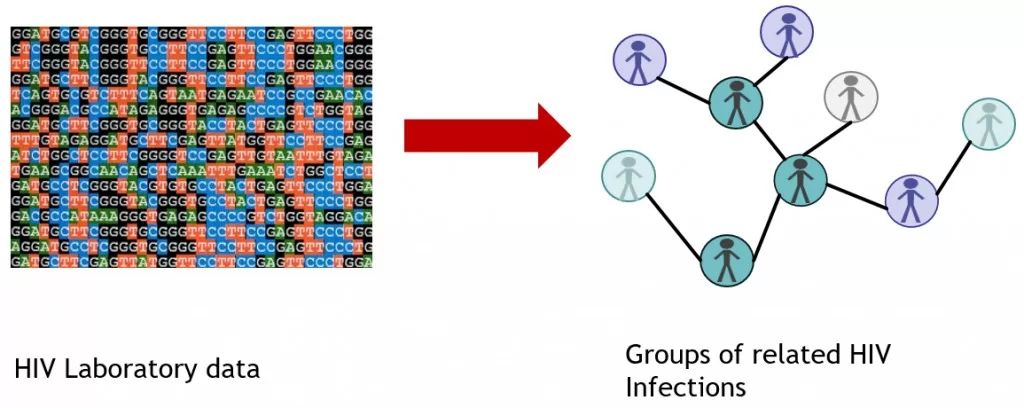
HIV molecular cluster detection is a vital strategy in managing and preventing the spread of HIV across the United States. By identifying rapid HIV transmission networks, this approach helps public health officials implement effective CDC HIV prevention strategies tailored to the unique needs of specific communities. Since its inception in 2016, the importance of molecular cluster detection has grown, allowing for timely responses to emerging HIV outbreaks. The innovative Secure HIV-TRACE application has enabled local and state health departments to efficiently analyze and report data on identified clusters, improving outreach and care services. Ultimately, enhancing HIV molecular cluster detection not only aids in curbing transmission but also strengthens the entire public health infrastructure.
Molecular detection of HIV clusters refers to the process of identifying groups of individuals where the virus is spreading rapidly within their sexual or drug-using networks. This proactive surveillance mechanism plays a crucial role in understanding and controlling HIV transmission dynamics. Through targeted responses to these clusters, public health agencies can enhance their responses to potential outbreaks and ensure that resources are directed where they are most needed. By employing cutting-edge technology and data analysis methods, health departments can effectively monitor and mitigate the spread of HIV, ultimately improving overall health outcomes in the population. This strategy marks a significant advancement in the ongoing battle against HIV, allowing for a more comprehensive and effective public health response.
Understanding HIV Molecular Cluster Detection
HIV molecular cluster detection is a critical public health strategy designed to identify and respond to concentrated outbreaks of HIV transmission. By analyzing genetic sequences from individuals diagnosed with HIV, health departments can detect clusters of rapid transmission, which often reveal hidden networks of infection. This approach provides invaluable insights into how HIV spreads within communities and helps in pinpointing specific populations that may be under-served by current prevention efforts. Through the identification of these clusters, public health officials can tailor interventions and allocate resources more efficiently, ultimately aiming to curb the spread of HIV.
The importance of HIV molecular cluster detection cannot be overstated, especially in light of the emergence of new transmission networks. By recognizing these clusters early, health departments can implement effective CDC HIV prevention strategies that target high-risk groups, such as men who have sex with men, substance users, and other marginalized populations. Furthermore, molecular cluster detection reinforces the CDC’s commitment to harnessing data-driven approaches in public health, ensuring that interventions are grounded in the latest scientific evidence and respond dynamically to evolving transmission patterns.
The Role of CDC in HIV Outbreak Response
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays an essential role in the nationwide outbreak response to HIV through the implementation of molecular cluster detection programs. Since its inception in 2016, the CDC has focused on identifying clusters of rapid HIV transmission in a proactive manner rather than relying solely on sporadic detection methods. This shift towards a systematic approach allows for a more responsive and comprehensive understanding of HIV transmission networks across the United States. By utilizing advanced sequence data, the CDC is able to identify outbreaks quicker, which is paramount in crafting timely interventions to prevent further spread.
Furthermore, the CDC’s focus on molecular cluster detection enhances collaboration with state and local health departments, ensuring that real-time data sharing facilitates rapid response efforts. The integration of applications like Secure HIV-TRACE enhances the capability of health departments to classify ongoing outbreaks, analyze trends, and respond effectively based on the characteristics of the identified clusters. This systemic engagement allows public health officials to streamline outreach efforts, improve service delivery, and ultimately achieve better health outcomes across affected populations.
