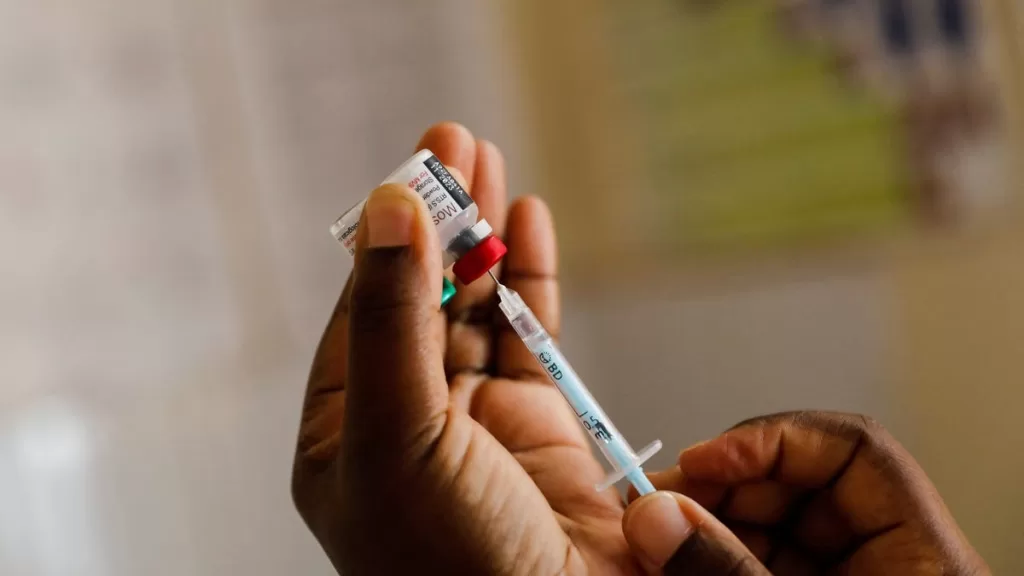
The arrival of the malaria vaccine in Nigeria marks a significant milestone in the fight against this deadly disease that claims thousands of lives annually. Nigeria, known for having the highest malaria burden globally, is gearing up for a transformative vaccination campaign set to launch in November. This initiative will initially target high-prevalence states like Kebbi and Bayelsa, focusing on children under one year old to build a healthier future. Administering the R21/Matrix-M vaccine, developed by Oxford University, is a crucial step towards reducing malaria cases and improving Nigeria’s overall health status. As we delve into this health breakthrough, notable Nigeria health news reveals a complex landscape that includes ongoing battles against foodborne diseases like Salmonella and the resurgence of polio cases in various regions.
Introducing the groundbreaking malaria immunization effort in Nigeria, this new vaccine rollout promises to change the narrative around preventable diseases in the nation. With much anticipation, health officials are preparing to implement this vaccination plan, which targets vulnerable populations affected by malaria. The R21/Matrix-M vaccine, recognized for its efficacy, represents hope in combating a disease that poses a persistent public health challenge. Alongside this critical development, Nigeria is also navigating various health issues, including outbreaks of bacterial infections and cases of vaccine-derived polio. This coordinated healthcare response highlights the country’s commitment to enhancing public health standards and reducing the impact of infectious diseases.
Introduction of the Malaria Vaccine in Nigeria
Nigeria has been at the forefront of the battle against malaria, a disease that poses a significant threat to public health, particularly among children under five. With the recent introduction of the malaria vaccine, the country’s efforts to reduce malaria prevalence are positioned for a significant boost. The R21/Matrix-M vaccine, developed by Oxford University and manufactured by the Serum Institute of India, has been endorsed as part of Nigeria’s routine immunization program. This initiative aims to protect vulnerable populations and is a vital step in mitigating the high malaria burden in Nigeria.
The first phase of the vaccination campaign will commence in November, targeting the states of Kebbi and Bayelsa, where malaria transmission rates are alarmingly high. By administering the vaccine to children under one year old, health officials are prioritizing the most susceptible demographic. The community’s response to the vaccine rollout will be critical in evaluating its effectiveness and uptake. With a total of four doses required for complete immunity, public awareness campaigns will play a crucial role in educating families about the importance of vaccination in combating malaria.
Rising Concerns Over Salmonella Outbreak Linked to Eggs
In light of the recent Salmonella outbreak associated with eggs from Milo’s Poultry Farms, the public must be vigilant about food safety. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a staggering increase in reported infections, leading to heightened concern among consumers. This outbreak highlights the challenges faced in preventing foodborne diseases, which can have severe health implications for affected individuals, especially children and the elderly. Precautionary measures such as thorough cooking and proper food handling practices become vital during such outbreaks.
