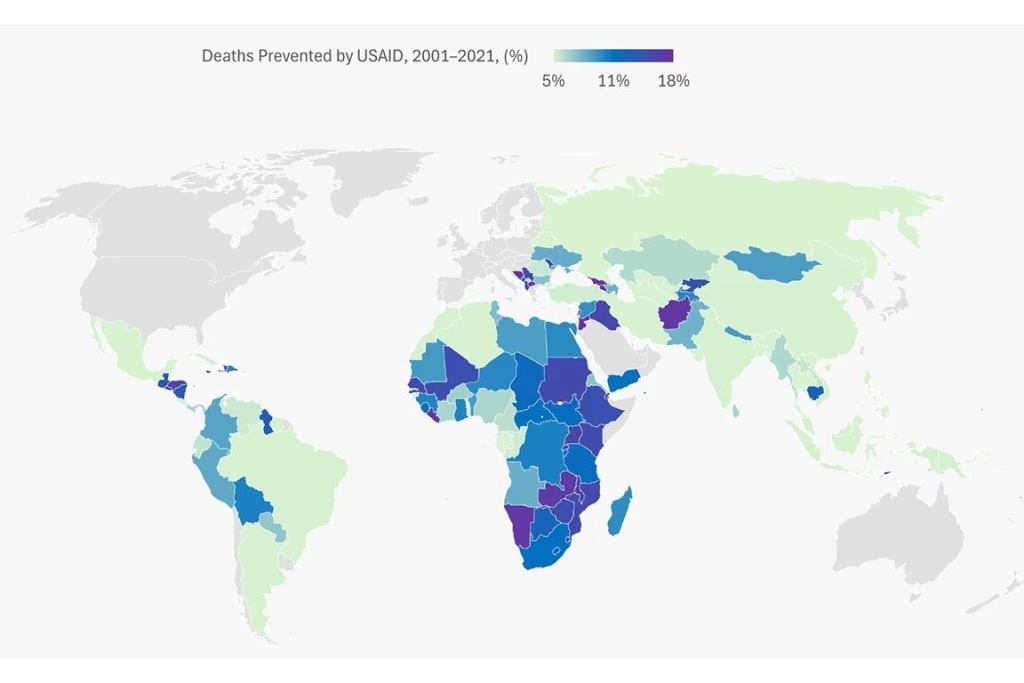
The impact of USAID cuts has been devastating, particularly in the realm of global disease prevention. Following funding cuts initiated by the Trump administration, over 762,000 lives have been lost, with half of those casualties being children. These reductions not only hinder essential health initiatives but also affect vaccine availability, as evidenced by the recent withdrawal of the chikungunya vaccine from the U.S. market. Furthermore, ongoing updates regarding the Ebola vaccine indicate a stalled progression in crucial immunization efforts, leaving vulnerable populations at risk. As the long-term effects of COVID-19 continue to unfold, the urgency for robust funding becomes clearer, emphasizing the critical need for sustained support in combating worldwide health challenges.
The repercussions of reduced financial support from the USAID have been alarmingly significant for health outcomes in various countries. The withdrawal of critical initiatives, such as the development of vaccines against viruses like chikungunya and Ebola, reflects a troubling trend. Health experts now face enhanced challenges in addressing global pandemics and health crises, which have seen a resurgence amid these cuts. With the ongoing ramifications from previous health emergencies, such as the long-lasting effects of COVID-19, the necessity for comprehensive funding and support is more critical than ever. As a result, many advocate for renewed investment in disease prevention techniques that can safeguard against future outbreaks.
The Consequences of USAID Funding Cuts on Global Health
The impact of USAID funding cuts on global health has been nothing short of catastrophic. According to recent estimates, the reduction in financial support has directly correlated with a staggering death toll exceeding 762,000 individuals over just one year, with vulnerable populations, including over 500,000 children, bearing the brunt of this crisis. This reality highlights a glaring neglect of global disease prevention initiatives, particularly in regions where healthcare systems are already strained. Organizations that relied on USAID funding for essential vaccination programs and epidemic response have been forced to scale back significantly, aggravating health disparities across various communities.
Moreover, the implications stretch beyond immediate health outcomes; they profoundly affect long-term disease prevention strategies. With fewer resources for vaccination campaigns and health education, diseases that were previously under control, such as measles and tuberculosis, could see a resurgence. The failure to maintain these programs not only places the health of populations at risk but also demands a reevaluation of international health partnerships. Countries that once benefited from USAID’s support must now navigate the complexities of funding shortages, impacting their preparedness against potential outbreaks.
