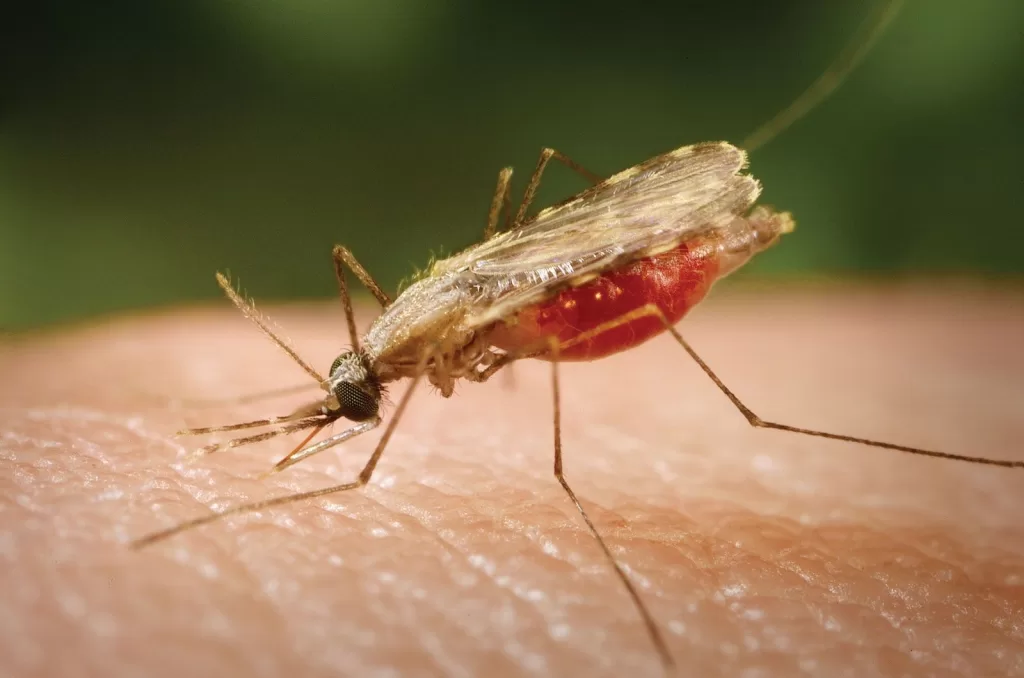
Malaria, a life-threatening disease caused by parasites transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes, has ravaged populations throughout history, showcasing its severe impact on human health. The evocative painting by Italian artist Giulio Aristide Sartorio, often dubbed “Malaria,” starkly captures the agony and loss associated with the disease, particularly evident in the Pontine Marshes—once a formidable battleground against this relentless illness. Over the years, the struggle against malaria has witnessed significant historical events and social challenges, informing contemporary public health initiatives. Efforts such as malaria vaccination programs are now seen as critical in combating the disease, which sadly leads to over 400,000 childhood fatalities in endemic regions each year. As we reflect on the malaria history and its lessons, it becomes clear that ongoing research and political resolve are essential to eliminate this scourge, especially with the legacy of malaria still looming large in places like Italy.
The fight against malaria can be seen as a longstanding battle between humans and a pervasive tropical illness that thrives in certain climates, particularly in the regions of Africa, Asia, and South America. This devastating illness, characterized by its transmission via mosquito vectors, continues to infiltrate communities, exerting a profound influence on public health policy and infrastructure. Artistic interpretations, such as Sartorio’s poignant work, not only illustrate the historical context of this struggle but also evoke emotional responses that underscore the urgency of addressing the disease. Furthermore, initiatives like malaria vaccinations represent a beacon of hope in the ongoing narrative of recovery and health improvements. Understanding the social and environmental implications of malaria extends beyond borders, inviting global collaboration to ultimately eradicate this disease.
Understanding Malaria: Historical Impact and Cultural Reflections
The historical significance of malaria cannot be understated, especially when analyzed through the lens of artistic expression. The 1883 painting by Giulio Aristide Sartorio, titled “Dum Romae consulitur, morbos imperat” or “While Rome Deliberates, the Disease Rules,” serves as a poignant reminder of malaria’s devastating effects on human life. This artwork captures the emotional and physical toll of the disease, particularly in the context of the Pontine Marshes, an area severely afflicted by malaria over the centuries. Through Sartorio’s grim realism, viewers are taken on a journey that reveals not only the plight of individuals but also the broader societal struggles tied to the disease’s prevalence and the efforts to combat it.
