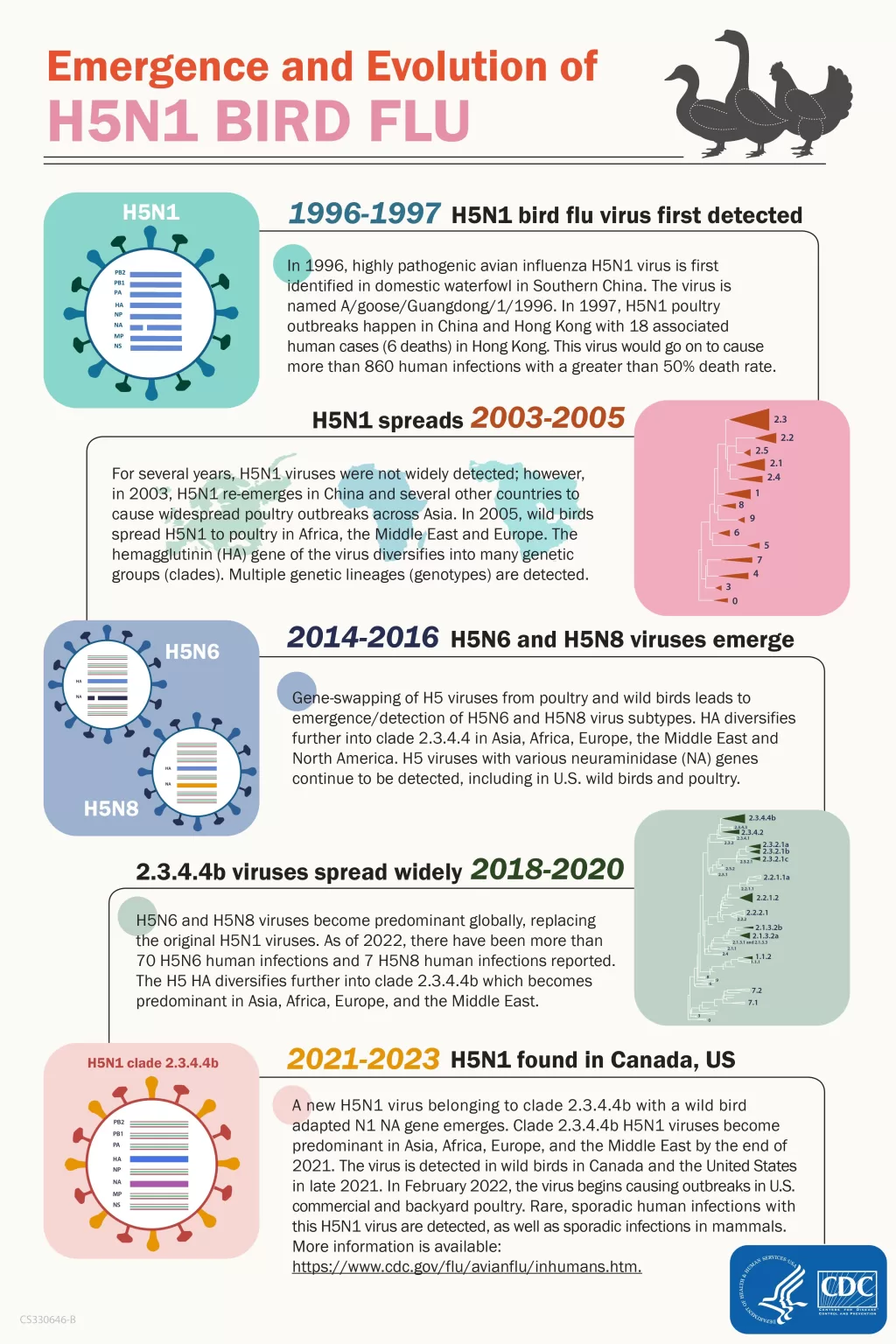
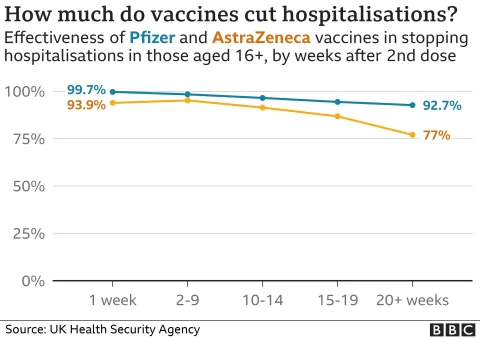
H5N1 bird flu, a strain of avian influenza, poses an alarming threat as it shows signs of adapting to mammalian hosts, which increases the risk of transmission to humans. This highly pathogenic virus has primarily circulated among birds for years, but its recent infections in mammals like cows highlight a concerning shift. The potential for an H5N1 transmission event among humans could spark a bird flu pandemic, raising urgent questions about human flu risk. Researchers are closely monitoring these adaptations, determining how this evolution might impact public health strategies and vaccine effectiveness. With at least 68 illnesses reported in North America alone, the necessity for vigilant surveillance is more pressing than ever to prevent a possible outbreak.
