Histoplasmosis in family members who visited a bat-colonized cave is more common than one might expect, especially when considering the risks associated with such environments. A recent outbreak tied to the Venado Caves in Costa Rica has highlighted this fungal infection’s potential dangers. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has documented cases of histoplasmosis symptoms ranging from mild respiratory issues to severe conditions, especially among infants and immunocompromised individuals. This alarming event follows a previous histoplasmosis outbreak in the same area, emphasizing the need for awareness when engaging in activities like exploring bat caves. By understanding how quickly histoplasmosis can be contracted, families can better protect themselves during their adventures.
The issue of family members contracting histoplasmosis, often referred to as the ‘bat cave illness,’ has gained attention in recent public health discussions. This fungal disease, caused by inhaling spores from the Histoplasma fungus, can emerge from disturbing environments rich in bat droppings. An analysis of a specific incident involving a family trip to the popular Venado Caves in Costa Rica reveals the implications of exposure to this kind of environment. The CDC’s reports shed light on histoplasmosis outbreaks, urging travelers to be informed about the signs and symptoms of this potentially severe infection. As more families engage in outdoor activities, understanding the risks of histoplasmosis becomes increasingly critical.
Understanding Histoplasmosis: Symptoms and Risk Factors
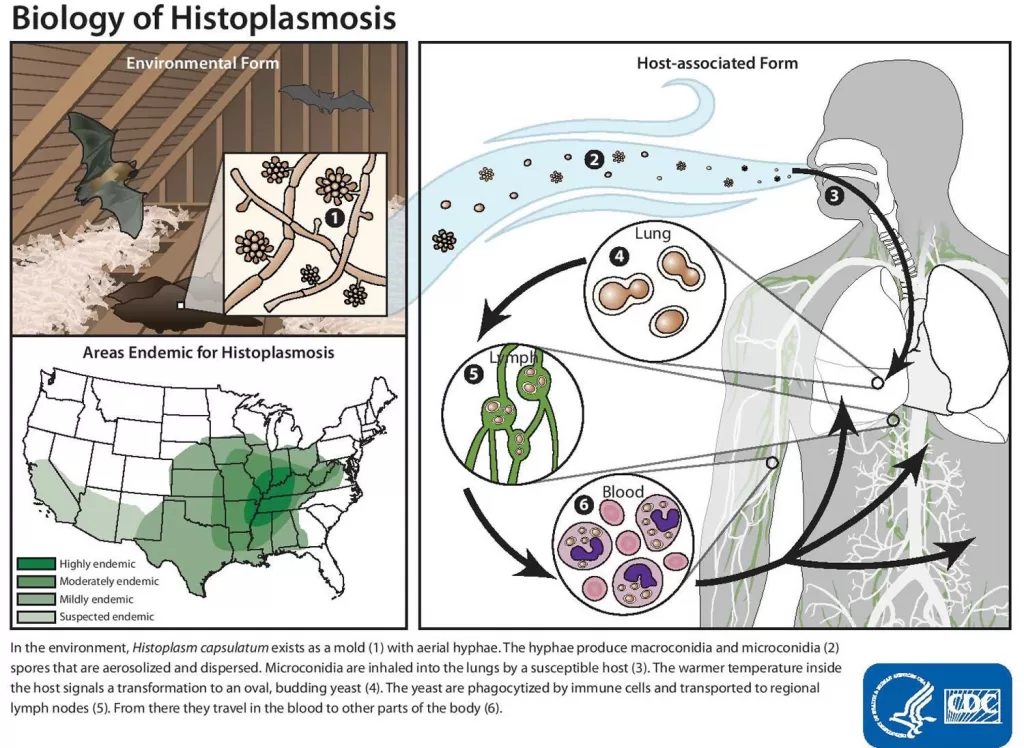
Histoplasmosis is primarily a respiratory illness caused by the inhalation of Histoplasma spores, often found in environments contaminated by bat droppings or bird excrement. Common symptoms include dry cough, fever, chills, fatigue, and body aches, which may appear as mild or severe reactions in individuals, especially those with weakened immune systems. Notably, in outbreaks such as the one reported in the Venado Caves, it is crucial to recognize that many infected individuals remain asymptomatic, complicating early diagnosis and public health responses.
Infants, the elderly, and individuals with compromised immune systems face an elevated risk of developing severe histoplasmosis, leading to chronic respiratory issues or even fatal outcomes if left untreated. Furthermore, the confusion surrounding histoplasmosis symptoms often results in misdiagnosis, where patients may be treated for other conditions such as bacterial infections instead of the fungal infection. Understanding these nuances plays a pivotal role in addressing the contagion and safeguarding public health.
