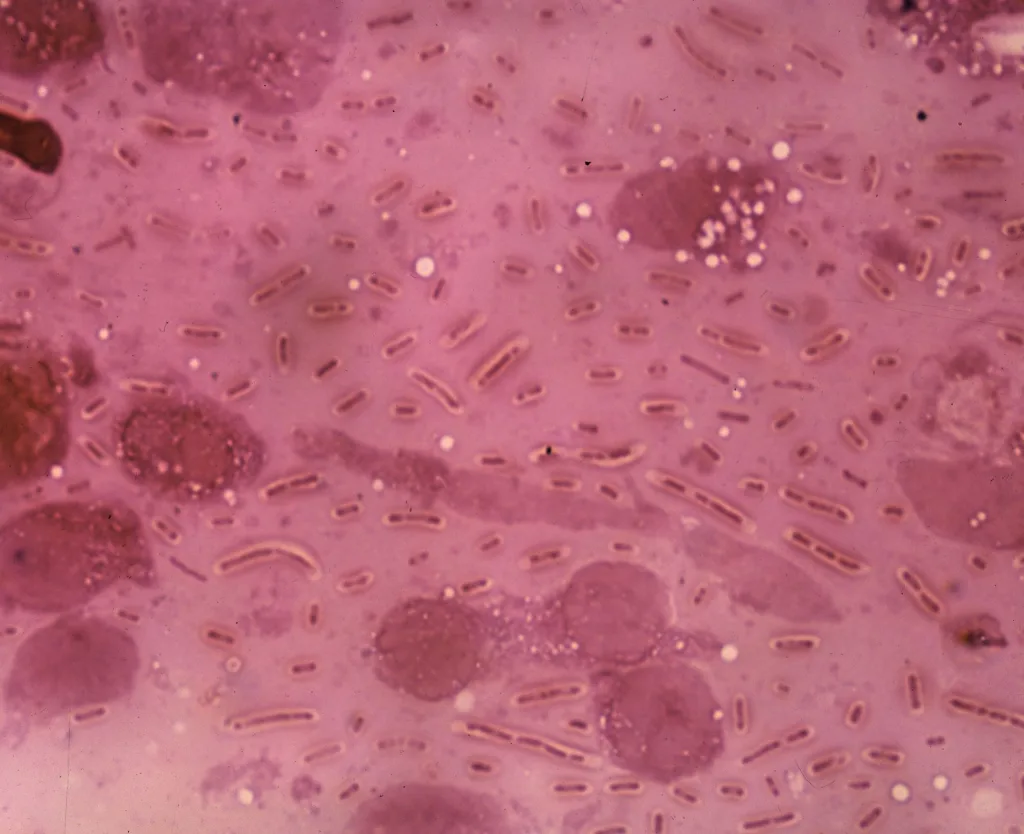
Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia is an alarming and increasingly recognized cause of pulmonary infections, particularly due to the emergence of hypervirulent strains such as Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23. Responsible for severe complications like septic shock, this pathogen poses a significant threat to global health, especially as its prevalence spreads beyond traditional geographical boundaries. Recently, a fatal case of pneumocephalus due to hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany underscores the urgent need for heightened awareness and surveillance of this pathogen. The rapid global spread of Klebsiella highlights a pressing public health concern, emphasizing the potential for local infections to escalate into deadly outcomes. Understanding the mechanisms and impact of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae could be crucial in preventing such fatal infections in vulnerable populations.
The infection caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae can also be referred to as a severe form of lung pneumonia, which is often exacerbated by the emergence of highly virulent strains. In this context, hypervirulent K. pneumoniae has gained attention due to its ability to cause devastating complications like fatal pneumocephalus and septic shock, making it a critical pathogen in clinical settings. As the global impact of this pathogen becomes clearer, it is vital to focus on its epidemiological patterns, particularly the alarming rise of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 strains. This shift highlights the importance of improving diagnostic and treatment strategies to manage and mitigate the risks associated with these potent bacterial infections. Increased awareness and understanding of its transmission dynamics are essential in addressing the challenges presented by this global health threat.
Understanding Klebsiella pneumoniae Pneumonia
Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia is an increasingly concerning respiratory infection, particularly due to the rise of hypervirulent strains like Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23. These strains are characterized by their ability to cause severe illness in previously healthy individuals, often leading to life-threatening complications such as septic shock. The implications of such infections are grave, as traditional treatments may fall short against these hypervirulent variants, necessitating a tailored therapeutic approach to managing the illness.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. Patients typically present with acute respiratory distress, fever, and cough, which can rapidly escalate if not properly treated. The global spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae, particularly from regions in Asia where these strains are prevalent, poses a significant health risk. Clinicians must stay vigilant to the evolving landscape of pathogen prevalence to effectively combat infections caused by this resilient bacterium.