Chikungunya Vaccine Withdrawal: A Setback for Global Disease Prevention
The recent announcement by Valneva regarding the withdrawal of its chikungunya vaccine from the US market serves as a notable setback in the fight against vector-borne diseases. Chikungunya, which had already posed a significant public health challenge, particularly in tropical regions, is exacerbated by such developments. The ultra-low storage requirements for the vaccine also deter wide-scale distribution, making it increasingly difficult to protect populations at risk. This withdrawal not only reflects the complex challenges vaccine developers face but also underscores the importance of consistent funding for research and deployment of vaccines.
The implications of withdrawing the chikungunya vaccine extend beyond immediate health concerns; they highlight vulnerabilities in the global health infrastructure. As we continue to combat emerging diseases, the lack of reliable vaccination options compounds the issues of global disease prevention efforts. Funding cuts from USAID and other initiatives threaten to create gaps in immunization coverage, leaving populations defenseless against infections that could have been prevented through effective vaccination strategies. This situation encourages public health advocates to push for renewed commitment towards supporting vaccine development and distribution.
Ebola Vaccine Updates and the Future of Disease Prevention
As the world grapples with the repercussions of USAID funding cuts, timely updates on the Ebola vaccine provide a glimmer of hope. Several pharmaceutical companies, backed by international health organizations, are in the race to develop an updated Ebola vaccine that could help curtail outbreaks effectively. The improvements in vaccine research and public health response systems are crucial, especially given the potential resurgence of diseases that were previously managed. These advancements serve as a reminder that while funding challenges persist, innovation in medical science continues to push forward.
However, the need for robust support mechanisms remains evident. The global community must prioritize disease prevention initiatives, including funding for updated vaccines to combat diseases like Ebola. Without sufficient financial resources, the progress made through research may stagnate, leaving populations susceptible to future outbreaks. The recent trends through partnerships and multi-sector collaborations illustrate the importance of collective efforts to ensure that advancements in vaccine technology translate into real-world health solutions.
COVID-19 Long-Term Effects on Children: A Growing Concern
Research from the CDC indicates alarming long-term effects of COVID-19 on school-aged children, revealing that those suffering from long COVID are significantly more likely to experience chronic absenteeism and learning problems. The study, highlighting the cognitive impacts of the virus, stresses the need for targeted intervention strategies that address the ongoing challenges faced by infected children. Such issues stem not just from the virus itself but also from the broader ramifications of health infrastructure strain exacerbated by funding cuts, including mental health resources and special education support.
As educators and health officials navigate this new landscape, it becomes crucial to develop policies that prioritize the wellbeing of affected students. Recognizing the long-term effects of COVID-19 means that educational institutions must adapt to better support young learners, ensuring that they receive the necessary accommodations. Ultimately, enhancing access to mental health resources and combining them with academic support can improve outcomes for children facing these unprecedented challenges, further highlighting the importance of stable and robust funding in public health education.
Global Health Implications of Resurgent Diseases Post-USAID Cuts
With the recent surge in diseases like measles reported in Utah and the potential for increases in outbreaks, the implications of USAID funding cuts on global health cannot be overstated. The CDC’s deputy director has reaffirmed that changes in the way diseases are managed, including the loss of measles elimination status, pose serious threats not only in terms of public health but also in the burden of disease on healthcare systems. As transmission chains within the US become problematic, the global ramifications of neglected vaccination and disease prevention efforts become pronounced.
This alarming trend indicates a pressing need to reinvest in public health strategies that encompass vaccination campaigns, education, and community health initiatives. A focused approach on global health and disease prevention can help mitigate these risks, and a sustainable funding route is critical. The international community must come together to address the gap left by the withdrawal of vital support systems, promoting a collaborative strategy aimed at enhancing health security worldwide.
Combating Antimicrobial Resistance through Improved Practices
The study highlighting gender dynamics in antibiotic use emphasizes the complicated intersection of social factors in combating antimicrobial resistance. An equitable healthcare approach is necessary to address the disparities that contribute to antibiotic misuse and over-prescription. This is pivotal as antibiotic resistance poses a significant threat to global health, necessitating comprehensive strategies that encompass education, public awareness, and rigorous monitoring of antibiotic prescriptions.
