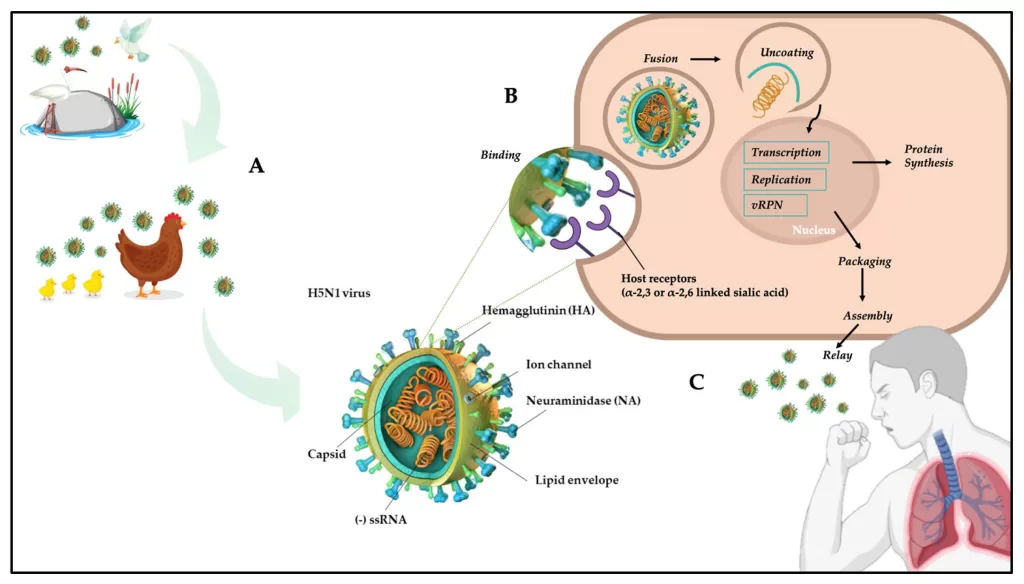
H5N1 transmission poses significant public health concerns, particularly as outbreaks of avian influenza continue to emerge. Recent studies reveal that the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus can spread through respiratory droplets, raising alarms over potential human cases H5N1. As the current H5N1 outbreak progresses, monitoring these transmissions is crucial for preventing severe symptoms among affected individuals. Known H5N1 symptoms range from mild respiratory issues to more severe complications, particularly in vulnerable populations. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of H5N1 transmission and its implications is vital to developing effective public health strategies.
The spread of the H5N1 virus, a strain of avian influenza, highlights essential health considerations that go beyond traditional avian-to-human transmission pathways. In light of recent findings, the airborne nature of the virus, particularly via respiratory droplets, underscores the urgency of surveillance in livestock and farm workers. Human infections from H5N1 can lead to varied outcomes, often presenting mild symptoms, yet pose a risk for severe illness. Epidemiologists emphasize the importance of tracking these outbreaks and evaluating potential human cases linked to the virus. Understanding the dynamics of influenza viruses and their transmission between species remains critical for public health safety.
Understanding H5N1 Transmission Risks
H5N1 transmission has become a pressing concern, particularly following recent outbreaks in U.S. dairy cattle. The highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) strain can potentially spread not only among birds but also to humans, notably farm workers in close proximity to infected animals. The implications of airborne transmission via respiratory droplets are significant; it emphasizes the necessity for robust monitoring and precautionary measures to mitigate risks. This occurrence raises awareness of how agricultural links could contribute to human cases of H5N1, thus underscoring the unique relationship between wildlife, livestock, and human health.
In the wake of confirmed human cases of H5N1, raised public health vigilance is crucial. Studies have indicated that while the direct transmission from infected birds to humans remains uncommon, the recent findings suggest that farm environments may facilitate conditions for transmission through respiratory droplets. The ongoing observation of such virus behavior will be vital. It guides public health policies and aids in the preparedness of health systems should transmission become more prevalent.
H5N1 Symptoms and Human Health Concerns
While many human cases of H5N1 have presented with mild respiratory symptoms or conjunctivitis, the underlying threat the virus poses cannot be overlooked. Infections can escalate quickly, leading to severe respiratory illness in vulnerable individuals. The mild cases, primarily documented among farm workers, highlight the virus’s potential to infect through respiratory routes and pose risks for more severe health outcomes, as evidenced by cases where infected individuals ultimately required hospitalization due to exacerbated symptoms.