The Threat of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Strains
Hypervirulent Klebsiella strains, especially those classified as type ST23, have become a significant concern in medical research and clinical settings. These strains possess enhanced virulence factors that contribute to their ability to cause severe disease, including fatal outcomes like pneumocephalus, as seen in the reported case in Germany. The rapid rise of such strains within Europe raises alarms about public health readiness and comprehensive surveillance systems necessary to manage outbreaks.
The emergence of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae underscores the need for ongoing research into its genetic makeup and transmission dynamics. Public health authorities must prioritize the tracking of these strains, as their characteristic rapid replication and resistance to conventional antibiotics can lead to increased rates of complicated hospitalizations. Proactively addressing the rise of hypervirulent strains is crucial to mitigating the risks they pose to vulnerable populations.
Fatal Pneumocephalus and Its Clinical Implications
Fatal pneumocephalus is a rare but serious condition often associated with severe infections. In the case discussed, the presence of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae was a contributor to the patient’s tragic outcome, illustrating the complexity of managing such infections. Patients with underlying health conditions or those experiencing septic shock are particularly susceptible to this complication, which can lead to increased intracranial pressure and subsequent neurological damage.
Effective management of fatal pneumocephalus requires rapid diagnosis and intervention. Treatment strategies may include addressing the underlying infection, in this case, targeting the hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, while also focusing on managing symptoms related to elevated intracranial pressure. Understanding the potential for severe complications like pneumocephalus in the context of K. pneumoniae infections is vital for improving patient outcomes and reducing mortality rates associated with these serious conditions.
Septic Shock as a Consequence of Infection
Septic shock represents one of the most dire consequences of infections caused by hypervirulent pathogens like Klebsiella pneumoniae. In the reported case, the patient succumbed to septic shock following the rapid deterioration of their condition, which can occur when bacterial infections trigger a systemic inflammatory response. This response can lead to multi-organ failure and is a critical area of concern for healthcare providers in managing severe infections.
Timely intervention in cases of septic shock is crucial. Early recognition and prompt administration of antibiotics tailored to combat hypervirulent strains, along with supportive therapies, can significantly improve survival rates. The rising incidence of septic shock associated with infections from Klebsiella pneumoniae highlights the need for heightened clinical awareness and effective treatment protocols to manage this severe complication.
Global Spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae
The global spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae, especially its hypervirulent strains, is a growing public health concern. Research indicates that these strains have traveled from endemic areas in Asia to various parts of Europe and beyond. This alarming trend necessitates comprehensive tracking and surveillance efforts to understand the distribution and evolving nature of this pathogen in different regions.
Efforts to control the global incidence of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae must include enhanced infection control protocols in healthcare settings and public awareness campaigns. Listening to healthcare professionals and bridging knowledge gaps about the pathogen’s transmission can foster better preparedness against potential outbreaks. Additionally, ongoing research into the genetic and pathogenic characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae will be vital for developing targeted therapeutic strategies.
Preventive Measures Against Klebsiella Infections
Preventive measures are crucial in managing Klebsiella pneumoniae infections, particularly those caused by hypervirulent strains. Hand hygiene and adherence to infection control practices in healthcare settings can mitigate the spread of this opportunistic pathogen. Increased training and awareness among healthcare personnel regarding the risks associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae can help prevent outbreaks and protect vulnerable patients from severe outcomes.
In addition to standard infection control practices, antimicrobial stewardship principles should be adopted to combat the rising resistance seen with hypervirulent strains. By ensuring that antibiotics are used judiciously, we can reduce selective pressure that often leads to the emergence of resistant strains. Strategies to enhance patient education about the significance of seeking timely medical intervention for respiratory symptoms are also vital in improving public health outcomes.
The Role of Genomic Studies in Understanding Klebsiella
Genomic studies play a pivotal role in understanding the epidemiology and virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. By analyzing the genetic makeup of hypervirulent strains like ST23, researchers can identify potential markers of virulence and resistance. These insights are crucial for developing effective diagnostics and treatment strategies, enabling healthcare providers to tailor their approaches to managing infections caused by these resilient bacteria.
