a significant advancement in understanding the dynamics of infectious diseases. Recent findings showcasing the presence of clade Ib DNA in wastewater samples provide a unique lens through which health officials can assess viral prevalence in communities. Employing sophisticated methods such as hydrolysis-probe PCR technology has allowed scientists to efficiently gather data from a vast array of locations, highlighting both the potential and limitations of surveillance techniques. As evaluations continue, these innovative approaches aim to bolster response strategies against emerging variants of monkeypox, ultimately reinforcing public health infrastructure. In an era where emerging infectious threats demand vigilant monitoring, the adaptation of wastewater surveillance for viruses like monkeypox is a noteworthy step forward.
Understanding Monkeypox Virus Detection in Wastewater
The detection of the monkeypox virus (MPXV) clade Ib in wastewater signals a significant advancement in public health surveillance. Researchers utilized wastewater solids collected from treatment plants to analyze over 3,000 samples using a sensitive PCR method. This innovative technique has proven effective in identifying the presence of MPXV clade Ib DNA, particularly in areas with confirmed cases. Given that nearly 36,000 monkeypox cases have been reported in Central and Eastern Africa, this study highlights the utility of wastewater surveillance as an emerging tool for infectious diseases monitoring.
By focusing on specific viral DNA sequences, the researchers were able to establish a direct link between wastewater analysis and active monkeypox cases. This approach not only offers insights into community transmission rates but also helps in predicting future outbreaks. The ability to detect infectious diseases like monkeypox through wastewater underscores the importance of continuous monitoring to ensure timely public health responses.
Implications of MPXV Clade Ib Identification
The identification of MPXV clade Ib carries important implications for public health policy and infectious diseases monitoring strategies. Clade Ib has rapidly spread primarily among adults through specific contact routes, making it crucial to raise awareness about the disease’s transmission dynamics. Detection in wastewater provides health officials with the ability to trace potential outbreak hotspots even before clinical cases become prevalent, allowing for preemptive action to mitigate spread.
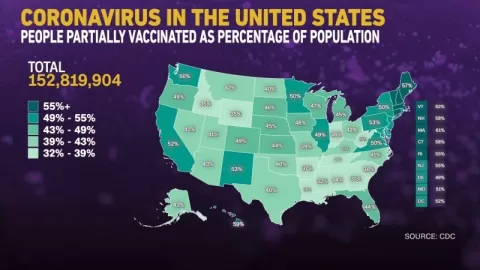
Moreover, the study emphasizes the need for robust wastewater surveillance systems across the United States. As the prevalence of infectious diseases continues to rise in diverse populations, the method’s adaptability to different environments is vital. Ensuring that public health systems integrate wastewater sampling as a routine practice could enhance overall health security and preparedness for future epidemics.
Challenges in Detecting Infectious Viruses in Wastewater
Detecting infectious viruses like monkeypox in wastewater presents various challenges that complicate public health efforts. One significant challenge is the variability in nucleic acid detection, which can be influenced by factors such as the rate of viral shedding from infected individuals and the wastewater treatment process itself. This variability necessitates the implementation of rigorous sampling protocols and sensitive detection methods to ensure accurate monitoring and assessment.
Additionally, the interpretation of results from wastewater surveillance must consider local epidemiological contexts. For example, the presence of MPXV clade Ib in a sample could indicate a larger outbreak or only isolated cases, thus complicating responses. Public health agencies must tailor their strategies to address these nuances, integrating wastewater surveillance with traditional disease tracking methods to provide a comprehensive picture of community health.
The Role of PCR Methods in Monkeypox Surveillance
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method plays a crucial role in detecting MPXV clade Ib, allowing for the amplification of viral DNA from complex wastewater samples. This sensitive detection technique is pivotal in identifying low concentrations of the virus, making it possible to detect MPXV clade Ib even in the absence of symptomatic cases. By employing hydrolysis-probe PCR, researchers can ensure high specificity, which is essential for distinguishing monkeypox from other viral pathogens in wastewater.
Furthermore, the success of PCR methods in this context opens avenues for similar applications in other infectious diseases monitoring. As the landscape of public health surveillance evolves, leveraging PCR technology for early detection can aid in managing potential outbreak threats. By drawing on the insights gained from wastewater analysis, health authorities can proactively address public health concerns associated with infectious diseases like monkeypox.
Future Directions for Monkeypox Surveillance
As the understanding of monkeypox evolves, future directions for surveillance must focus on refining wastewater monitoring techniques. Emphasizing research on the persistence and degradation of MPXV in various environmental contexts will enhance the reliability of detection. Additionally, developing standardized protocols for sampling and analysis across different regions can help establish comprehensive surveillance networks, ensuring that public health officials can respond swiftly to changes in virus prevalence.
Innovative technologies, such as next-generation sequencing, may also play a key role in the future of monkeypox surveillance. By providing detailed genomic data about MPXV clade Ib, these techniques can aid in tracking variant emergence and spread more effectively than traditional methods. As the interplay between environmental monitoring and epidemiology continues to grow, collaboration among research institutions and public health agencies will be crucial in fortifying defenses against infectious diseases.
Public Health Implications of Wastewater Surveillance
The public health implications of wastewater surveillance for detecting monkeypox virus are profound. By proactively identifying viral DNA in wastewater, health officials can implement timely interventions, such as awareness campaigns and resource allocation in at-risk communities. This forward-thinking approach not only helps mitigate the spread of monkeypox but also reinforces trust in public health systems by demonstrating a proactive stance against emerging infectious diseases.
