Human metapneumovirus, or HMPV, is gaining attention as reports of its increase emerge from various parts of the world, notably China and India. This respiratory virus presents a range of symptoms including cough, fever, and nasal congestion, posing significant health concerns about respiratory infections, especially for vulnerable populations such as young children and the elderly. While the rise in HMPV cases has sparked discussions about potential outbreaks, experts assure that it is not a novel virus, having been identified over two decades ago. With the ongoing monitoring of HMPV transmission and its relationship to other respiratory viruses, such as influenza, understanding its patterns and impact is crucial in controlling its spread. As public awareness grows, it’s essential to recognize the measures that can mitigate health risks associated with this virus and its symptoms.
Also known as HMPV, the human metapneumovirus is a viral pathogen linked to acute respiratory illnesses that can affect individuals across different age groups. Characteristically manifesting symptoms akin to those of other respiratory infections, HMPV poses particular risk factors for specific demographics like infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. As global health agencies continue to track the transmission and potential outbreaks of this virus, there is an urgent need for public education regarding its health implications and preventive measures. The familiar patterns observed in common respiratory infections like colds and flu are relevant here, as HMPV circulates primarily in colder months. Understanding the overall landscape of respiratory viruses and their interrelationships will be vital in managing public health effectively.
Understanding Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
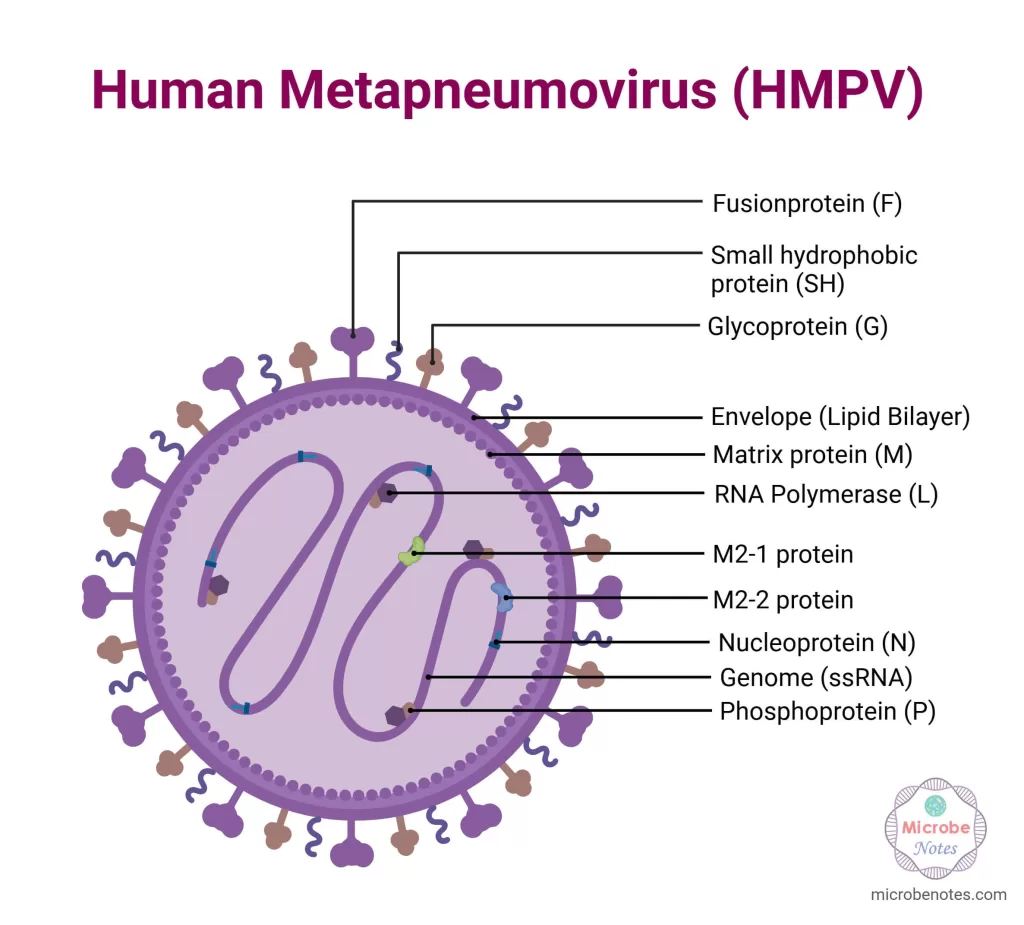
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is an important viral pathogen that can lead to respiratory tract infections in individuals across all age groups. First discovered in 2001, this virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, which also includes the commonly known respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Since its identification, HMPV has been recognized as a leading cause of upper and lower respiratory illnesses, especially in vulnerable populations such as young children, elderly adults, and those with compromised immune systems. Symptoms of HMPV typically mirror those of other respiratory infections, making accurate diagnosis challenging.