Tailoring intervention strategies that respond to the unique challenges posed by gender disparities can lead to better outcomes in antibiotic stewardship. The global community needs to emphasize the importance of responsible antibiotic consumption and ensure that healthcare providers and patients are equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions. With ongoing threats from resistant bacteria, it is imperative to adopt a multifaceted approach that integrates educational initiatives focused on the proper use of antibiotics within the community.
The Importance of Mental Health Resources Amidst Disease Resurgence
As healthcare systems strain under the pressure of rising illnesses, including those stemming from long COVID and antibiotic resistance, mental health resources become increasingly vital. Addressing mental health is often seen as secondary to physical health concerns; however, the compounding effects of chronic illness and public health crises can lead to significant mental wellbeing issues in populations. Efforts to bolster healthcare infrastructure must include adequate support systems for mental health services, particularly for those impacted by long-term health conditions.
The recent focus on mental health highlights how closely intertwined physical and mental health are when dealing with chronic diseases. As communities work to build resilience against emerging threats, a comprehensive approach that includes mental health support can lead to improved health outcomes. Furthermore, integrating mental health resources into overall public health strategies is crucial, demonstrating a commitment to addressing all facets of health as communities work towards recovery in the wake of significant health crises.
Awareness and Preparedness: Facing Future Health Threats
In the wake of reduced support for global health infrastructures, awareness and preparedness to handle emerging health threats are paramount. The CDC’s recent alerts regarding diseases like the New World screwworm remind us that potential dangers can arise unexpectedly and require quick, coordinated responses. Enhancing surveillance systems and building health capacity across borders are vital strategies to mitigate the risks posed by new pathogens and vector-borne diseases.
Preparedness involves not only immediate responses to outbreaks but also long-term strategies for vaccine development, health resource allocation, and public engagement. Investing in these areas is crucial for maintaining robust defense mechanisms against future health threats. A focused commitment to public health infrastructure, supported by both domestic and international funding avenues, will be essential in creating a resilient health system capable of preventing and responding to potential crises.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the consequences of USAID funding cuts on global disease prevention efforts?
USAID funding cuts have severely impacted global disease prevention efforts, leading to an estimated 762,000 deaths, including more than 500,000 children. These cuts weaken essential health programs that combat diseases such as HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis, ultimately increasing vulnerability to outbreaks and preventing timely interventions.
How does the USAID funding cuts affect vaccine development and availability?
The withdrawal of vaccines like the chikungunya vaccine by companies such as Valneva demonstrates the adverse effects of USAID funding cuts on vaccine development. Reduced financial support can hinder research and development processes, impacting the timely availability of critical vaccines for global health.
What updates are there regarding the Ebola vaccine in the context of USAID funding cuts?
USAID funding cuts have curtailed resources necessary for the development and distribution of updated Ebola vaccines. This limitation poses significant challenges in controlling outbreaks and protecting communities in affected regions, potentially leading to devastating health crises in the absence of effective immunization strategies.
What are the long-term effects of COVID-19 on public health, particularly related to USAID funding cuts?
With USAID funding cuts, long-term public health consequences of COVID-19 may worsen, as the cuts limit resources for addressing long COVID effects. This can exacerbate conditions such as chronic absenteeism in schools due to health-related issues, subsequently impacting education and overall community resilience.
What is the link between USAID funding cuts and rising public health threats, including measles?
The cuts in USAID funding contribute to a decline in vaccination rates, leading to the resurgence of preventable diseases like measles. The loss of measles elimination status in regions such as Utah highlights how decreased investment in immunization programs makes communities more susceptible to outbreaks.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Death Toll from USAID Cuts | Over 762,000 deaths attributed to USAID funding cuts, including 500,000 children. |
| Withdrawal of Chikungunya Vaccine | Valneva withdraws its chikungunya vaccine from the US market due to storage requirements. |
| Impact on Global Health Programs | The funding cuts have severely impacted global disease prevention programs, particularly those addressing Chikungunya and Ebola. |
Summary
The impact of USAID cuts has been devastating, resulting in more than 762,000 deaths linked to funding reductions for crucial health programs. These cuts have not only affected immediate healthcare responses but have also led to the withdrawal of vital vaccines, such as the chikungunya vaccine, from the market, further jeopardizing global health initiatives. As we evaluate the ramifications of these cuts, it is essential to understand the long-term consequences on both public health and national safety measures.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.