Sartorio’s work embodies the intersection of health crises with political and environmental dynamics in Italy. The marshes, once a breeding ground for malaria mosquitoes, stand as a symbol of ongoing human resilience and the fight against disease, demonstrating how art can highlight critical public health issues. This historical perspective helps us understand the complex relationship between malaria and society, linking cultural representations to the real impact of the disease throughout history.
Furthermore, the socio-political landscape around malaria in Italy provides a rich backdrop for discussing public health interventions. During Benito Mussolini’s regime in the 1930s, large-scale reclamation projects were launched to drain the marshes and reduce malaria’s spread. Despite these efforts, the disease saw a resurgence during World War II, illustrating how conflict can exacerbate public health crises. The devastation caused by flooding strategies employed by occupying forces not only intensified suffering for the local population but also underscored the need for consistent public health policies.
By examining the historical impact of malaria and the cultural responses to it, we can better appreciate the ongoing challenges surrounding malaria today. Understanding the legacy of malaria in places like Italy reminds us that the fight against this disease is far from over, as modern efforts continue to focus on eradication and vaccination to prevent future outbreaks.
The Modern Battle Against Malaria: Vaccination and Global Health Initiatives
As we advance into the 21st century, the fight against malaria remains a global health priority. Recent developments in malaria vaccination offer hope amid the continued threat of this deadly disease. The recent approval of malaria vaccines represents a significant breakthrough in public health, aimed at reducing the annual loss of over 400,000 children who succumb to malaria. Countries in endemic regions are now focusing on mass vaccination campaigns, with the objective of achieving herd immunity in vulnerable populations while educating communities about preventive measures against malaria infection.
Malaria vaccination initiatives are critical to mitigating the disease’s impact globally, but they require robust international support and funding to succeed. Global health organizations are increasingly recognizing that sustained investment in research and community health infrastructures can lead to substantial reductions in malaria cases and mortality rates. This multifaceted approach, integrating vaccination alongside education, vector control, and treatment strategies, provides a comprehensive method for addressing malaria’s persistent threats.
Moreover, the importance of collaboration among nations cannot be overstated in the fight against malaria. Countries affected by malaria often share borders and face similar risks, making it essential for international partnerships to share knowledge, resources, and strategies aimed at containment and eradication. Programs like the World Health Organization’s Global Malaria Strategy emphasize collaborative efforts and the need for holistic health systems that can adapt to the unique challenges posed by malaria in different regions.
The success of malaria vaccination programs is contingent on community trust and engagement, which can be fostered through education campaigns that inform populations about the benefits and safety of vaccines. By enhancing public understanding surrounding malaria vaccination, global health organizations can drive increased participation in vaccination drives, ultimately leading to a greater decline in malaria prevalence and a healthier future for those at risk.
The Legacy of Malaria in Italy: Past Insights for Future Solutions
The legacy of malaria in Italy is a complex narrative that illustrates both historical challenges and contemporary health triumphs. The story begins with the brutal impact malaria had on the Italian population, particularly in regions like the Agro Pontino, where the disease flourished due to environmental conditions. The efforts to reclaim these marshy lands during Mussolini’s regime not only reduced malaria incidences significantly but also marked a turning point in how societies confront endemic diseases. Historical reflections reveal both the dire consequences of neglecting public health and the transformative potential of proactive health policies and infrastructure improvements.
These past experiences in managing malaria underscore crucial lessons for current public health initiatives worldwide. The successful eradication of malaria in Italy by the 1970s showcases the effective role of health education, community engagement, and government commitment. By analyzing Italy’s journey, other nations grappling with malaria can derive valuable strategies that prioritize disease prevention through sustained health promotion and infrastructure development.
In today’s context, the situation in Italy serves as a reminder that while we have advanced in our understanding and treatment of malaria, vigilance is still necessary to prevent the disease from resurfacing. Close monitoring of eradicated regions and proactive health policies are essential to ensure that history does not repeat itself. Combating potential malaria re-establishment requires ongoing community education about the disease’s risks and how citizens can contribute to its prevention.
Thus, the legacy of malaria in Italy connects the past with present and future health strategies, highlighting the importance of addressing social, economic, and environmental factors that influence disease spread. Ultimately, drawing from historical insights can inform current practices and foster a more resilient public health framework that can withstand future challenges posed by malaria and other infectious diseases.