Moreover, integrating wastewater monitoring into broader public health strategies can aid in early detection of various pathogens, creating a more resilient framework for managing infectious diseases. The lessons learned from monitoring MPXV clade Ib can serve as a model for incorporating wastewater analysis as a standard practice in public health surveillance, ensuring that communities remain vigilant against potential future outbreaks.
Innovations in Infectious Disease Detection Methods
Innovations in detection methods for infectious diseases, especially monkeypox, are pivotal in addressing public health threats effectively. The use of advanced PCR techniques has revolutionized how we detect and monitor viral pathogens from contaminated sources like wastewater. These innovations facilitate rapid response capabilities that are critical during outbreaks, allowing researchers and health officials to stay ahead of rapidly evolving viruses.
Furthermore, integrating digital technologies with wastewater surveillance can enhance data interpretation and public health responses. For instance, machine learning algorithms can analyze trends in viral loads detected in wastewater, providing predictive analytics that inform resource allocation and intervention strategies. As we harness technology to track the emergence and spread of diseases like monkeypox, the potential for improved health outcomes increases.
Understanding Clade Ib and Its Transmission Dynamics
Clade Ib of the monkeypox virus presents unique transmission dynamics that require thorough understanding for effective public health response. The rapid spread of this clade, particularly through sexual contact among adults, underscores the need for targeted health education initiatives. Understanding how different clades transmit aids health officials in crafting focused communication strategies that raise awareness about transmission routes and preventive measures.
Moreover, the association of MPXV clade Ib with specific demographic patterns can inform tailored interventions. By analyzing data from wastewater surveillance along with clinical case reports, public health initiatives can prioritize high-risk groups for vaccination and resources. This evidence-based approach enhances the overall effectiveness of public health strategies against monkeypox clade Ib and underscores the importance of comprehensive monitoring.
The Future of Wastewater Surveillance in Public Health
The future of wastewater surveillance in public health looks promising, as it offers innovative avenues for early detection of multiple pathogens, including the monkeypox virus. As more communities adopt wastewater testing protocols, the wealth of data generated will enable health officials to monitor trends effectively over time. This proactive strategy positions wastewater surveillance as a key component of a modern public health toolkit.
Additionally, expanding research on viral load dynamics in wastewater can provide critical insights into community transmission patterns. With advancements in detection technology, public health authorities will be better equipped to respond to emerging infectious diseases, making wastewater surveillance not just a supplementary tool, but an essential part of infectious disease control and prevention efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Monkeypox Virus Detection and why is it important?
Monkeypox Virus Detection refers to the methods used to identify the presence of the monkeypox virus (MPXV) in various environments, such as wastewater. This detection is crucial for monitoring the prevalence of infectious diseases, helping public health officials respond to potential outbreaks effectively.
How does monkeypox wastewater surveillance contribute to public health?
Monkeypox wastewater surveillance detects traces of MPXV clade Ib in wastewater, providing valuable data on infection rates within communities. By analyzing wastewater samples, public health agencies can identify potential outbreaks early and implement necessary preventive measures.
What is the PCR method used for monkeypox virus detection?
The PCR method, specifically the hydrolysis-probe PCR format, is a sensitive technique used to detect MPXV clade Ib DNA in wastewater samples. This method amplifies viral genetic material, allowing for precise detection even in low concentrations.
What were the findings of the study on MPXV clade Ib detection in wastewater?
The study found MPXV clade Ib DNA in only one of over 3,000 wastewater samples analyzed from 147 treatment plants across the U.S. This finding indicates localized presence, mirroring confirmed cases of infection, and highlights the method’s potential in infectious diseases monitoring.
Can environmental monitoring detect different clades of the monkeypox virus?
Yes, environmental monitoring, including wastewater surveillance, can detect various clades of the monkeypox virus, such as clade Ib, allowing for a broader understanding of the virus’s spread and evolution.
What impacts the variability of monkeypox virus detection in wastewater?
Variability in monkeypox virus detection in wastewater can be influenced by factors such as the rate of viral shedding from infected individuals, environmental conditions, and the timing of sample collection relative to infection periods.
How can wastewater surveillance improve response to monkeypox outbreaks?
Wastewater surveillance can improve responses to monkeypox outbreaks by serving as an early warning system. Early detection of MPXV in wastewater can alert health officials to rising infection levels, enabling timely public health interventions.
What are the limitations of using wastewater as a source for monkeypox virus detection?
Limitations of wastewater as a detection source for monkeypox include potential dilution of viral particles, variability in shedding rates from individuals, and the need for comprehensive surveillance strategies to ensure community-wide coverage.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Detection Method | Sensitive PCR technique used to analyze wastewater samples. |
| Sample Size | Over 3,000 samples collected from 147 treatment plants across the U.S. |
| Positive Detection | MPXV clade Ib DNA was detected in one sample from a known infected location. |
| Concerns of Spread | Clade Ib has spread rapidly since 2024 among adults, mainly through sexual contact. |
| Public Health Application | Monitoring wastewater can serve as an early warning system for outbreaks. |
| Conclusion | Establishing wastewater monitoring as a public health tool is essential. |
Summary
Monkeypox Virus Detection is crucial for understanding and managing potential outbreaks. The study discussed highlights that the presence of MPXV clade Ib DNA in wastewater can serve as an effective monitoring strategy. With rising cases attributed to its spread since 2024, this innovative approach may help in identifying outbreaks early, thereby enhancing public health response efforts. The methodology’s effectiveness underscores the importance of continued surveillance to mitigate the risks associated with infectious diseases like monkeypox.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.