The emergence of H5N1 bird flu, also known as avian influenza, has raised significant alarm among health experts regarding its potential impact on human populations. As this virus adapts, particularly within mammalian hosts, concerns regarding its transmission dynamics and the possibility of a widespread outbreak come to the forefront. The increasing number of infections hints at an escalating risk related to the human flu threat, prompting urgent calls for enhanced monitoring and research. Indeed, the evolving nature of this pathogen could reshape strategies aimed at preventing a future pandemic caused by such influenza strains. Thorough understanding and international collaboration are vital in addressing the challenges posed by avian influenza as it interacts more closely with various species, including humans.
Understanding H5N1 Bird Flu and Its Capabilities
H5N1 bird flu, known for its resilience and adaptability, primarily resides within avian populations. However, recent outbreaks have demonstrated its capacity to jump species, raising alarm among public health officials. This virus, classified as avian influenza, has been documented infecting other mammals, including humans. Understanding the mechanics of H5N1 transmission is critical as scientists examine the mutations that enable this pathogen to thrive in non-avian hosts.
The implications of H5N1’s adaptability extend beyond initial infections; researchers are concerned about its potential for human-to-human transmission. By analyzing the genetic changes in H5N1, experts can gain insights into whether the virus could eventually lead to a human flu risk akin to previous pandemics. Surveillance is paramount, as monitoring these mutations will help inform vaccine development and public health policies aimed at preventing a bird flu pandemic.
The Rising Threat of a Bird Flu Pandemic
The risk of a bird flu pandemic is increasing as H5N1 continues to evolve. Reports from various regions, including North America, highlight a troubling trend of rising human cases linked to this virus. The transmission dynamics indicate that if H5N1 adapts further, it could facilitate more significant outbreaks, stressing the importance of preparedness among global health organizations. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs can help mitigate the panic and inform communities about what preventative measures they can adopt.
Historical precedents, such as the 1918 influenza pandemic, underscore the devastating impact that a bird flu pandemic could have on global health. With the potential for H5N1 to spread rapidly among humans, a coordinated response strategy must include enhanced vaccination programs and rapid identification of cases. Scientists urge for comprehensive research into the virus’s behavior to effectively manage and minimize the risks associated with potential pandemic scenarios.
The Importance of Global Surveillance for H5N1
Global surveillance is crucial for monitoring the evolution of H5N1 bird flu and its current epidemiological trends. By establishing networks that transcend borders, health organizations can share vital data about outbreaks and transmission patterns. This collaborative approach allows for a more robust response strategy, enabling investigators to track the mutations that could enhance the virus’s infectivity. Engaging wildlife researchers alongside public health experts enriches the understanding of viral dynamics in both avian and mammalian hosts.