Enhancing Public Health through HIV Transmission Networks Analysis
Analyzing HIV transmission networks is pivotal for enhancing public health responses to the epidemic. By understanding the specific dynamics of how HIV spreads in communities, public health officials can better strategize on preventive measures and educational campaigns. Networks of transmission often reveal critical gaps in prevention services, allowing for targeted outreach to groups that may not be adequately reached by standard care practices. The ability to map these networks through molecular cluster detection enables a more nuanced approach to HIV prevention, ensuring that interventions are based on sound epidemiological evidence.
Moreover, understanding these transmission networks helps highlight areas where the CDC HIV prevention strategies can be refined. Whenever a new outbreak is identified, ongoing analysis of the affected network provides insights into behaviors and conditions contributing to increased HIV transmission. This feedback loop not only informs immediate responses but also aids in shaping long-term strategies that reduce vulnerabilities among populations at risk, creating a more robust public health framework for controlling and ultimately preventing HIV.
Impact of Secure HIV-TRACE on Molecular Cluster Detection
Secure HIV-TRACE is a transformative application that significantly enhances the efficacy of HIV molecular cluster detection initiatives across the nation. By allowing health departments to access and analyze comprehensive molecular data, the application supports timely intervention strategies in response to identified clusters. This capability is crucial for addressing areas experiencing rapid HIV transmission, facilitating targeted outreach and prevention efforts tailored to specific populations. The integration of Secure HIV-TRACE into routine cluster detection practices enables health departments to stay ahead of potential outbreaks.
The impact of Secure HIV-TRACE extends beyond immediate detection; it fosters an environment of collaboration and knowledge sharing among health departments. With a centralized platform for reporting and analyzing data, state and local health agencies can learn from each other’s experiences and best practices. This collaborative approach improves the operational efficiency of HIV outbreak response efforts, ensuring that resources are effectively utilized. The continued development of such technologies is essential in the fight against HIV and the goal of reducing new infections across diverse populations.
Data-Driven Approaches in HIV Surveillance
Adopting data-driven approaches in HIV surveillance marks a significant step forward in the public health response to the epidemic. By leveraging molecular sequence data and demographic statistics, health departments can create robust models to track the spread of HIV within communities. This epidemiological insight equips officials with the tools necessary to identify at-risk groups, assess the effectiveness of current prevention strategies, and determine where resources should be deployed. The result is a proactive healthcare system that can respond to disease outbreaks before they become unmanageable.
Moreover, these data-driven practices support the implementation of the CDC’s HIV prevention strategies by painting a clearer picture of how and where transmission occurs. Through regular analysis and reporting of molecular clusters, public health agencies can identify emerging trends and make real-time adjustments to their initiatives. This agility is essential in adapting to the evolving landscape of HIV epidemiology and ensuring that prevention efforts are not only effective but also equitable, addressing the needs of the most vulnerable populations.
Building Collaborative Networks for Effective HIV Prevention
The importance of building collaborative networks in HIV prevention cannot be overemphasized. Engaging stakeholders across various sectors—including healthcare providers, community organizations, and public health officials—creates a holistic approach to addressing the epidemic. These networks facilitate the sharing of resources and expertise, ensuring that services are aligned with the needs of the community. By working together, stakeholders can develop seamless pathways for individuals to access care, testing, and education about HIV transmission and prevention.
Furthermore, collaboration enhances the effectiveness of molecular cluster detection efforts. When health departments are integrated within a wider network of partners, it allows for real-time data sharing and a coordinated response to outbreaks. This collaboration enables stakeholders to take immediate actions based on collective insights, such as organizing targeted outreach programs in areas identified as high-risk. Ultimately, fostering collaborations not only strengthens the public health response but also empowers communities to take an active role in controlling the spread of HIV.
Addressing Gaps in HIV Prevention Services
One of the core objectives of molecular cluster detection is identifying and addressing gaps in HIV prevention services. Many individuals at risk for HIV may not have access to appropriate healthcare services, education, or preventive measures, leading to increased rates of transmission. By pinpointing these gaps through clustering analysis, health departments can tailor their interventions to meet the specific needs of underserved communities. These tailored approaches may include increasing testing availability and providing educational resources to high-risk populations.
Moreover, understanding the socio-economic factors that contribute to these gaps is critical in designing effective public health interventions. Social determinants of health, such as access to healthcare, stigma, and levels of education, play significant roles in an individual’s risk for HIV. By employing a comprehensive analysis of these elements in conjunction with molecular data, public health initiatives can create more impactful solutions aimed at reducing transmission and improving overall health outcomes for vulnerable populations.