In the wake of this outbreak, health officials recommend that consumers stay informed about food recalls and follow guidelines issued by the CDC. Although no fatalities have been reported, the hospitalization of several individuals underscores the seriousness of Salmonella infections. This incident serves as a reminder of the importance of strict regulations and monitoring of poultry farming practices, as well as continuous public health initiatives aimed at preventing foodborne illnesses within the country.
The Impact of Polio Cases on Global Health Initiatives
The recent reports of new polio cases in Pakistan and Ethiopia bring alarm to the global health community, emphasizing the ongoing challenges in eradicating this highly infectious disease. With four additional cases of wild poliovirus reported in Pakistan, the rise in numbers signals the urgent need for continued vaccination efforts. Meanwhile, Ethiopia’s confirmation of vaccine-derived poliovirus cases in previously unaffected regions showcases how quickly the threat of polio can re-emerge, even in countries that have made significant progress towards eradication.
These developments prompt renewed discussions about the importance of maintaining high vaccination coverage. The Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) advocates for robust immunization programs that can prevent outbreaks. In light of the recent data, health officials and organizations must mobilize resources and strengthen community engagement to address gaps in vaccination and prevent further spread. High-profile campaigns and educational outreach can play a significant role in reminding communities about the importance of vaccines in public health.
The Role of Vaccines in Combatting Infectious Diseases
Vaccines have played a pivotal role in the fight against infectious diseases, from measles to polio, and now malaria. The recent introduction of the malaria vaccine in Nigeria represents a significant milestone in public health, offering hope in reducing the disease’s impact on vulnerable populations, particularly children. Vaccination not only protects individuals but also contributes to herd immunity, which is essential for controlling outbreaks. As more countries adopt such vaccines, the potential for eradicating diseases globally becomes more attainable.
Moreover, the effectiveness of vaccines against diseases like polio serves as a lesson in the importance of sustained immunization efforts. Despite substantial progress, the emergence of new cases due to vaccine-derived strains underlines the necessity of maintaining high vaccination rates. Public health organizations must continue to prioritize vaccination campaigns and research to develop new and effective vaccines, ensuring that strategies adapt to the evolving landscape of infectious diseases.
Importance of Public Awareness in Health Campaigns
Public awareness is a critical component of effective health campaigns, especially when introducing new vaccines. For Nigeria’s malaria vaccination initiative to succeed, the government and health organizations must engage with communities to raise awareness about the benefits of vaccination. Educating parents about the risks of malaria and the importance of immunization can help improve vaccine uptake among young children. Local community leaders and healthcare providers can play a vital role in disseminating this information and addressing any hesitations or misconceptions.
In addition, public health campaigns should leverage various media platforms to reach a broader audience. From social media to community gatherings, utilizing diverse channels enables targeted messaging that can significantly influence public perception. As seen in the response to the Salmonella outbreak, timely communication about potential risks and preventive measures is essential in empowering individuals to make informed health decisions, ultimately fostering healthier communities.
Collaborative Efforts in Global Health Initiatives
The interconnected nature of global health calls for collaborative efforts in managing public health threats such as malaria, polio, and foodborne diseases. The response to Nigeria’s malaria vaccine introduction showcases how international partnerships can bolster local health initiatives. Organizations like Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, have played a vital role in ensuring that vaccines reach the areas that need them most. Collaborative efforts are critical in pooling resources, sharing knowledge, and best practices across regions to tackle these significant health challenges.
Moreover, tackling issues like the Salmonella outbreak exemplifies the importance of coordination among health authorities. By sharing data and strategies, states can implement more effective surveillance and control measures against foodborne diseases. Ultimately, a collaborative approach strengthens global health systems, enhances preparedness for future outbreaks, and ensures that all countries can access essential healthcare resources, fostering a healthier world for everyone.
Future Directions for Immunization Programs
As Nigeria launches its malaria vaccine program, it sets a precedent for the future of immunization initiatives worldwide. With malaria still posing a significant health threat, the success of this program can provide invaluable insights into how best to implement similar strategies in other countries facing high malaria burdens. Ongoing research and continuous monitoring will be crucial in fine-tuning vaccination strategies, allowing for the adaptation and optimization of programs based on real-world data.
Looking forward, the integration of newer technologies in vaccine distribution and public health education will be vital. Digital health solutions can facilitate better tracking of immunization rates and help identify areas needing targeted intervention. It is crucial that programs also adapt to feedback from community members to ensure that they are culturally appropriate and responsive to the specific needs of the population. The future of immunization relies not just on the development of vaccines but on robust support systems that encourage their uptake and ensure comprehensive coverage.
Preventing Infectious Diseases in High-risk Areas
High-risk areas for infectious diseases such as malaria and foodborne pathogens require targeted interventions to reduce disease prevalence. By focusing on regions with the highest burden, public health campaigns can maximize their impact and resources. Such strategic planning is essential for addressing the unique health challenges faced by communities with limited access to healthcare facilities and education.