Investing in technology and surveillance systems means that we can identify emerging strains of H5N1 more swiftly. Effective monitoring can lead to early warnings that trigger responsive measures, such as vaccine updates and public health advisories. In a world interconnected by travel and commerce, it’s essential that nations work together to track avian influenza’s potential pathways and preemptively address the hazards they present.
Deciphering H5N1 Transmission Pathways
Understanding the transmission pathways of H5N1 is essential for predicting its potential spread among human populations. The ability of the virus to jump from birds to mammals, and subsequently infect humans, raises significant concerns about its threat level. Researchers focus on how environmental factors contribute to the survival and transmission of H5N1. By examining these mechanisms, scientists can develop targeted strategies to interrupt the virus’s transmission cycles.
Moreover, studying the interactions between H5N1 and different species helps illuminate the virus’s adaptations. Insights gained from these studies can inform the development of vaccines that are effective against emerging strains. As researchers uncover more about H5N1 transmission, they will be better positioned to assess its risks and propose timely interventions that could avert a future human flu pandemic.
Strategies for Mitigating Human Flu Risk from H5N1
In light of the rising human flu risk posed by H5N1, health authorities must implement effective strategies to mitigate transmission. Vaccination programs and public health interventions play a critical role in managing outbreaks. Promoting awareness about the symptoms of bird flu and the need for immediate medical attention can limit the virus’s spread as cases emerge. Furthermore, community-led initiatives aimed at educating the public about hygiene and biosecurity practices are vital.
Public health responses must also prioritize research into the efficacy of current vaccines against emerging H5N1 strains. As the virus evolves, vaccine formulations may need to be adjusted; therefore, ongoing studies are crucial. Health leaders must remain vigilant, ready to collaborate in developing new strategies that protect populations and reduce the likelihood of a bird flu pandemic.
The Role of Evolution in H5N1 Adaptations
The evolution of H5N1 bird flu plays a pivotal role in its adaptability to new hosts, including mammals. Genetic mutations enable the virus to alter its surface proteins, making it capable of evading the immune response of different species. This evolutionary advantage poses a substantial challenge for public health as it complicates the development of long-lasting vaccines. Understanding these adaptations is critical for predicting how H5N1 may behave in the future.
Scientists studying the molecular biology of H5N1 are working to identify the specific mutations that facilitate its transmission. This knowledge helps inform vaccine research and public health strategies aimed at reducing the risk of spread. A keen focus on evolution allows researchers to remain one step ahead, ensuring that health systems are prepared to tackle potential future outbreaks effectively.
Impact of H5N1 on Global Health Policies
As concerns about H5N1 expand, global health policies must adapt to accommodate this evolving threat. The potential for H5N1 to transition from avian to human hosts requires a reassessment of existing policies, emphasizing the need for enhanced surveillance, research funding, and rapid response capabilities. Policymakers must engage with researchers, public health officials, and international bodies to develop comprehensive strategies that address the multifaceted nature of avian influenza.
Collaboration across nations can lead to the establishment of standardized protocols that ensure a coordinated response to outbreaks. These policies should also prioritize education and training for healthcare professionals, equipping them to recognize and manage cases of bird flu effectively. By taking proactive measures, the global community can bolster its defenses against the threats posed by H5N1, safeguarding public health and minimizing the risk of widespread infection.
The Need for Preparedness Against Bird Flu Pandemics
Preparedness is key to mitigating the impact of a potential bird flu pandemic. As H5N1 continues to mutate, the imperative for healthcare systems to have robust response plans in place becomes increasingly evident. Governments must invest in resources, training, and infrastructure to ensure readiness in the face of an outbreak. This includes stockpiling vaccines and antiviral medications specifically tailored for H5N1, as well as establishing rapid response teams.
Public education also plays a critical role in preparedness. Awareness campaigns that inform communities about hygiene practices and the risks associated with bird flu will empower individuals to take proactive measures. By fostering a well-informed public, health authorities can enhance community resilience in the face of potential outbreaks, thereby reducing the overall impact of transmission and illness.