Future Directions in HIV Molecular Cluster Detection
As we advance into the future, the evolution of HIV molecular cluster detection will continue to play a pivotal role in the national response to the epidemic. Ongoing advancements in genetic sequencing technologies promise to enhance the precision and speed of cluster identification. With the landscape of HIV transmission continuously changing, health departments must adapt their detection strategies to keep pace with emerging transmission dynamics and public health challenges.
Additionally, the prospect of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into molecular cluster detection presents exciting opportunities for predictive modeling. By harnessing these technologies, public health officials can improve their capacity to forecast outbreaks and allocate resources even more effectively. These innovations, combined with a commitment to addressing the social determinants of health, will ensure a comprehensive and effective response to HIV transmission in communities across the United States.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is HIV molecular cluster detection and why is it important?
HIV molecular cluster detection is a public health strategy that identifies rapid HIV transmission networks among individuals. By analyzing genetic data from HIV cases, health departments can detect clusters where transmission is occurring frequently. This method is crucial for targeting prevention efforts, informing HIV outbreak response, and ensuring effective distribution of care and resources to impacted populations.
How does CDC utilize HIV molecular cluster detection in its prevention strategies?
The CDC employs HIV molecular cluster detection as a vital component of its HIV prevention strategies. By systematically analyzing national surveillance data, the CDC identifies clusters of rapid HIV transmission, enabling targeted interventions. This proactive approach helps health departments to address specific networks that may require urgent prevention services, thereby reducing the spread of HIV.
What role does the Secure HIV-TRACE application play in molecular cluster detection?
Secure HIV-TRACE is an essential tool developed by the CDC to support state and local health departments in the molecular cluster detection process. This application facilitates real-time analysis and reporting of HIV sequences, enhancing the ability to monitor and respond to emerging transmission clusters effectively. Through Secure HIV-TRACE, health departments can collaborate and share data, improving outbreak response strategies.
What are the recent findings concerning HIV molecular cluster detection since its implementation?
Since its implementation in 2016, the CDC has identified 404 molecular clusters of rapid HIV transmission, with a significant number involving multiple jurisdictions. This highlights the expansive nature of HIV transmission networks. Additionally, health departments reported 298 clusters during 2020-2023, demonstrating the effectiveness of molecular cluster detection in guiding public health responses and improving service delivery.
How does identifying HIV transmission networks contribute to public health interventions?
Identifying HIV transmission networks through molecular cluster detection allows public health officials to pinpoint areas with elevated transmission rates. This insight enables targeted interventions, such as increased testing, treatment, and prevention services, addressing specific populations or locations most at risk. Ultimately, effective public health interventions informed by these findings can minimize the spread of HIV within communities.
Why is it important to report clusters of rapid HIV transmission to the CDC?
Reporting clusters of rapid HIV transmission to the CDC is critical for understanding the epidemic’s dynamics. This data allows for a comprehensive national overview of HIV transmission patterns, promoting coordinated responses among health departments. Accurate and timely reporting ensures that resources and strategies are optimized to address the most pressing HIV outbreaks across the country.
What improvements have been observed in HIV service delivery due to molecular cluster detection?
The implementation of molecular cluster detection has led to significant improvements in HIV service delivery. By effectively identifying and responding to transmission networks, health departments can allocate resources more strategically, enhance outreach efforts, and improve access to care and prevention services for populations affected by rapid HIV transmission.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Initiation of Detection | In 2016, CDC began molecular cluster detection to respond to rapid HIV transmission. |
| Expansion and Reporting | By 2020, use of cluster report forms was established for routine reporting of detected clusters. |
| Clusters Identified | CDC identified 404 molecular clusters of rapid HIV transmission from 2018 to 2023. |
| Jurisdictional Involvement | 80% of clusters involved multiple jurisdictions, emphasizing the nationwide impact. |
| Data Reporting and Analysis | Health departments reported demographic, clinical, and behavioral data to CDC for analysis. |
| Secure HIV-TRACE Application | This application supports the routine detection and monitoring of HIV clusters. |
| Importance of Cluster Detection | Improves public health interventions and identifies gaps in prevention and care services. |
Summary
HIV molecular cluster detection is a pivotal strategy in combating the epidemic by identifying rapid transmission networks. Since its initiation by the CDC in 2016, significant progress has been made in detecting and responding to HIV clusters, facilitating essential public health interventions. The collaboration between the CDC and state and local health departments has established a robust framework for monitoring HIV transmission patterns, ultimately enhancing care and preventive measures in high-risk populations.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.