The Cultural Significance of Malaria in Historical Art
Art has always served as a powerful medium for conveying social and political messages, and this is poignantly illustrated in the works depicting malaria, particularly Sartorio’s famous painting. By capturing the essence of the human suffering inflicted by malaria, the artwork transcends mere visual representation and encourages viewers to engage with the deeper implications of health crises. The raw emotion expressed in Sartorio’s portrayal of a grieving mother not only highlights the personal tragedy that malaria inflicts on families but also reflects broader societal truths regarding neglect and the brutality of disease during historical times.
In analyzing this artwork, one can appreciate how artists use their craft to articulate the human condition amidst suffering. The portrayal of malaria’s impact through cultural lenses facilitates a greater understanding of the disease’s historical and ongoing implications, allowing us to appreciate not only the aesthetic value of such pieces but also their importance in shaping public health discourse.
Furthermore, examining the intersection of malaria and cultural production reveals a landscape where art acts as a historical document. Many artistic representations, like Sartorio’s, capture moments in time that reflect societal responses to public health challenges. These artworks serve as reminders of the past, offering insights into how communities have historically grappled with disease, thus informing contemporary efforts to address malaria.
Artistic depictions of malaria encourage societal reflection and dialogue about ongoing public health issues, reminding audiences of the human stories behind statistics. As we continue to engage with the cultural significance of malaria, it becomes clear that historical art offers valuable lessons on resilience and the inherent human struggle against infectious diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of Giulio Aristide Sartorio’s painting ‘Malaria’?
Giulio Aristide Sartorio’s painting ‘Malaria’, also known as ‘Dum Romae consulitur, morbos imperat’, vividly illustrates the devastating impact of malaria through its stark imagery, showing a grieving mother in the Pontine Marshes. This 1883 artwork symbolizes the historical suffering and struggles faced by communities affected by malaria, highlighting the disease’s dramatic effect on human life.
How did the history of malaria impact Italy during the 20th century?
The history of malaria in Italy saw significant changes throughout the 20th century. The disease was prevalent in areas like the Agro Pontino and was a major public health challenge. Reclamation efforts led by Benito Mussolini in the 1930s initially helped reduce malaria cases, but the disease reemerged during World War II. It wasn’t until the 1970s that sustained health initiatives successfully eradicated malaria in Italy, though its history continues to inform contemporary public health strategies.
What advancements have been made in malaria vaccination recently?
Recent advancements in malaria vaccination have provided a hopeful outlook in the fight against this deadly disease. Several malaria vaccines have shown promise in clinical trials, demonstrating effectiveness in reducing infection and mortality rates. Continued investment and support for malaria vaccination programs are essential to combat the disease, especially in regions most affected by malaria.
What are the long-term impacts of malaria on childhood mortality?
Malaria continues to be a significant contributor to childhood mortality in many endemic areas, with over 400,000 reported deaths annually. The disease disproportionately affects young children, weakening their immune systems and leading to severe health complications. Addressing these impacts requires global cooperation in strengthening health initiatives and vaccination programs to reduce malaria’s threat to children.
What role did the Pontine Marshes play in the history of malaria in Italy?
The Pontine Marshes were historically significant in the struggle against malaria in Italy. This region experienced high malaria prevalence, serving as a battleground for public health efforts throughout the centuries. The transformation of the marshland through reclamation initiatives marked a critical point in combating malaria, ultimately leading to the successful eradication of the disease in Italy by the 1970s.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Painting Overview | Features the 1883 painting ‘Dum Romae consulitur, morbos imperat’ by Giulio Aristide Sartorio, illustrating the impact of malaria. |
| Historical Context | The Pontine Marshes served as a significant battleground against malaria, illustrating Italy’s environmental and health struggles. |
| Reclamation Efforts | Initiated by Mussolini in the 1930s, aimed to reduce malaria spread, but the disease resurfaced during WWII due to flooding tactics. |
| Eradication Success | Malaria was eradicated in Italy by the 1970s through health initiatives, yet its legacy remains. |
| Current Impact | Malaria causes over 400,000 childhood deaths annually in endemic regions, emphasizing the need for continued vaccination support. |
| Future Outlook | Recent advances in malaria vaccines provide hope, but sustained international cooperation is essential to combat mortality rates. |
Summary
Malaria remains a critical global health challenge that demands immediate attention. The historical significance of malaria in places like the Pontine Marshes showcases the disease’s long-standing impact on communities, leading to immense human suffering. Despite Italy’s successful eradication efforts by the 1970s, malaria continues to threaten lives worldwide, particularly affecting children in endemic regions. The recent developments in malaria vaccines signify a promising step forward, but ongoing support for vaccination initiatives is vital for reducing mortality rates and ultimately eliminating malaria as a public health threat.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.