Despite its prevalence, there remains a significant gap in public awareness regarding HMPV in the U.S., contributing to rising concerns during recent outbreaks reported in countries like China and India. Although health officials have jumped to announce infection cases, expert opinions indicate that these instances do not signify a new, imminent threat akin to what was experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic. The historical stability of HMPV means that a certain level of immunity exists within the population, further alleviating panic that may stem from information surrounding rising cases.
HMPV Symptoms: Recognizing the Illness
The symptoms of human metapneumovirus infection are critical to understand for effective management and prevention. Common HMPV symptoms include cough, fever, nasal congestion, and in more severe cases, shortness of breath. These manifestations can escalate to more serious conditions like bronchitis or pneumonia, particularly in high-risk groups. This similarity in symptoms with other respiratory viruses, including the flu and RSV, highlights the importance of medical consultation for accurate diagnosis and treatment, especially during peak respiratory infection seasons.
Furthermore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasizes that awareness of HMPV symptoms is vital for distinguishing it from influenza and COVID-19. As respiratory illnesses are common in colder months, understanding the typical symptomatology associated with HMPV can aid parents and caregivers in making informed decisions regarding seeking medical attention for affected children and vulnerable adults. Monitoring symptoms and the progression of respiratory illness is essential, especially since hospitals may see a surge in patients during flu season.
Transmission and Prevention of HMPV
HMPV transmission primarily occurs through direct contact with infected individuals or surfaces contaminated with the virus. In light of the absence of a vaccine for human metapneumovirus, the prevention strategies mirror those employed to guard against other respiratory illnesses like flu and COVID-19. Basic hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water and maintaining distance from individuals exhibiting illness signs, are the cornerstone of prevention efforts.
Additionally, individuals who are symptomatic are encouraged to wear masks and practice good cough etiquette to minimize potential exposure to others, especially in public spaces or crowded environments. Experts recommend staying vigilant during peak respiratory infection seasons to prevent HMPV outbreaks from spreading further, particularly given that it has been linked to increased hospitalizations among children during such times. Emphasizing community awareness and cooperation could help mitigate health concerns associated with HMPV.
HMPV Outbreaks and Current Trends
Recent outbreaks of human metapneumovirus highlight ongoing public health concerns, especially with cases being reported in various countries. The current surge in cases, as flagged by health authorities in China and India, prompts discussions around monitoring and controlling HMPV amidst seasonal epidemics. Despite lower incidence levels when compared to seasonal flu or COVID-19 infections, the visibility of HMPV in health news underscores the need for continued surveillance and responsiveness by health officials.
The appearance of HMPV outbreaks generally correlates with increased awareness and consequent testing for respiratory viruses during winter months. While the CDC reports HMPV responsible for less than 2% of current respiratory infections, maintaining readiness and public education regarding respiratory illness symptoms is still vital. As respiratory infections can overlap significantly, a clear understanding of HMPV, combined with effective health communication, is key in preventing widespread outbreaks.
Comparing HMPV to COVID-19 and Influenza
When discussing human metapneumovirus in the context of public health, it is essential to compare its impact with other respiratory infections like COVID-19 and influenza. Experts suggest that while current cases of HMPV should not be ignored, they do not reach alarming levels compared to the widespread implications of COVID-19. CDC data reveals that HMPV accounts for a very minimal percentage of positive tests, contrasting sharply with the nearly 19% prevalence of influenza and around 7% for COVID-19 in surgeries and emergency departments across the U.S.
The public response to respiratory infections also varies greatly due to each virus’s historical context and perceived severity. Unlike COVID-19, which emerged as a novel virus with high levels of morbidity and mortality, HMPV is established in the viral landscape, with lower associated risks. However, this should not detract from the ongoing importance of proactive public health measures to control infections and safeguard those who are more vulnerable to respiratory illnesses.
The Importance of Public Awareness on HMPV
Increasing public awareness about human metapneumovirus is cornerstone to improving community health outcomes. Lack of knowledge about HMPV can lead to unnecessary panic and confusion, particularly during outbreaks. Educational initiatives focusing on HMPV symptoms, transmission methods, and prevention tips can equip people with the tools to recognize illness early and act sensibly to mitigate spread. Experts highlight that heightened awareness can also ease worries, especially given that many people may unknowingly have existing immunity against HMPV.
Moreover, fostering clarity about HMPV can promote proactive health measures within communities, reducing the risk of severe outbreaks during known respiratory infection seasons. This means implementing good hygiene practices and encouraging regular check-ups during periods of heightened viral activity. Creating a culture of knowledge and preparedness within communities is critical to effectively managing respiratory infections and ensuring that high-risk populations receive the care and precautions they require.
Impact of HMPV on Vulnerable Populations
Vulnerable populations, such as young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals, are at increased risk for complications arising from human metapneumovirus infections. Studies suggest that HMPV can lead to severe respiratory illness in these groups due to their already compromised health status. Understanding this heightened risk emphasizes the need for attentive care and vigilance among caregivers and healthcare providers to ensure timely diagnosis and intervention when necessary.