The Venado Caves: A Hotspot for Histoplasmosis
The Venado Caves in Alajuela, Costa Rica, have gained notoriety as a potential site of histoplasmosis exposure due to the high density of bat populations residing within. This tour destination not only attracts adventure seekers but also poses grave health risks because of the spores present in the bat guano. The recent case involving a U.S. family who visited the caves draws attention to the importance of awareness and preventative measures that should be communicated to tourists to mitigate the risks associated with exposure.
Despite the potential for histoplasmosis transmission in the Venado Caves, information about these risks is scant, as current tour guidelines do not adequately inform visitors of the dangers. The CDC has initiated collaborations to incorporate histoplasmosis information in tour waiver forms to ensure guests understand the possible health ramifications of their visit. It is vital for tour providers to enhance their communication strategies regarding the dangers of fungal infections to protect the well-being of their clientele.
Histoplasmosis in Family: Case Study Insights
The case of the U.S. family infected with histoplasmosis after their visit to the Venado Caves illuminates the real-world implications of this fungal infection. Following their trip, several family members reported symptoms reminiscent of histoplasmosis due to the exposure they encountered while navigating through the bat-infested areas of the cave. This scenario underscores the significance of considering travel histories in patient assessments, particularly when symptoms align with exposure risks associated with histoplasmosis.
Health professionals must maintain a high index of suspicion for diagnosing conditions like histoplasmosis, especially following potential exposure during caving activities. The CDC’s prompt investigation following the family’s reported illnesses exemplifies the need for rapid response and collaboration among health departments to mitigate further infections. Such case studies enrich the understanding of transmission pathways and encourage health authorities to develop preventive strategies for future outbreaks.
CDC’s Response and Recommendations on Histoplasmosis
In response to the histoplasmosis cases linked to Venado Caves, the CDC launched a thorough investigation in collaboration with state health departments. This proactive approach emphasizes the necessity of surveillance and reporting mechanisms to identify and address public health threats effectively. Given that misdiagnosis is common, healthcare providers are urged to consider histoplasmosis during differential diagnosis for patients exhibiting pulmonary or constitutional symptoms after engaging in high-risk activities.
Moreover, the CDC’s recommendations for antifungal treatments indicate a cautious approach, emphasizing that only severe cases warrant such interventions. Misunderstandings around treatment efficacy highlight the need for enhanced training among healthcare professionals regarding fungal infections, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care based on accurate diagnoses. Awareness of the history of histoplasmosis outbreaks is essential in shaping future health campaigns and educational outreach, particularly in areas where exposure is a tangible risk.
Long-Term Effects of Histoplasmosis Infection
While many individuals affected by histoplasmosis recover without receiving antifungal treatment, some may experience long-term effects. Chronic respiratory problems can persist, particularly in those who developed severe illness during the initial infection. This lingering health issue often results from both the immune response to the pathogen and the damage caused by the infection itself. Therefore, it is crucial for clinicians to monitor patients who exhibit persistent symptoms post-recovery for potential chronic complications.
Educational programs should inform both healthcare providers and the public about the possible long-term ramifications following a histoplasmosis infection. Increased awareness can lead to better management strategies, as well as support for individuals whose lives may continue to be adversely affected by the disease long after the acute phase has passed. Research into this fungal infection’s lasting impact is essential to guide best practices in patient care and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Preventing Histoplasmosis: Awareness and Education
Preventing histoplasmosis fundamentally relies on increasing awareness and education about its associated risks. Tourists visiting bat caves or regions where bat guano is present should be educated on preventive measures like wearing masks and avoiding direct contact with contaminated soil. Health agencies should collaborate with local tour providers to disseminate information regarding the transmission of histoplasmosis and the symptoms to watch for post-exposure.
Public awareness campaigns can empower individuals to take charge of their health, ensuring they recognize the importance of reporting recent exposure to potential histoplasmosis sources when symptoms arise. Educational materials that detail the relationship between bat habitats and histoplasmosis can play a critical role in empowering travelers to mitigate risk while enjoying their adventures.
Histoplasmosis Treatment: Understanding Healthcare Options
When it comes to treating histoplasmosis, understanding the available healthcare options is essential. Mild infections may require little to no treatment, as individuals often recover spontaneously. However, for moderate to severe cases, healthcare providers typically recommend antifungal medication such as itraconazole or amphotericin B based on the patient’s specific condition. Such medications can effectively manage progressions of the disease and improve patient outcomes.