It is vital to educate at-risk populations, especially those working in agriculture, about recognizing H5N1 symptoms early. Common signs include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing, which can develop rapidly. Monitoring these symptoms and ensuring swift medical intervention could potentially reduce hospitalizations and severe health risks. Additionally, the presence of the virus in various body tissues, while presenting mild symptoms initially, raises flags for healthcare providers to stay alert for atypical presentations that could relate to H5N1 infection.
The Role of Airborne Transmission in H5N1 Outbreaks
The study conducted by Dr. Kawaoka’s team sheds light on the potential for airborne transmission of H5N1, particularly in farm settings. By observing infected ferrets, it was revealed that the virus could indeed spread through respiratory droplets, a factor not prevalent in earlier studies focused on cow-derived viruses. This realization emphasizes that H5N1 could infect humans under certain conditions and suggests that biosecurity measures in agriculture must account for airborne transmission risks.
Effective prevention strategies must involve both preventative practices for animals and heightened awareness among humans in contact with livestock. Identifying the nuances of H5N1 transmission patterns is key to preventing future outbreaks. As researchers continue to monitor such variants, maintaining open lines of communication between agricultural sectors, public health agencies, and veterinary services will be necessary to foster comprehensive strategies that encompass all avenues of transmission.
Clinical Insights on H5N1 Effects
Clinicians need to be aware of the potential clinical implications of H5N1 infection in humans. Recent studies have indicated that while initial symptoms may be mild, the severity of infections in animal models speaks to the need for rigorous monitoring and assessment of human cases. The existence of lethal mutations that affect viral replication adds another layer of complexity that healthcare professionals must navigate when diagnosing respiratory illnesses in at-risk populations.
Furthermore, understanding the specific mutations found in the H5N1 virus, particularly those linked with enhanced pathogenicity in mammals, could aid in developing targeted therapies. Treatments such as polymerase inhibitors show promise in managing infections, emphasizing the importance of ongoing research and potential for evolutionary mutations in H5N1 that could redefine its interaction with human hosts. Health care providers must remain vigilant and prepared for a spectrum of symptoms, ensuring that those with exposure receive timely evaluations.
Addressing Public Health Concerns with H5N1
The emergence of H5N1 cases among humans raises significant public health concerns. Continued monitoring of viral reservoirs, particularly in animal populations, is crucial for prompt responses to any signs of increased transmissibility to humans. Public health organizations play an essential role in educating both agricultural workers and the general population about potential risks associated with H5N1 virus exposure.
Public health strategies must be proactive rather than reactive, fostering robust surveillance systems and rapid response protocols to contain outbreaks. This approach includes vaccination strategies for poultry and biosecurity measures to limit contact between wild birds and domesticated livestock. The collaborative efforts of public health, veterinary services, and agricultural sectors will be pivotal in preventing potential H5N1 outbreaks from escalating into public health crises.
The Importance of Research in H5N1 Studies
Research into H5N1 transmission, particularly studies like those conducted by Dr. Kawaoka, is invaluable for understanding how the virus adapts and spreads. Insights gained from such research contribute not only to scientific knowledge but also shape public health policies aimed at containment and prevention. Investigating the virus’s behavior in both animal models and human cases helps identify critical factors that influence its transmission among populations.
Moreover, comprehensive studies underscore the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in tackling zoonotic diseases. By bridging gaps between virology, epidemiology, and public health, researchers can provide solutions that prevent the transmission of H5N1 by identifying interventions that are effective across both animal and human populations. This multi-faceted approach ensures a coordinated response to threats posed by H5N1 outbreaks.
Educating Farm Workers on H5N1 Risks
Educating farm workers about the risks associated with H5N1 is essential for preventing infections. Given that many human cases have been reported among individuals in direct contact with infected animals, tailored education campaigns can provide critical information on recognizing symptoms and implementing safety practices. Workshops, informational pamphlets, and regular training sessions on biosecurity protocols can greatly enhance awareness among agricultural workers.
Additionally, empowering these individuals with knowledge about proper hygiene practices, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and reporting procedures can further minimize the likelihood of transmission. Institutions focusing on occupational health must prioritize H5N1-related training, ultimately fostering a safer work environment and reducing risks associated with potential outbreaks.
Monitoring and Surveillance of H5N1
Ongoing monitoring and surveillance of H5N1 in livestock and wild bird populations are imperative. Public health institutions and agricultural agencies must collaborate to establish systems that effectively track viral strains and potential mutations. Comprehensive surveillance can facilitate timely reporting and rapid response efforts to mitigate the impact of outbreaks.
Moreover, surveillance activities should extend to testing animal populations regularly for H5N1 to identify and isolate infections among livestock promptly. This proactive approach allows for real-time data collection and analysis, essential for assessing the risk of transmission to humans. By integrating veterinary monitoring and public health assessments, authorities can better predict and control potential outbreaks, ensuring both food security and public health safety.
