The hepatitis B vaccine birth dose is a crucial component of childhood immunization, ensuring infants are protected against this serious viral infection from their very first moments. Recommended by the CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics since 1991, administering the hepatitis B vaccine at birth has proven to be a safe and effective strategy in reducing the prevalence of hepatitis B infections in the U.S. by an impressive 95%. As vaccine safety remains a top priority, the ongoing review by the Vaccine Integrity Project aims to solidify the importance of this universal birth dose within the child vaccination schedule. With potential changes on the horizon, adhering to established CDC hepatitis B guidelines is essential for maintaining public health standards. As we explore the landscape of vaccine recommendations, understanding the benefits and impact of the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose is more critical than ever.
Introducing the initial dose of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth is an essential practice in early childhood vaccination strategies. Known for its effectiveness in preventing hepatitis B infections, this birth dose aligns with the broader framework of child health initiatives. As healthcare providers discuss the implications of vaccine protocols, the focus on timely immunizations, including the hepatitis B shot, embodies a commitment to children’s well-being. Additionally, recent discussions around the safety and timing of this vaccination highlight the ongoing evaluation of practices to uphold the efficacy of public health measures. Emphasizing a universal birth dose for newborns not only safeguards individual health but also promotes community-wide immunity against hepatitis B.
Understanding Hepatitis B Vaccine Birth Dose
The hepatitis B vaccine birth dose plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of hepatitis B among newborns. Since the inception of the universal birth dose policy in the United States, there has been a remarkable decline of up to 95% in hepatitis B infections among children. The vaccine is recommended by key health organizations, including the CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics, as part of the standard child vaccination schedule. This policy not only protects infants but also contributes to community immunity, thereby ensuring that the population as a whole is less susceptible to outbreaks.
Moreover, administering the hepatitis B vaccine at birth aligns with the principles of proactive healthcare. By vaccinating newborns immediately after birth, we establish an early defense against hepatitis B, a virus that can lead to serious health complications later in life, such as liver disease or cancer. As research continues to underscore the effectiveness and safety of the birth dose, health committees, including the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), are tasked with reviewing current guidelines and recommendations to ensure they reflect the most accurate scientific data available.
The Role of Vaccine Safety in Hepatitis B Immunization
Vaccine safety is a pivotal component of any immunization strategy, particularly for newborns and children. Given the concerns that have been raised during recent ACIP meetings regarding the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose, it is crucial to examine existing data that consistently support its safety. Numerous studies have highlighted the low incidence of adverse effects associated with the hepatitis B vaccine. Health organizations rely on extensive surveillance systems and data collection from health providers to maintain high standards of vaccine safety, ensuring that the benefits far outweigh any potential risks.
In the context of the hepatitis B immunization, the assurance of safety helps foster public trust in vaccination programs. Parents need to feel confident that the vaccines their children receive are safe and effective. The continued advocacy for the universal birth dose is underpinned not only by a decline in hepatitis B cases but also by transparent communication about the rigorous safety evaluations conducted by the CDC and other health authorities. These evaluations are paramount to shaping policies that resonate with the needs of the community while supporting overall public health objectives.
Evaluating CDC Hepatitis B Guidelines
The CDC hepatitis B guidelines emphasize the importance of timely vaccination as a strategy to prevent the virus from transmitting at birth. With ongoing debates about adjusting the timing of the hepatitis B shot if the mother tests negative for the virus, it is essential to assess the implications of such changes. The ACIP’s upcoming meetings will clarify whether existing evidence supports modifications to the current birth dose protocol. Having a clear understanding of the data will help ensure that any suggestions made are based on evidence-driven recommendations.
In recent years, the CDC has consistently advocated for the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose, citing its role in virtually eliminating pediatric hepatitis B infections. Evaluating these guidelines against current research findings, including rigorous reviews of published studies, will be crucial in maintaining the integrity of the immunization schedule. Adherence to these guidelines is instrumental for healthcare professionals, as they navigate the complexities of immunizations and ensure that every child receives the best possible start in life.
Addressing Public Concerns About Hepatitis B Vaccine
Public concerns surrounding the hepatitis B vaccine primarily focus on safety, necessity, and timing of the vaccine administration. With misinformation about vaccines circulating widely, it is vital for health agencies and professionals to engage with communities, providing accurate information about the risks of hepatitis B versus the benefits of vaccination. Transparency about vaccine safety studies and potential side effects can help alleviate fears and encourage parents to adhere to the immunization schedule outlined by the CDC.
