The recent decline in MMR vaccine uptake is a pressing concern for public health officials, as studies indicate a potential surge in measles cases if vaccination rates continue to fall. Measles vaccination is vital to prevent outbreaks and maintain community immunity, especially amid increasing vaccine hesitancy and misinformation. Researchers have highlighted that restricting non-medical vaccine exemptions could significantly bolster MMR uptake across the United States, thereby enhancing pandemic preparedness. With alarming trends showing that the kindergarten MMR vaccination rate has dropped from 98.5% to 94.3% in Texas, the urgency for action becomes apparent. Amid ongoing discussions on vaccine policies, understanding the factors influencing vaccine uptake is crucial in combating future MMR outbreaks.
The issue surrounding the uptake of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine has become increasingly important as public health experts monitor vaccination trends. With vaccination rates dipping and many parents opting for vaccine exemptions, the implications for community health are dire. Various strategies, including revising exemption policies and enhancing public awareness, are essential for maintaining robust measles vaccination coverage. The interplay of factors such as vaccine hesitancy and misinformation could threaten years of progress in disease elimination. Overall, addressing the challenges of MMR vaccination is critical for safeguarding public health.
Understanding the Decline in MMR Vaccine Uptake
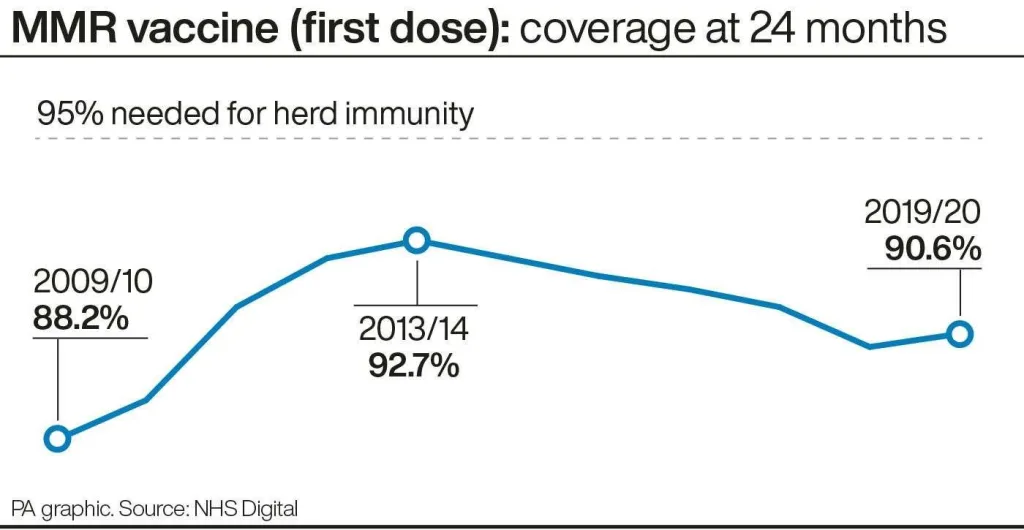
The decline in MMR vaccine uptake has become a pressing public health concern, with current statistics revealing a worrisome trend. Recent studies indicate that kindergarten MMR vaccination rates in Texas have dropped from 98.5% in the 2013-14 school year to just 94.3% in 2024-25. This decrease in vaccination coverage could significantly impact herd immunity, leading to potential outbreaks of measles, mumps, and rubella. Such declines are often fueled by misinformation campaigns and increased vaccine hesitancy among parents, creating an environment where children are left vulnerable to these preventable diseases.
As the importance of the MMR vaccine becomes clearer, community awareness about the consequences of falling vaccination rates is essential. Public health officials emphasize that maintaining a high rate of vaccination is crucial in preventing outbreaks and protecting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. The rise of non-medical vaccine exemptions in various states has compounded the issue, allowing more families to opt-out of immunizations for their children. To combat this trend, it is vital to promote accurate information about the benefits of vaccines and the risks associated with vaccine-preventable diseases.
Impact of Non-Medical Exemptions on MMR Uptake
Research has shown that states with less restrictive non-medical exemption (NME) policies experience significant declines in MMR vaccine uptake. For instance, the recent study from Johns Hopkins University found that states allowing both religious and philosophical exemptions reported the largest drops in vaccination rates. This is particularly concerning because these exemptions can create pockets of unvaccinated individuals, increasing the risk of outbreak situations. Analyzing policies across 33 states, the research indicated that only a select few states that tightened their NME laws, such as New York and Connecticut, saw significant increases in MMR vaccination rates.