The Future of H5N1 Research and Public Health
Looking ahead, the importance of H5N1 research cannot be overstated. Innovative studies will continue to uncover the complexities of H5N1 interactions with hosts and its pathogenesis. By focusing on viral mutations and their impacts on transmissibility and virulence, researchers can better inform public health strategies that mitigate risks posed by this virus.
Public health authorities must adapt their approaches to emerging zoonotic threats, promoting a One Health perspective that recognizes the interconnectedness of animal, human, and environmental health. As global trade and climate change contribute to shifts in viral behavior, continued funding and attention to H5N1 research will be critical in safeguarding public health against future threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is H5N1 transmitted from infected farm workers to humans?
H5N1 transmission can occur from infected farm workers to humans primarily through respiratory droplets. These droplets are released when an infected individual coughs or sneezes, potentially infecting those nearby. The ongoing monitoring during the recent H5N1 outbreak highlights this need for caution.
What are the symptoms of human cases of H5N1 infection?
Human cases of H5N1 typically exhibit mild respiratory symptoms, which can include cough, fever, and conjunctivitis (pink eye). Physicians remain vigilant as the risks from H5N1 transmission can escalate, especially among farm workers with exposure to infected animals.
What did recent studies reveal about H5N1 transmission via respiratory droplets?
Studies indicated that H5N1 transmission via respiratory droplets is possible, particularly from infected farm workers. Research involving infected ferrets showed that between 1 in 6 to 1 in 3 of them could transmit the virus to uninfected neighbors, underlining the importance of understanding H5N1 transmission dynamics.
Are there concerns about the efficiency of H5N1 transmission in humans?
Yes, there are ongoing concerns about the efficiency of H5N1 transmission in humans. Although the transmission is limited, the finding that the H5N1 virus from infected individuals can spread via respiratory droplets suggests that continued surveillance is crucial, especially during outbreaks.
What potential treatments exist for H5N1 infections in humans?
Potential treatments for H5N1 infections include a class of antiviral drugs known as polymerase inhibitors. These have shown effectiveness against H5N1 viruses from cows and may also be applicable for treating human cases, should they occur.
What is the relationship between avian influenza and human cases of H5N1?
Avian influenza, specifically H5N1, is a virus primarily affecting birds, but it can also infect humans, especially those in contact with poultry or contaminated environments. The recent H5N1 outbreak has resulted in confirmed human cases, emphasizing the interplay between avian and human health.
How does H5N1 outbreak impact public health monitoring?
The H5N1 outbreak necessitates rigorous public health monitoring to detect new cases among farm workers and prevent transmission to humans. Continuous testing and monitoring of both H5N1 viruses in animal populations and human cases is essential to control possible outbreaks.
What role do respiratory droplets play in H5N1 transmission?
Respiratory droplets play a significant role in H5N1 transmission, as they can carry the virus from infected individuals to others, especially in close quarters. Understanding this transmission pathway is essential for mitigating risks associated with the current H5N1 outbreaks.
What has research shown about the lethality of H5N1 viruses from humans compared to cows?
Research has shown that H5N1 viruses isolated from humans tend to be more lethal in animal studies compared to those found in cows. The recent findings suggest that human H5N1 strains can cause severe infections, thus reinforcing the need for careful monitoring.
What preventive measures should be taken during an H5N1 outbreak?
During an H5N1 outbreak, preventive measures should include minimizing contact with infected animals, implementing strict hygiene protocols, and vaccinating domestic birds where applicable. Furthermore, public awareness campaigns can help educate those at risk, particularly farm workers.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Transmission Risks | H5N1 can spread through airborne droplets; observed lethal effects in lab animals. |
| Current Situation | H5N1 outbreak in U.S. dairy cattle since early 2024, with 40+ human cases mainly among farm workers. |
| Research Findings | Virus from an infected farm worker was highly pathogenic in lab animals, more so than the earlier cow virus studied. |
| Mutation Impact | Specific mutation in the human-derived virus enhances replication in mammals, raising concerns. |
| Public Health Assessment | CDC currently assesses the public risk as low, but emphasizes monitoring for virus transmission. |
Summary
H5N1 transmission poses significant concerns due to the potential for lethal infections and airborne spread. The recent studies highlight the pathogenicity of H5N1 viral strains in farm workers and laboratory animals, raising alarms for potential outbreaks. Continuous monitoring and response strategies are essential to prevent severe public health crises.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.