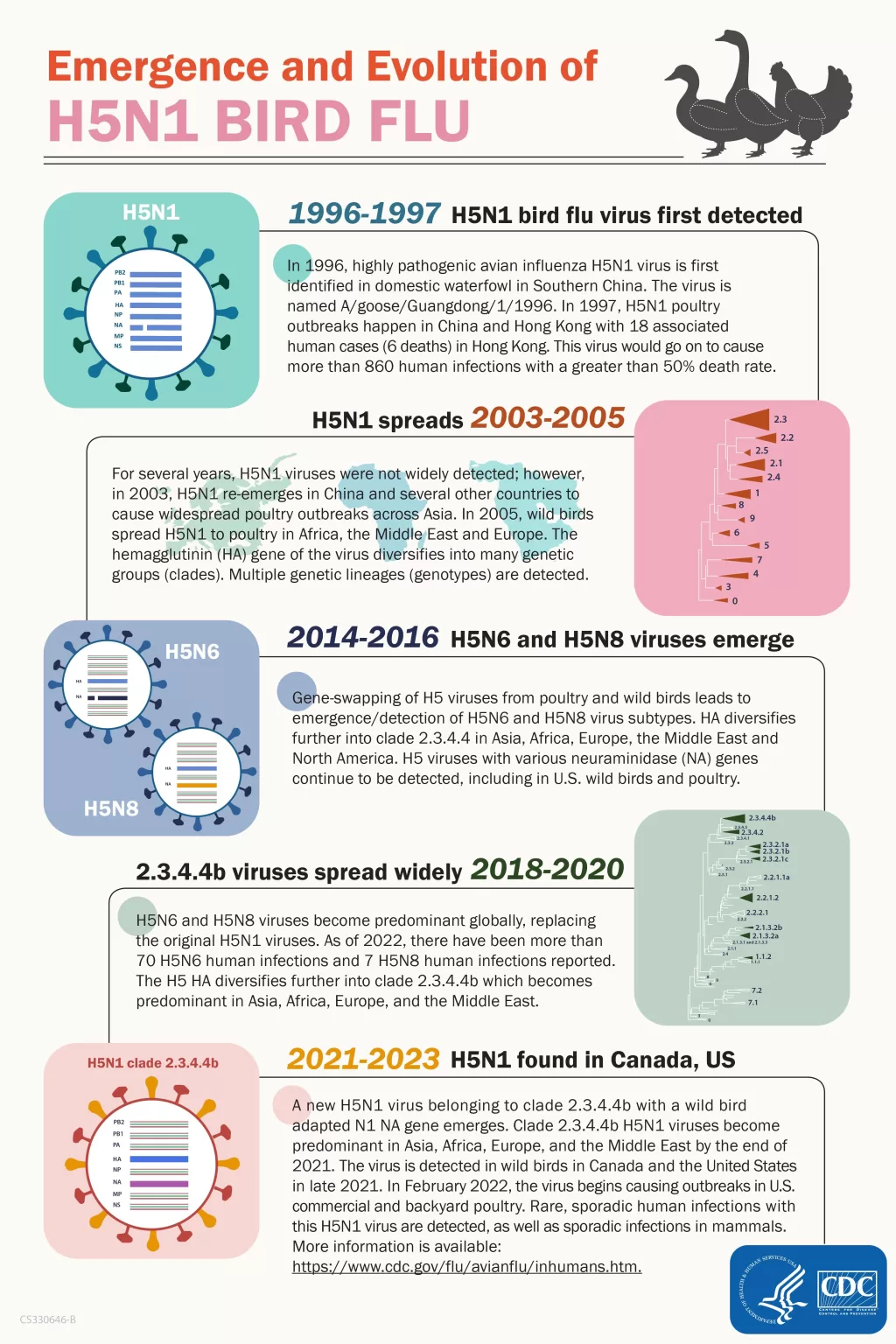
H5N1 bird flu has emerged as a significant concern for public health, especially following the tragic news of the first bird flu death reported in the United States. On January 6, 2025, the CDC confirmed that an individual in Louisiana succumbed to severe avian influenza A(H5N1) illness. This heartbreaking event marks a critical moment in the ongoing battle against H5N1, with the CDC noting that there have been 66 confirmed human cases in the U.S. since 2024 alone. While the risk to the general public remains low, this incident emphasizes the serious potential of H5N1 to cause severe illness and death, reminiscent of avian influenza deaths worldwide. Authorities are closely monitoring H5N1 cases in the USA and continue to provide public health guidance to mitigate risks associated with bird flu.
Avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, represents a complex public health issue that has garnered international attention. The recent report of H5N1’s deadly impact underscores the pressing need for heightened awareness of this viral infection, particularly its potential to leap from birds to humans. With the CDC documenting its first severe case of H5N1 in the U.S., it highlights the ongoing public health challenges posed by this zoonotic disease. As the number of H5N1 cases increases, especially among those in contact with infected birds, preventive measures are crucial for safeguarding human health. Understanding the dynamics of these infections is vital for effectively managing their risks and protecting communities from future outbreaks.
First Reported H5N1 Bird Flu Death in the U.S.
On January 6, 2025, the CDC tragically announced the first recorded death from H5N1 bird flu in the United States, marking a significant point in public health concerns. This incident involved a patient who had been hospitalized due to severe avian influenza A(H5N1) in Louisiana. Such a death, while heart-wrenching, aligns with the historical understanding of H5N1’s potential lethality, which has been a topic of consistent research and surveillance by health organizations globally.
Since 2024, the U.S. has seen a total of 66 confirmed human cases of H5N1 bird flu, with 67 reported since 2022. The CDC’s analysis assures that while the risk to the general population remains low, particularly due to the absence of human-to-human transmission detected, the number of avian influenza deaths worldwide, half of which have occurred among reported cases, remains a significant public health alert. Continuous monitoring and investigations are ongoing to understand better the implications of H5N1 cases in the USA and ensure public safety.
Understanding Avian Influenza Deaths
Avian influenza deaths, particularly those caused by the H5N1 strain, have been observed as part of a broader narrative regarding zoonotic diseases that can leap from animals to humans. The CDC emphasizes the likelihood of H5N1 cases being linked predominantly to direct contact with infected birds or environments where they reside. This reinforces the necessity for heightened surveillance and preventive measures, especially among individuals who routinely engage with birds in agricultural or recreational contexts.
Moreover, the CDC continues to underscore the importance of understanding how avian influenza strains, like H5N1, impact both public health and farming economies. Recommendations to protect oneself from H5N1 and other avian flu variants include avoiding interactions with sick or dead birds and understanding the symptoms of H5N1 infection. As the world has become more interconnected, monitoring avian influenza deaths globally must remain a priority to prevent outbreaks from escalating.
CDC’s Role in Monitoring H5N1 Cases in the USA
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a pivotal role in managing and monitoring H5N1 bird flu cases within the United States. Their proactive approach includes close collaboration with state and local health departments to conduct extensive epidemiological investigations. This includes tracking exposure levels among people who may have come into contact with infected birds and ensuring that appropriate public health responses are implemented immediately.
In addition to investigating confirmed cases of H5N1, and corresponding avian influenza deaths, the CDC is vigilant about potential viral changes that might enhance the viruses’ ability to spread among mammals. Through active surveillance programs and research initiatives, the agency aims to detect any mutations in the virus that could affect transmissibility or the efficacy of current vaccines and antiviral medications.
Public Health Implications of H5N1 Bird Flu
The emergence of H5N1 bird flu in humans raises several public health implications that demand immediate attention from health officials worldwide. The CDC and other health organizations stress the importance of public awareness regarding the potential risks associated with avian influenza. This includes understanding how bird flu can impact not just individual health but also the broader community through potential outbreaks.
Furthermore, while the risk to the general population has been assessed as low, especially given that no person-to-person transmission has been reported, the importance of preparedness and education surrounding bird flu continues to be paramount. Public health campaigns designed to inform citizens about H5N1, its transmission routes, and prevention measures are essential to mitigate risks and promote awareness.
The Role of Surveillance in H5N1 Management
Effective surveillance is instrumental in managing H5N1 bird flu cases and preventing potential outbreaks. The CDC’s continuous monitoring strategies involve detailed analysis of reported cases and active engagement with local health authorities. This process allows for the immediate application of necessary precautions to shield at-risk populations while ensuring informed decision-making across public health departments.
Through targeted surveillance of H5N1, public health entities can anticipate potential changes in virus transmission dynamics, enabling rapid response mechanisms. This monitoring not only applies to human cases but also extends to observing how the virus behaves in avian populations, thereby maintaining a preventative posture against possible zoonotic spillover events.
Community Engagement in Bird Flu Prevention
Community engagement forms a cornerstone of effective bird flu prevention strategies. The CDC advocates for inclusive dialogue between health officials and the communities most likely to encounter H5N1—the agricultural sectors and individuals involved in bird keeping. Providing localized prevention resources and education materials ensures that individuals are adequately informed about the potential risks associated with bird flu.
Informed communities become empowered to take proactive steps when it comes to avoiding H5N1 infections, such as proper hygiene practices around poultry and understanding how to report sick birds. This involvement enriches public health efforts and fosters a collective responsibility in minimizing the spread of avian influenza.