Moreover, given that HMPV can induce illnesses ranging from mild symptoms to severe pneumonia, healthcare systems must remain equipped to respond appropriately. This includes ensuring adequate surveillance and reporting mechanisms are in place during peak seasons, allowing healthcare providers to allocate resources efficiently. Recognizing the implications for vulnerable individuals is paramount in forming a comprehensive approach to managing the health concerns associated with HMPV.
Future Research Directions for HMPV
Ongoing research into human metapneumovirus plays a crucial role in understanding its behavior, transmission patterns, and potential impacts on public health. Despite being identified over two decades ago, there remains a necessity for enhanced studies focusing on vaccine development and improved therapeutic interventions. With a growing number of reported cases during recent outbreaks, further research could provide insights into effective control measures and strategies to mitigate the spread, particularly in crowded or vulnerable settings.
Moreover, as HMPV shares features with other significant respiratory viruses, research into cross-reactive immune responses could lay groundwork for developing broad-spectrum vaccines. Exploring these avenues will be essential for optimizing strategies for respiratory infection management, enhancing overall preparedness for future outbreaks. Investing in research not only contributes toward understanding HMPV more thoroughly but also reinforces the global health infrastructure necessary to combat respiratory infections effectively.
Addressing Health Concerns Related to HMPV
As HMPV continues to circulate globally, addressing health concerns surrounding the virus should take center stage. Health professionals emphasize that while the recent outbreak has drawn attention, it is essential not to conflate HMPV with more severe viral infections that are currently dominating health news, such as COVID-19. By effectively communicating the actual risk posed by HMPV relative to more common respiratory infections, public anxiety may be reduced, fostering a more rational approach to health threats.
Targeted communication strategies regarding HMPV can empower communities with knowledge about symptoms and preventive measures, helping them navigate respiratory infection seasons more effectively. A well-informed public is better positioned to engage in preventive practices, seek timely medical care, and adhere to health recommendations, ultimately contributing to a more resilient society in facing the challenges of viral outbreaks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of human metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) symptoms typically include cough, fever, nasal congestion, and shortness of breath. In more severe cases, symptoms may progress to bronchitis or pneumonia, resembling other respiratory infections.
How does human metapneumovirus (HMPV) spread?
HMPV transmission occurs through direct contact with infected individuals or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus. It’s important to practice hygiene such as hand washing to reduce the spread of HMPV.
Is there a vaccine for human metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Currently, there is no vaccine available for human metapneumovirus (HMPV). This makes prevention through hygiene practices, similar to those used for flu and COVID-19, critical in controlling its spread.
Is HMPV a major health concern in the U.S.?
While there have been recent HMPV outbreaks in countries like China and India, experts do not consider it a major health concern in the U.S. The virus typically accounts for less than 2% of positive respiratory virus tests.
How serious is an HMPV infection compared to COVID-19?
HMPV infections are generally less severe than COVID-19. While HMPV can cause respiratory illnesses, it does not reach the infection rates or severity associated with COVID-19, flu, or RSV.
What precautions can be taken to avoid human metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
To prevent HMPV illness, practice good hand hygiene, avoid close contact with sick individuals, and use protective measures like wearing masks when in crowded places, especially during respiratory virus season.
What should I do if I think I have an HMPV infection?
If you suspect an HMPV infection, it’s advisable to rest, stay hydrated, and consult a healthcare provider for advice on managing symptoms and determining if further evaluation is necessary.
How long does an HMPV infection usually last?
The duration of an HMPV infection varies by individual but is generally comparable to other respiratory infections, lasting from a few days to a couple of weeks depending on severity.
Does human metapneumovirus (HMPV) affect children differently?
Yes, human metapneumovirus (HMPV) can affect children, with an estimated 10% to 12% of respiratory illnesses in children attributed to HMPV, leading to mild cases or, in some cases, more serious lower respiratory tract infections.
When is human metapneumovirus (HMPV) most prevalent?
HMPV most commonly circulates during the winter and spring months in the U.S., often alongside other respiratory viruses like RSV and the flu.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Virus Name | Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) |
| Current Situation | On the rise in China and confirmed cases in India with limited public knowledge in the U.S. |
| Symptoms | Cough, fever, nasal congestion, shortness of breath; may progress to bronchitis or pneumonia. |
| Risk Groups | Young children, elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems at higher risk for severe illness. |
| Not a New Virus? | First identified in 2001; may have circulated for decades before its discovery. |
| Comparison to COVID-19 | Current outbreak is not a major concern; HMPV accounts for less than 2% of respiratory virus cases compared to higher percentages for influenza and COVID. |
| Transmission | Spread through direct contact or contaminated surfaces; no vaccine available. |
| Prevention Measures | Wash hands, avoid close contact with sick individuals, and practice good respiratory hygiene. |
Summary
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a viral infection that is increasingly being reported in regions such as China and India. Although there are concerns over its spread, especially given the limited awareness in the United States, experts emphasize that HMPV is not a newly emergent virus and does not pose a significant risk comparable to COVID-19. With a primarily mild illness course for most individuals, preventive measures such as good hygiene practices can effectively reduce transmission. Overall, while HMPV merits attention, the public should remain informed without undue alarm.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.