Efforts to restrict NMEs could be crucial in reversing the declining MMR vaccine uptake trend across the United States. Policymakers must recognize the correlation between NME availability and vaccination rates to initiate effective reforms. Implementing evidence-based policies that promote vaccination and protect public health is critical, especially in light of the ongoing challenges posed by vaccine hesitancy. By limiting exemptions, states can encourage higher vaccination rates, fostering a healthier population and preventing outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current trends in MMR vaccine uptake in the United States?
Recent studies indicate declining MMR vaccine uptake across various states, which has alarmed health officials. Specifically, kindergarten MMR vaccination rates in Texas fell from 98.5% to 94.3% from 2013-14 to 2024-25. This decline may contribute to increased vulnerability to outbreaks of measles, mumps, and rubella.
How do vaccine exemptions affect MMR vaccine uptake?
Vaccine exemptions, particularly non-medical exemptions, have a significant impact on MMR vaccine uptake. States allowing broad exemption options, such as religious and philosophical exemptions, have observed notable declines in vaccination rates. The relationship between these policies and MMR uptake emphasizes the need for stricter regulations to enhance vaccination coverage.
What is the connection between vaccine hesitancy and MMR outbreak risk?
Vaccine hesitancy contributes to decreased MMR vaccine uptake, increasing the risk of outbreaks. As misinformation spreads, it fuels doubts about vaccine safety, resulting in lower vaccination rates. The correlation between hesitancy and rising measles cases highlights the importance of public education in maintaining community immunity.
How can restricting non-medical exemptions increase MMR vaccine uptake?
Research shows that restricting non-medical exemptions can lead to increased MMR vaccine uptake. A study found that states which prohibited these exemptions saw slight declines in vaccination rates, but overall, these rates remained above the herd immunity threshold. Implementing more stringent exemption policies could bolster public health by encouraging higher vaccination rates.
What strategies can improve MMR vaccine uptake during pandemics?
Improving MMR vaccine uptake during pandemics requires a multifaceted approach that includes promoting public awareness about vaccine safety and efficacy, enforcing stricter vaccine compliance laws, and providing access to educational resources. Strengthening pandemic preparedness by ensuring high immunization rates can help mitigate the risk of MMR outbreaks.
Why is maintaining high MMR vaccination rates crucial for public health?
Maintaining high MMR vaccination rates is essential for achieving herd immunity, which protects the entire community from outbreaks. As seen in recent Texas measles cases, declining vaccination rates correlate with increased disease transmission. Protecting public health through robust vaccination programs is vital to prevent future outbreaks.
What role do health organizations play in MMR vaccine promotion?
Health organizations play a critical role in promoting MMR vaccine uptake by providing reliable information, advocating for vaccine accessibility, and supporting evidence-based policies. Recommendations from organizations like the CDC and ACIP are significant in guiding vaccination practices and addressing public concerns regarding vaccine safety.
How can communities combat misinformation about the MMR vaccine?
Communities can combat misinformation about the MMR vaccine through targeted education campaigns that provide factual information from credible sources. Engaging healthcare professionals in discussions, utilizing social media for outreach, and offering public forums for questions can help address concerns and encourage vaccine acceptance.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Declining MMR Uptake | Recent studies indicate a significant drop in MMR vaccination rates, with Texas reporting a fall from 98.5% to 94.3% in kindergarten vaccination from 2013-2024. |
| Impact of Lower Vaccination | A 5% drop in vaccination leads to increased outbreaks of measles, with predictions of up to 21 cases per 1,000 people in some counties under certain scenarios. |
| Role of Non-Medical Exemptions | States allowing non-medical exemptions saw greater declines in vaccination rates. In contrast, states prohibiting these exemptions experienced a slight decrease. |
| Policy Changes | ACIP now recommends against using MMRV for children under 4 years, favoring separate vaccinations instead, as part of an effort to promote immunization. |
| Need for Evidence-Based Policy Reform | With proposed legislation in over 15 states to increase vaccine exemptions, there’s a strong call for reforms to uphold public health. |
Summary
MMR vaccine uptake is critical for maintaining herd immunity and preventing outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases. Studies show that a decline in vaccination rates, particularly due to misinformation and ease of non-medical exemptions, poses significant risks to public health. There’s an urgent need for policy reforms to ensure evidence-based strategies are in place to promote higher MMR vaccine uptake and safeguard communities against outbreaks.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.