Implementing preventive measures, such as ensuring proper sanitation, improving access to clean water, and promoting good hygiene practices, are crucial elements of effectively reducing the spread of diseases like Salmonella. Additionally, training local health workers to educate communities about disease prevention and encouraging prompt medical care for suspected illnesses can play a significant role in building resilience against infectious diseases in vulnerable populations.
Monitoring and Evaluating Health Interventions
Effective monitoring and evaluation are foundational to the success of health interventions like the malaria vaccine rollout in Nigeria. By setting up robust assessment frameworks, health officials can track the program’s progress, ensure vaccine compliance, and analyze data on malaria incidence. This ongoing evaluation process aids in identifying potential challenges and adapting strategies to improve outcomes.
Furthermore, engaging with the community to gather feedback and insights on the vaccination process allows for transparency and trust-building among the population. By incorporating local voices into evaluation efforts, health programs can enhance their effectiveness and ensure that they are addressing the needs and concerns of community members. Continuous monitoring initiatives will contribute significantly to achieving long-term health goals, particularly in countries like Nigeria, where the burden of infectious diseases remains a pressing issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the malaria vaccine in Nigeria?
The malaria vaccine in Nigeria is a crucial development in the fight against malaria, a disease that significantly impacts the country’s health system. With the highest malaria burden globally, Nigeria’s introduction of the R21/Matrix-M vaccine aims to reduce transmission and protect vulnerable children under 1 year old, thereby decreasing morbidity and mortality rates.
How will the malaria vaccine be administered in Nigeria?
In Nigeria, the malaria vaccine will be administered as part of the routine immunization schedule starting in November. The initial phase focuses on Kebbi and Bayelsa states, where malaria prevalence is high. A total of 4 doses of the vaccine will be required for full immunization of children.
What role does the R21/Matrix-M vaccine play in combating malaria in Nigeria?
The R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine plays a vital role in combating malaria in Nigeria by providing immunity to young children, who are most at risk of severe malaria. Developed by Oxford University and produced by the Serum Institute of India, this vaccine aims to reduce the incidence of malaria, contributing to the overall health improvements in Nigeria.
When is the malaria vaccination campaign starting in Nigeria?
The malaria vaccination campaign in Nigeria is set to begin in November 2024. This campaign will kick off in Kebbi and Bayelsa states, targeting children under 1 year old, and is part of a broader effort to include malaria vaccination in the country’s health initiatives.
What has prompted Nigeria to include the malaria vaccine in its immunization schedule?
Nigeria’s inclusion of the malaria vaccine in its immunization schedule is prompted by the urgent need to address the country’s high malaria prevalence rates. This strategic decision is part of the government’s commitment to improving child health outcomes and reducing the disease’s impact on communities.
What potential impact could the malaria vaccine have on Nigeria’s health outcomes?
The potential impact of the malaria vaccine in Nigeria includes a significant decrease in malaria cases and related fatalities among children. By providing early immunity, the vaccine could lead to improved health outcomes and a reduction in healthcare costs associated with treating malaria.
Are there any concerns regarding the administration of the malaria vaccine in Nigeria?
While the introduction of the malaria vaccine is a positive development, concerns about public awareness, vaccine accessibility, and storage conditions in rural areas need to be addressed to ensure a successful vaccination campaign in Nigeria.
How can the malaria vaccine contribute to Nigeria’s overall health system?
The malaria vaccine can contribute to Nigeria’s overall health system by alleviating the burden of malaria on healthcare facilities, reducing hospitalization rates, and allowing for better allocation of resources to other health initiatives, ultimately leading to improved public health.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Malaria Vaccine Nigeria | Nigeria received its first malaria vaccine delivery on October 17, 2024. The vaccination campaign will start in November, focusing on Kebbi and Bayelsa states, targeting children under 1 year old. |
| Vaccine Details | The vaccine is the R21/Matrix-M developed by Oxford University, requiring 4 doses and included in Nigeria’s routine immunization schedule. |
| Salmonella Outbreak | An outbreak linked to eggs from Milo’s Poultry Farms resulted in 93 infections across 12 states, with 34 hospitalizations but no fatalities. |
| Polio Cases | Pakistan reported 4 new polio cases, raising its total to 32 for the year. Ethiopia confirmed 2 cases of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus. |
Summary
The introduction of the malaria vaccine in Nigeria is a significant milestone in the country’s fight against malaria, the largest contributor to preventable deaths among children. With the launch of the vaccination campaign scheduled for November, Nigeria aims to reduce malaria prevalence significantly. The R21/Matrix-M vaccine, which will be administered to children under 1 year, demonstrates the commitment to improving public health in Nigeria amidst existing challenges like salmonella outbreaks and rising polio cases. Overall, the malaria vaccine Nigeria initiative will play a pivotal role in safeguarding the lives of vulnerable populations.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.