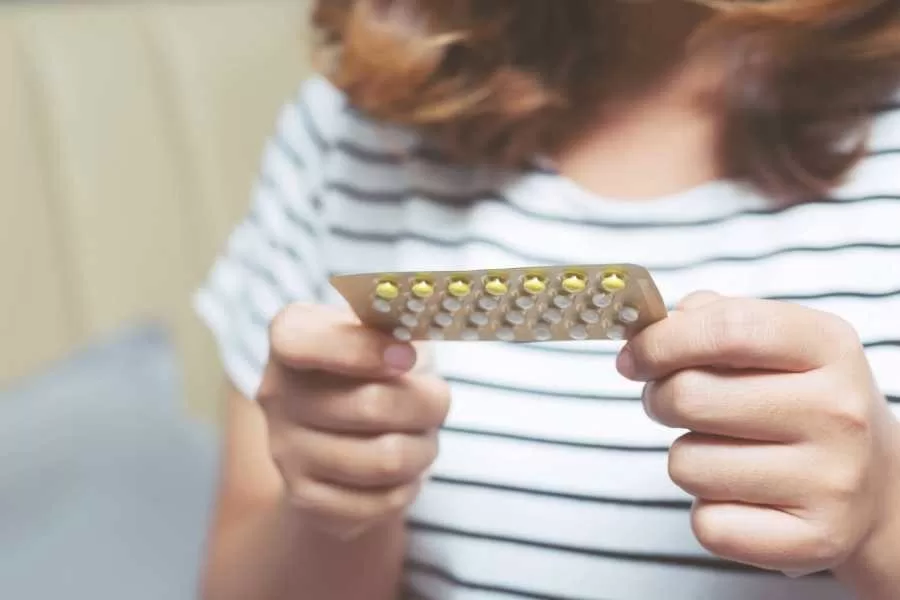
Understanding the nuances of high-dose vs. low-dose birth control is crucial for those considering their contraceptive options. Combination birth control pills, which include both estrogen and progesterone, vary significantly in their estrogen levels, impacting birth control effectiveness and potential side effects. High-dose pills, typically containing 50 micrograms or more of estrogen, may offer benefits for some but can also lead to discomfort and increased side effects. In contrast, low-dose birth control options often contain 20-35 micrograms of estrogen, making them a preferable choice for those looking to minimize adverse effects such as nausea and headaches. Ultimately, the choice between high-dose and low-dose options should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, taking into account individual health needs and lifestyle factors.
When navigating the world of contraceptive options, particularly focusing on the spectrum of hormone levels found in combination contraceptives, one often encounters high-dose and low-dose birth control alternatives. These hormonal pills, which blend progesterone with varying doses of estrogen, present different levels of effectiveness and side effects. While traditional high-dose variants contain significant amounts of estrogen that may lead to complications, low-dose variants have gained popularity for their reduced hormonal footprint and lower incidence of adverse reactions. The effectiveness of these hormonal options is generally comparable, yet their side effect profiles can greatly differ. To make an informed choice, individuals should explore these terms and options thoroughly.
Understanding High-Dose vs. Low-Dose Birth Control
When it comes to birth control pills, understanding the differences between high-dose and low-dose options is essential. High-dose birth control pills typically contain 50 micrograms of estrogen or more, which can often lead to increased side effects such as headaches and nausea. These pills work effectively to prevent pregnancy but are usually prescribed when no other alternatives are suitable. Their higher estrogen content, while effective, can pose risks, particularly for individuals with a history of blood clots or other health concerns.
In contrast, low-dose birth control pills, which contain 20-35 micrograms of estrogen, are increasingly common due to their lower risk profile. For many individuals, these pills provide the same level of effectiveness in preventing pregnancy, without the heightened risk of adverse effects. Studies show comparable pregnancy prevention rates between high and low-dose options, making these lower doses a viable choice for those sensitive to the side effects commonly associated with higher estrogen levels.
Exploring Birth Control Effectiveness
The effectiveness of birth control pills is a primary concern for many users. Despite common misconceptions, research indicates that both high-dose and low-dose combination pills have similar effectiveness rates in preventing pregnancy. When used perfectly, there is a mere 0.3% chance of pregnancy within a year, regardless of the estrogen level in the pill. This means that effectiveness does not directly correlate with the dosage of estrogen in the pill, allowing users to choose options based on tolerance rather than effectiveness.