In scenarios where the diagnosis is delayed or mismanaged, the initiation of appropriate treatment can be substantial. Physicians need to keep an open mind regarding histoplasmosis and consider it during differential diagnoses for patients with respiratory or constitutional symptoms. The earlier the intervention, the better the outcomes for those affected, reducing the risks of complications related to untreated fungal infections.
The Importance of Reporting and Monitoring Histoplasmosis Cases
Reporting and monitoring histoplasmosis cases are critical components in controlling outbreaks and preventing future infections. The CDC and local health departments work collaboratively to track cases, assess potential sources of infection, and implement preventive measures. Timely reporting of suspected cases allows health authorities to respond swiftly to emerging clusters, helping mitigate risks and protect public health.
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in this monitoring framework as they are often the first line of detection. Ensuring that all suspected cases of histoplasmosis are reported helps to unify data collection and improves our understanding of the epidemiology of the disease. This proactive approach ultimately enhances public health initiatives, safeguarding communities from potential histoplasmosis outbreaks.
Future Research Directions for Histoplasmosis
Future research into histoplasmosis should focus on various aspects, including identifying at-risk populations, improving diagnostic tests, and understanding the long-term effects of the infection. Scientific studies should explore environmental factors contributing to outbreaks, particularly in high-risk areas where bats reside. Gathering comprehensive data will inform targeted preventive measures and enable health authorities to develop strategic responses to emerging threats associated with histoplasmosis.
Additionally, there is a pressing need for advancements in diagnostic methodologies. Enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of tests will facilitate earlier diagnoses of histoplasmosis, ultimately leading to better clinical outcomes. Moreover, investigating the potential for vaccinations could provide a preventive strategy to mitigate the impact of this fungal infection among populations vulnerable to its severe forms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common histoplasmosis symptoms to watch for after visiting a bat cave?
After visiting locations like bat caves, common histoplasmosis symptoms include headaches, fevers, malaise, night sweats, muscle pains, respiratory issues, and gastrointestinal problems. It’s important for families exposed to bat guano or bird droppings to monitor these symptoms, as many individuals may not show signs of the fungal infection.
How does a family potentially contract histoplasmosis during a visit to Venado Caves in Costa Rica?
A family can contract histoplasmosis during visits to places like Venado Caves by inhaling spores from disturbed soil that contains bat guano. This fungal infection, often associated with caves inhabited by bats, can lead to severe respiratory illnesses, particularly in infants or individuals with weakened immune systems.
What should families do if they suspect histoplasmosis after a cave visit?
If families suspect histoplasmosis after visiting a cave, they should seek medical attention promptly. Symptoms may develop between eight to nineteen days after exposure, and it is crucial to inform healthcare providers about recent cave visits to facilitate accurate diagnosis and treatment of any potential fungal infection.
What does the CDC recommend for families regarding histoplasmosis exposure in bat-colonized areas?
The CDC recommends that families be aware of the risks of histoplasmosis when visiting bat-colonized areas like the Venado Caves. They advise using protective gear, such as masks, and being vigilant for symptoms associated with the fungal infection, while also encouraging reporting of any suspected cases to local health departments.
What are the treatment options for families diagnosed with histoplasmosis?
Treatment for families diagnosed with histoplasmosis generally includes antifungal medications, especially for severe cases. Antibiotics are not effective against the fungal infection, and corticosteroids may worsen the condition. It is vital for healthcare providers to consider histoplasmosis in patients with respiratory symptoms and a recent history of exposure.
| Key Points |
|---|
| A family of 12 in the U.S. was affected by histoplasmosis after visiting a bat-colonized cave in Costa Rica. |
| All family members reported close contact with bat droppings during a cave tour on December 24. |
| Symptoms emerged 8 to 19 days after the visit, including fevers, malaise, and respiratory issues. |
| CDC began a multistate investigation after the cases were reported to them by a Georgia physician. |
| Treatment included antifungal medication for one patient suspected to have lung cancer; outcomes were generally positive. |
| The U.S. Embassy issued a health alert about the risks of histoplasmosis related to the cave. |
| Recommendations include understanding the risks associated with caving activities and recognizing symptoms of histoplasmosis early. |
Summary
Histoplasmosis in family members can be a serious concern especially after exposure to environments where Histoplasma spores thrive, such as bat-colonized caves. A recent case reported after a family vacation highlights the importance of awareness and early diagnosis. Even mild symptoms can indicate significant health risks, particularly in vulnerable groups. Thus, recognizing potential histoplasmosis exposure is crucial for families engaging in outdoor activities that may involve contact with bat droppings.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.