Furthermore, education initiatives centered on the foundational importance of the hepatitis B vaccine can empower parents to make informed health decisions about their children. By highlighting how the vaccine protects against a virus that can cause serious chronic health issues, health advocates can counter hesitations rooted in misconceptions. Clear communication from healthcare providers, alongside supportive data from organizations like the CDC, will fortify public trust in the vaccine and advance community health goals.
The Science Behind the Universal Birth Dose Policy
The universal birth dose policy for hepatitis B vaccination is deeply rooted in scientific research and public health strategy. Analyzing decades of epidemiological data reveals that administering the vaccine at birth significantly reduces the incidence of hepatitis B infections among infants. This policy, supported by organizations such as the CDC and AAP, is part of a greater effort to eradicate hepatitis B within vulnerable populations. By focusing on immunizing newborns as soon as feasible, healthcare systems can harness the protective benefits of the vaccine early on.
The forthcoming review from the Vaccine Integrity Project emphasizes the use of robust scientific methodologies to assess the impact of the birth dose. This comprehensive evaluation will consider various factors, including healthcare access, long-term health outcomes, and the effectiveness of existing vaccination programs. As discussions around vaccination policies continue to evolve, evidence-based recommendations will ensure that public health strategies remain effective in combating hepatitis B.
Implications of Changing Hepatitis B Vaccination Timing
The discussions surrounding potential changes to the timing of the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose bring to light significant implications for public health. If new recommendations suggest delaying vaccination for mothers who test negative for the virus, the risk of hepatitis B transmission could increase. Maintaining the current guidance underscores the importance of immediate protection at birth, especially given the vulnerability of newborns. Evaluating these changes requires a holistic approach that weighs the benefits against possible negative outcomes.
The implications extend not only to individual health but also to broader population health strategies. Variations in vaccination timing could complicate the already established child vaccination schedule, potentially affecting the effectiveness of herd immunity. Stakeholders in public health, including pediatricians and family practitioners, must stay informed on these developments and advocate for data-backed practices that prioritize the health and safety of infants across all demographics.
Future Directions for Hepatitis B Vaccination Research
As the landscape of vaccine research evolves, future directions for hepatitis B vaccination must focus on continued exploration of its efficacy and safety. Ongoing research should aim to examine the long-term effects of the universal birth dose and how changes in vaccination policy could influence future generations. By prioritizing studies that include diverse populations, researchers can ensure that all communities receive equitable access to critical vaccination resources, thereby addressing health disparities linked to hepatitis B.
Moreover, the integration of new technologies in vaccine delivery and monitoring can enhance public health efforts. The use of data analytics to track vaccination rates and health outcomes can guide policymakers in making informed decisions that impact the efficacy of future hepatitis B immunization programs. Comprehensive research will not only inform best practices but also reinforce confidence in the vaccination process, ensuring that public health initiatives continue to thrive.
Maintaining High Vaccination Rates for Hepatitis B
Ensuring high vaccination rates for hepatitis B is essential in sustaining the progress made in combating this virus. Significant declines in infection rates over the years can largely be attributed to rigorous adherence to vaccination protocols, particularly the universal birth dose. Public health initiatives focused on increasing awareness and accessibility are critical to maintaining and improving vaccination rates. It is vital to engage families through education on the importance of immunization and to offer convenient vaccination services.
Outreach programs targeting underserved communities may also be necessary to bridge gaps in vaccination coverage. By addressing barriers, such as socio-economic factors and limited access to healthcare resources, public health officials can ensure that more families comply with the vaccination recommendations outlined by the CDC. Sustaining high vaccination rates not only protects individuals but also strengthens community health, reducing the burden of hepatitis B in vulnerable populations.
The Impact of Legislative Changes on Hepatitis B Vaccination
Recent legislative changes regarding vaccination requirements can have significant implications for hepatitis B immunization efforts. As discussions continue about the timing and necessity of the hepatitis B birth dose, policymakers must consider the potential impact on public health outcomes. Legislation that promotes vaccination adherence and mandates immunization for school entry can help ensure that families prioritize the hepatitis B vaccine, safeguarding future generations against this virus.
Moreover, fostering discussions among legislators, healthcare providers, and the public can lead to more nuanced policies that reflect the scientific evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of the hepatitis B vaccine. As stakeholders navigate the complex landscape of vaccine policy, it is crucial to advocate for legislation that upholds scientific integrity while protecting the health of the community. Transparent communication of research findings will be key in shaping policies that effectively mitigate the risks associated with hepatitis B.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose and why is it important?