Moreover, birth control effectiveness is also influenced by consistent use and proper administration. Whether one opts for low or high doses, adherence to the pill regimen is key. Irregular usage can elevate the risk of unintended pregnancies, which can be a concern for those less disciplined about taking their medication. Thus, it’s essential to discuss the choice of pill with a healthcare provider, ensuring that personal health needs align with the appropriate dosage.
Highlighted Types of Birth Control Pills
Combination birth control pills are broadly classified into two categories: those containing both estrogen and progesterone, and progestin-only pills. The first type contains varying amounts of estrogen (from 10 to 50 micrograms), offering a range of options tailored to individual side effects and medical histories. The dual hormone approach effectively prevents ovulation and alters uterine lining, making it a popular choice.
Progestin-only pills, often referred to as “mini pills,” may be suitable for those unable to tolerate estrogen due to health conditions or side effects. These options are particularly beneficial for individuals with a risk of blood clots or those over 35 years of age who smoke. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers make informed decisions about which birth control method is best for their lifestyle and health needs.
Assessing Side Effects and Risks of Birth Control Pills
Every medication, including birth control pills, comes with potential side effects and risks. High-dose birth control options, typically containing over 50 micrograms of estrogen, have been associated with higher risks such as blood clots, headaches, and nausea. These side effects can significantly impact the quality of life for those who experience them, making it critical to weigh the benefits against the potential downsides.
Conversely, low-dose birth control pills are designed to minimize such adverse effects. Reducing estrogen levels can alleviate symptoms like breast tenderness and mood swings for some individuals. However, it is important to note that lower doses may not resolve issues like decreased libido. Therefore, consulting with a healthcare provider to find the right balance of benefits and risks is essential for effective birth control management.
The Advantages of Low-Dose Birth Control Options
Low-dose birth control pills offer numerous advantages, particularly regarding tolerance and side effects. Patients often report fewer instances of nausea and headaches when switching from high-dose options, emphasizing their suitability for a broader audience. Additionally, lower estrogen levels may reduce the risk of serious complications like venous thromboembolism, making these pills a safer choice for many.
Moreover, the accessibility of low-dose options means that healthcare providers can better tailor birth control methods to individual needs, leading to more personalized healthcare. Benefits such as lighter periods and a decrease in PMS symptoms can significantly enhance the quality of life for users, promoting adherence to birth control regimens. Overall, low-dose contraceptives represent a crucial development in reproductive health care.
Evaluating the Benefits and Disadvantages of Birth Control Pills
Both high-dose and low-dose birth control pills come with distinct benefits and disadvantages. The primary benefits include a reduction in menstrual pain, lighter menstrual flow, and a decrease in the risk of certain cancers. Users can effectively manage their menstrual cycles and enjoy predictable periods, which is a significant advantage for many women.
However, disadvantages such as the potential for side effects, including mood fluctuations and breast soreness, are prevalent across both categories. Therefore, individuals must consider these factors carefully, weighing the benefits against the disadvantages to determine which pill aligns with their health goals and lifestyle preferences. Open communication with healthcare professionals is vital in navigating these decisions.
Who Should Consider Consulting a Doctor?
While many people can safely take combination birth control pills, certain individuals should consult with a healthcare provider to prevent complications. Those with risk factors such as smoking, obesity, or a family history of blood clots need to approach their birth control choices with caution. Doctors can provide personalized guidance based on health histories, potentially recommending low-dose options as a safer alternative.
Furthermore, people with certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, should discuss their contraceptive options thoroughly. A physician’s expertise can help individuals navigate their choices, ensuring optimal health outcomes while using birth control. Recognizing personal limits and seeking professional advice is a crucial step in maintaining reproductive health.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Birth Control Decisions
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in helping individuals navigate their birth control options. They possess the knowledge and expertise to assess medical histories, understand potential side effects, and provide recommendations based on personal health needs. Through consultations, individuals can make informed decisions about whether high, low, or ultra-low doses are appropriate for them.
Additionally, healthcare professionals can monitor patients’ progress and address any emerging side effects or concerns, leading to a more tailored and effective birth control experience. The ongoing support of a healthcare provider is essential in promoting not just effective contraception, but also overall reproductive health.