Advancements in H5N1 Research and Development
Research and development surrounding H5N1 bird flu are vital to staying ahead of its evolution and potential threat to humans. Continuous advancements in virology, epidemiology, and genetic engineering facilitate the creation of better vaccines and treatments. Collaborative research initiatives allow scientists to pool resources and knowledge, leading to breakthroughs that can enhance global health strategies against H5N1.
Investing in cutting-edge technologies such as genomic sequencing also plays a pivotal role in understanding how H5N1 adapts to new hosts. These tools provide critical insights into the virus’s genetic makeup and its transmission pathways, informing public health responses. As the scientific community continues to explore innovative solutions, the hope remains that effective strategies can be developed to counter the risks posed by this evolving virus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is H5N1 bird flu and how does it relate to avian influenza?
H5N1 bird flu is a subtype of the avian influenza virus that primarily affects birds but can also infect humans and mammals. It is known for its high mortality rate in infected humans and has raised concerns regarding its potential to cause a bird flu pandemic due to its capability to adapt to new hosts.
How does H5N1 transmission occur between species?
H5N1 transmission primarily occurs through direct contact with infected birds, their droppings, or contaminated environments. The virus can also be transmitted to mammals, which has raised alarms about the possibility of further adaptations leading to human-to-human transmission.
What is the human flu risk associated with H5N1 bird flu?
The human flu risk associated with H5N1 bird flu is significant because the virus has been observed to infect humans, albeit rarely. With increasing cases in mammals and evidence of H5N1 adaptations, there is a rising concern that these changes could enhance its ability to spread among humans, potentially resulting in a pandemic.
Are there effective vaccines against H5N1 bird flu?
Currently, there are vaccines developed specifically for H5N1 bird flu, but their effectiveness can vary depending on the strain. Ongoing mutations pose challenges to vaccine efficacy, highlighting the need for further research and adaptation of vaccines to match the evolving virus.
What measures are being taken to monitor H5N1 bird flu outbreaks?
Experts emphasize the importance of intensified monitoring and global surveillance efforts to track H5N1 bird flu outbreaks. This includes studying the virus’s transmission dynamics, updating public health strategies, and implementing rapid response measures to mitigate potential impacts of a bird flu pandemic.
Could H5N1 lead to a new bird flu pandemic?
Yes, the potential for H5N1 to lead to a new bird flu pandemic is a growing concern among researchers. Its increasing ability to infect mammals and the rate of mutations suggest that it could evolve to spread more effectively among humans, necessitating proactive public health measures.
What role do environmental conditions play in H5N1 bird flu transmission?
Environmental conditions play a crucial role in H5N1 bird flu transmission by influencing the virus’s survival and spread among hosts. Changes in climate, habitat, and wildlife interactions can affect how often the virus circulates and its potential to infect new species, including humans.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Risk of Human Pandemic | H5N1 is adapting to infect mammals, increasing the chances of human transmission. |
| Recent Cases in North America | At least 68 infections and 1 death reported, indicating the virus’s impact on humans. |
| Need for Increased Monitoring | As the virus evolves, experts emphasize the necessity for vigilant surveillance and research on its transmission. |
| Historical Context | Past influenza pandemics call for proactive global response strategies to mitigate potential outbreaks. |
| Research Gaps | Limited data on transmission rates and vaccine effectiveness against H5N1 strains. |
| Global Collaboration | Enhanced cooperation among scientists could lead to better understanding and management of the virus. |
Summary
H5N1 bird flu poses a significant risk for a potential human pandemic as the virus adapts to mammalian hosts, increasing its chances of spreading among humans. The alarming rise in cases, especially in North America, highlights the urgent need for heightened surveillance and research to monitor transmission dynamics. Furthermore, historical precedents indicate that the consequences of a bird flu pandemic could be severe, necessitating robust preparedness and response strategies from the global health community.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.