Future Directions in H5N1 Research
The future of H5N1 research is crucial in understanding the complexities of avian influenza and its impact on human health. As new strains emerge, scientific inquiry must adapt to address these changes comprehensively. Studies focusing on the virology of H5N1, its transmission mechanisms, and potential vaccine development will continue to be a priority for the CDC and global health partners.
Through collaboration with international health organizations, the CDC aims to foster advancements in research that can lead to more effective prevention strategies. Promoting funding and resources for H5N1 research will bolster public health initiatives, ensuring that preparedness against avian influenza remains at the forefront of global health agenda in the years to come.
Impacts of H5N1 on Poultry Industry
H5N1 bird flu poses significant threats to the poultry industry, affecting not only animal health but also economic stability and food security. The detection of H5N1 in domestic flocks can lead to stringent culling measures and trade restrictions, which in turn affect farmers’ livelihoods and food supply chains. The CDC continuously monitors bird populations to identify outbreaks swiftly and mitigate their impacts.
Additionally, public health organizations collaborate with the poultry industry to implement biosecurity measures to prevent the spread of H5N1. These measures are critical in maintaining consumer confidence and ensuring the sustainable operation of poultry farms across the U.S. Continued investment in biosecurity research and best practices is crucial for protecting both animal and human health.
Global Context of H5N1 Cases
Globally, H5N1 cases have raised alarm bells among health experts due to their association with high fatality rates in reported cases, underpinning the need for global readiness. With roughly half of the over 950 reported cases leading to death, the ongoing monitoring and reporting of H5N1 bird flu are critical for understanding and managing the threat it poses. Collaborative initiatives across nations aim to improve response protocols and public health education.
The global community, including organizations like the World Health Organization, is focused on enhancing surveillance systems to track H5N1 cases effectively. Establishing stringent guidelines for outbreak response will be key to averting vast public health crises, particularly in areas where the virus presents a higher risk owing to environmental and agricultural conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest statistics on H5N1 bird flu cases in the USA?
As of January 6, 2025, there have been 66 confirmed human cases of H5N1 bird flu in the United States since 2024 and 67 cases since 2022. This includes the first reported death due to H5N1 bird flu in Louisiana.
How many deaths have been caused by H5N1 bird flu in the USA?
As of January 6, 2025, the recent death in Louisiana marks the first death from H5N1 bird flu in the United States. Globally, the virus has resulted in significant mortality, with approximately half of the over 950 cases reported to the WHO resulting in death.
What does the CDC H5N1 report indicate about public health risks?
The CDC H5N1 report indicates that, despite the confirmed cases in the US, the overall risk to the general public remains low. Most infections arise from animal-to-human exposure, and currently, there is no evidence of person-to-person transmission of H5N1 bird flu.
What precautions should individuals take to avoid H5N1 bird flu infection?
Individuals, particularly those with occupational or recreational exposure to infected birds or animals, should follow CDC recommendations for prevention. This includes avoiding contact with sick birds and practicing good hygiene when handling poultry.
Are there any effective vaccines for H5N1 bird flu?
While there are candidate vaccine viruses for H5N1 bird flu, the CDC is monitoring for any changes in the virus that may affect vaccine effectiveness. Currently, no specific H5N1 vaccine is widely available for the general public.
How does H5N1 bird flu spread to humans?
H5N1 bird flu typically spreads to humans through direct contact with infected birds or contaminated environments. The majority of human cases have occurred in individuals who had occupational exposure to infected poultry.
What is the CDC doing about H5N1 bird flu and public health?
The CDC is actively supporting epidemiologic investigations related to H5N1 bird flu, collaborating with state and local partners on surveillance, and monitoring for any changes that could increase the risk of human infection or more severe outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| First Death from H5N1 | A person in Louisiana has died after being hospitalized with severe H5N1 bird flu. |
| Confirmed Cases | 66 confirmed human cases of H5N1 bird flu reported in the U.S. since 2024. |
| Global Cases | Over 950 global cases reported, with approximately half resulting in death. |
| Risk Assessment | CDC assesses the risk to the general public as low, with no person-to-person transmission identified. |
| Preventive Measures | CDC has developed resources for individuals at higher risk due to exposure to infected birds. |
Summary
H5N1 bird flu remains a serious concern, as highlighted by the recent report of the first death in the United States. While the CDC emphasizes that the risk to the general population is low, it underscores the importance of continued surveillance and preventive measures, particularly for those with direct exposure to infected animals. The ongoing monitoring of H5N1 virus changes is crucial in protecting public health and preventing future outbreaks.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.