The incorporation of genomic data into public health strategies can enhance surveillance efforts globally. By mapping out how hypervirulent strains spread and evolve, health authorities can implement targeted interventions aimed at controlling outbreaks. Continued investment in genomic research is essential for staying ahead of potential threats posed by emerging infectious diseases like Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Clinical Guidelines for Managing Klebsiella Infections
Developing robust clinical guidelines is essential for effectively managing infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Healthcare providers should be equipped with up-to-date information on recognizing and treating various manifestations of the infection, including pneumonia, septic shock, and pneumocephalus. Support for standardized protocols can enhance patient outcomes and streamline care during critical situations.
Additionally, integrating multidisciplinary approaches in treatment plans can provide comprehensive care for patients infected with hypervirulent strains. Collaboration amongst infectious disease specialists, critical care physicians, and clinical microbiologists can ensure that all aspects of care, from early diagnosis to timely intervention, are addressed efficiently. These efforts are crucial in combating the challenges posed by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae globally.
Community Awareness and Education on Klebsiella
Community awareness and education are vital components of public health initiatives aimed at addressing the rising concerns surrounding Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Informing the public about the risks associated with this pathogen, particularly its hypervirulent strains, can lead to better recognition of symptoms and urgent medical consultations. Providing accessible information through community health programs can empower individuals to protect themselves and their families.
Educational campaigns that focus on hygiene practices, vaccination, and antibiotic use can further enhance community resilience against such infections. Encouraging individuals to seek medical advice for respiratory issues or post-surgical infections can ensure early detection and treatment, ultimately reducing the impact of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae on public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia and why is it concerning?
Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia is a type of lung infection caused by the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae. It is concerning because it can lead to severe health complications such as septic shock and may involve hypervirulent strains, like Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23, which are increasingly recognized for their ability to cause fatal outcomes.
How does hypervirulent Klebsiella contribute to severe pneumonia cases?
Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains, especially those like Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23, produce virulence factors that enhance their ability to cause severe infections, including pneumonia. These strains can lead to complications such as septic shock and fatal pneumocephalus, highlighting the need for rigorous diagnostic and treatment measures.
What are the implications of the global spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae?
The global spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae, particularly hypervirulent strains, poses significant public health threats. It increases the risk of outbreaks and complicated infections worldwide, necessitating improved surveillance and awareness among healthcare providers to manage and contain these infections effectively.
What are the symptoms associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia?
Symptoms of Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia can include high fever, chills, coughing, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and severe malaise. In severe cases, it may progress to septic shock, as seen in cases involving hypervirulent strains like Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23.
What treatments are effective against Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia?
Treatment for Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia typically involves antibiotics such as piperacillin/tazobactam. However, treatment efficacy can be complicated by the presence of antibiotic-resistant strains. Therefore, timely antibiotic susceptibility testing is crucial to ensure appropriate therapy.
Why is surveillance important for hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains?
Surveillance is crucial for hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains, such as ST23, because it helps track their prevalence, understand their epidemiology, and detect potential outbreaks. Enhanced monitoring can lead to early intervention strategies, thereby reducing fatal outcomes from infections.
Can patients without recent travel still contract Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia?
Yes, patients without recent travel can still contract Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia. Local emergence of hypervirulent strains has been documented, indicating that these infections may occur even in endemic regions without prior exposure to high-risk environments.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Fatal case of pneumocephalus due to hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) sequence type 23 in Germany. |
| The patient was a 71-year-old male with septic shock, confirmed by clinical and imaging studies. |
| Intravenous treatment was initiated with piperacillin/tazobactam and clarithromycin, based on imaging findings. |
| Cranial CT revealed extensive pneumocephalus; the patient died three days after admission. |
| Postmortem findings included hypoxic-ischemic damage and leptomeningitis confirmed by histopathological evaluation. |
| This case indicates that hypervirulent ST23 K. pneumoniae may be more prevalent in Europe than previously recognized. |
| Emphasizes the need for systematic surveillance of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae strains. |
| Calls for heightened awareness among clinicians regarding hypervirulent strains in severe infections, even without prior travel history. |
Summary
Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia represents a serious and potentially lethal condition, particularly when caused by hypervirulent strains like ST23. This case in Germany underscores the need for increased awareness and monitoring of such pathogens, highlighting that they may be more common in regions without prior recognition. As hypervirulent K. pneumoniae spreads globally, it poses a substantial health threat, necessitating ongoing research and public health initiatives to mitigate risks and control infections effectively.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.