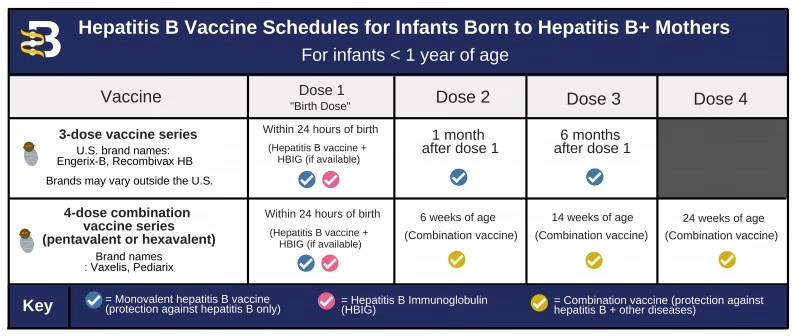
The hepatitis B vaccine birth dose is the first shot administered to newborns, ideally within 24 hours of birth. It is crucial for preventing hepatitis B infection, which can lead to severe liver disease and liver cancer. The CDC recommends this universal birth dose as it has significantly reduced hepatitis B infections among infants in the United States since its implementation.
What are the CDC hepatitis B guidelines regarding the birth dose?
According to CDC hepatitis B guidelines, all newborns should receive the hepatitis B vaccine within the first 24 hours of life, regardless of the mother’s hepatitis B status. This universal birth dose is part of the recommended child vaccination schedule to ensure early protection against potential transmission.
How does the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose fit into the child vaccination schedule?
The hepatitis B vaccine birth dose is the first immunization received by infants in the child vaccination schedule. Administered within 24 hours of birth, it lays the foundation for a series of vaccinations aimed at providing lifelong protection against hepatitis B.
What is the vaccine safety profile of the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose?
The hepatitis B vaccine birth dose has an excellent safety profile, with extensive research supporting its use. Studies have shown that adverse effects are rare and generally mild, such as redness at the injection site. The CDC and WHO endorse its safety as part of routine immunizations for newborns.
What has been the impact of the universal birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine in the U.S.?
The universal birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine has led to a remarkable 95% reduction in hepatitis B infections in the United States since it was recommended. This significant public health impact highlights the effectiveness of the birth dose policy in protecting infants from hepatitis B.
Are there any recent discussions regarding changes to the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose recommendations?
Yes, recent discussions by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) have considered potential changes to the timing of the hepatitis B vaccination, particularly for infants born to mothers who test negative for hepatitis B. However, many experts caution against altering the current universal birth dose policy without strong evidence supporting such a change.
What role does the Vaccine Integrity Project play in reviewing hepatitis B vaccine birth dose data?
The Vaccine Integrity Project (VIP) at the University of Minnesota is conducting a comprehensive review of data on the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose to assess its safety, efficacy, and public health impact. This review aims to provide evidence for ongoing discussions and recommendations surrounding the hepatitis B immunization policy.
How often is the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose recommended for other childhood immunizations?
The hepatitis B vaccine birth dose is the initial vaccine in a series of recommended doses. Following the birth dose, it is typically followed by two additional doses at 1-2 months and 6-18 months, to ensure full protection against hepatitis B as part of the child vaccination schedule.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The Vaccine Integrity Project at CIDRAP is reviewing data on the hepatitis B vaccine birth dose. |
| The birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine has been recommended since 1991 by the CDC and AAP. |
| There has been a 95% decline in hepatitis B infections in the US since the adoption of the universal birth dose policy. |
| ACIP has postponed a vote on changing recommendations regarding the timing of the birth dose, pending new data. |
| The review will rely on various analyses and data sources to assess the impact of the birth dose recommendation. |
| CIDRAP’s Director emphasized the need for strong scientific evidence before making any recommendation changes. |
Summary
The hepatitis B vaccine birth dose is a critical intervention that has dramatically reduced pediatric hepatitis B infections in the United States. Initiated in 1991, this policy is currently under review by the Vaccine Integrity Project at CIDRAP, which aims to analyze extensive data on its safety and efficacy. The findings from this review will inform future recommendations from federal advisors, ensuring that any changes to vaccination practices prioritize the health and safety of newborns.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.