A Quick Review of Birth Control Pill Options
In summary, birth control pills represent a critical component of reproductive health management. High-dose pills may be effective but often come with increased side effects, while low-dose options provide a safer alternative for many. With similar effectiveness rates, the choice between high and low doses should be based on personal tolerance and health considerations.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances among various birth control options and their side effects is essential for individuals to make informed decisions. Consulting with healthcare providers ensures a customized approach to contraceptive choices, fostering not only effective control over reproduction but also improved overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between high-dose and low-dose birth control options?
High-dose and low-dose birth control options differ primarily in the amount of estrogen they contain. High-dose birth control pills usually have 50 micrograms of estrogen, which may lead to more significant side effects. In contrast, low-dose pills contain 20-35 micrograms of estrogen, and may help reduce side effects while still maintaining birth control effectiveness.
How effective are low-dose birth control pills compared to high-dose options?
Both high-dose and low-dose birth control pills are equally effective in preventing pregnancy. Studies indicate that lower doses, such as those containing 20 micrograms of estrogen, provide similar effectiveness to higher doses. In ideal conditions, the chance of pregnancy is as low as 0.3% per year for both types.
What are the side effects of high-dose birth control compared to low-dose?
High-dose birth control pills are associated with more side effects, such as nausea, headaches, and an increased risk of blood clots. Low-dose birth control options may reduce these side effects, making them a preferable choice for individuals sensitive to estrogen.
Can side effects decrease if I switch from high-dose to low-dose birth control?
Yes, switching from high-dose to low-dose birth control may help decrease certain side effects, such as breast soreness and irregular bleeding, as they contain less estrogen. However, some side effects may not improve with a lower dose.
Who should consider using low-dose birth control options?
Individuals who experience side effects from high-dose birth control or those who have health concerns related to estrogen may benefit from low-dose birth control options. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best dosage and type based on individual health needs.
What types of combination birth control pills are available?
Combination birth control pills primarily come in three categories based on estrogen content: high-dose (50 micrograms), low-dose (20-35 micrograms), and ultra low-dose (10-20 micrograms). Each type caters to different patient needs concerning estrogen sensitivity and side effects.
Are there risks associated with high-dose birth control pills?
Yes, high-dose birth control pills have a higher risk of side effects, including increased chances of blood clots, stroke, and elevated blood pressure. These risks make them less commonly prescribed compared to low-dose options, especially for individuals with certain health conditions.
What benefits do combination birth control pills provide, irrespective of dosage?
Combination birth control pills, whether high-dose or low-dose, offer benefits such as shorter or absent periods, reduced PMS symptoms, lower cancer risks (ovarian, uterine, and colon), relief from polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) symptoms, and reduced incidence of ovarian cysts.
Which individuals should avoid high-dose birth control pills?
Individuals who should avoid high-dose birth control pills include those with a history of blood clots, certain cancers (like breast cancer), smokers over 35, individuals with high blood pressure, and those recovering from surgery. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine suitability.
How does estrogen level impact the effectiveness of birth control pills?
Estrogen levels in birth control pills, whether high or low, do not significantly impact their overall effectiveness in preventing pregnancy. Both high-dose and low-dose birth control pills have similar effectiveness rates when used correctly, focusing instead on individual tolerance and side effects.
| Aspect | High-Dose Birth Control Pills | Low-Dose Birth Control Pills |
|---|---|---|
| Estrogen Content | 50 micrograms of estrogen or less | 20-35 micrograms of estrogen (20-25 recommended for side effects reduction) |
| Effectiveness | Similar effectiveness to low-dose pills (0.3% pregnancy rate with perfect use) | Equally effective (0.3% pregnancy rate with perfect use) |
| Side Effects | Higher risk of negative side effects like blood clots, nausea, headaches | Fewer side effects, more suited for sensitive individuals |
| Benefits | Shorter periods, reduced PMS symptoms, but higher side effects risk | Similar benefits with lower side effect impact |
| Who Should Avoid | Generally not recommended for those with blood clot risks or certain cancers | Recommended for those avoiding estrogen due to medical reasons |
Summary
High-Dose vs. Low-Dose Birth Control options cater to different needs when it comes to hormonal contraception. High-dose birth control pills, with higher estrogen content, may be less prescribed due to their association with increased side effects like blood clots and nausea. In contrast, low-dose birth control pills, which contain less estrogen, are often more suitable for individuals sensitive to hormonal side effects, while maintaining effective pregnancy prevention. Ultimately, consulting with a healthcare provider can help individuals make an informed decision about which option aligns best with their health needs and lifestyle.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.