Understanding gout triggers is crucial for those who suffer from this painful condition, as they can lead to debilitating gout flare-ups. Common triggers include high-purine foods such as red meat and seafood, which can significantly elevate uric acid levels in the body. These elevated uric acid levels contribute to the formation of needle-like crystals in the joints, resulting in painful gout symptoms. Moreover, beverages high in fructose and certain medications can exacerbate the situation, making it essential for individuals with gout to be mindful of their gout diet. By recognizing and avoiding these triggers, you can effectively manage your condition and reduce the frequency of painful attacks.
When exploring the factors that contribute to uncomfortable joint pain, it’s vital to consider the elements that can influence gout episodes. The term ‘gout triggers’ encompasses a wide range of external and internal factors that may potentiate gout attacks, including dietary choices and certain medical treatments. Many individuals may be surprised to learn that common items on their grocery list—like rich meats and sweetened beverages—can significantly affect their uric acid levels and hence their overall joint health. By understanding these dietary nuances and recognizing how various substances play a role in managing inflammation, sufferers can pave the way for a healthier, more symptom-free lifestyle. Additionally, keeping a vigilant eye on factors such as weight and stress levels can further empower those at risk to proactively combat their condition.
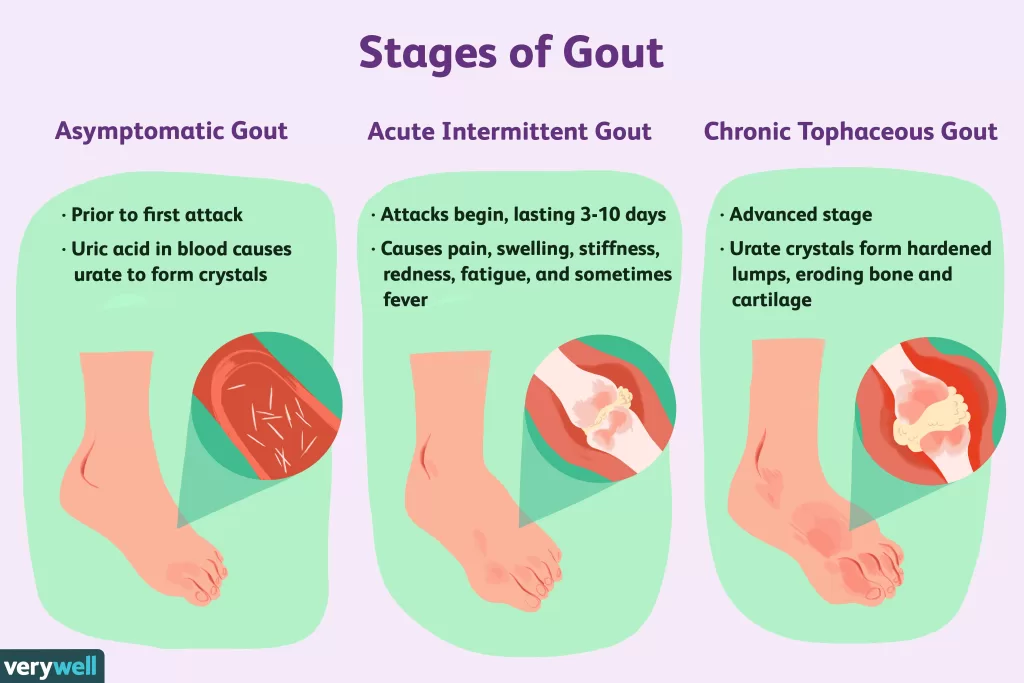
Understanding Gout Symptoms and Their Impact
Gout symptoms typically manifest suddenly and can vary in intensity, often starting with a sharp pain in the big toe or other joints. This pain can be so severe that it’s practically impossible to touch the affected area. In addition to the intense pain, many individuals experience swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, signaling an attack. These symptoms may persist for several days to weeks, often causing significant discomfort and limiting mobility.
Aside from the physical pain, gout symptoms can also have emotional and psychological impacts. People suffering from gout may experience anxiety about their condition, leading to heightened awareness of their dietary choices and lifestyle habits. The unpredictable nature of gout flare-ups can create stress, as individuals fear the next attack and its potential disruption to their daily lives.
Recognizing Gout Triggers in Your Diet
Identifying gout triggers in your diet is essential for managing this condition effectively. Foods high in purines, primarily found in certain meats and seafood, are notorious for increasing uric acid levels in the body. By avoiding or reducing the intake of foods like red meat, organ meats, and shellfish, individuals can potentially lower the frequency and severity of gout flare-ups. Understanding which foods are safe can empower individuals to craft a balanced gout diet that minimizes the risk of painful attacks.
In addition to meats, alcohol and sugary beverages are significant contributors to increased uric acid levels. Heavy drinking, particularly beer, can trigger gout symptoms quickly due to the high purine content. Moreover, drinks high in fructose can elevate uric acid levels in the blood. Whenever possible, opting for non-alcoholic drinks and monitoring sugar intake can be crucial for those prone to gout.
The Role of Medications in Gout Management
Certain medications can inadvertently raise uric acid levels or trigger gout flare-ups. For example, diuretics, often prescribed for high blood pressure, can lead to an increase in uric acid retention, making attacks more likely. Additionally, low-dose aspirin has been shown to raise uric acid levels, presenting a paradox for patients who may need it for cardiovascular health. Therefore, it is vital for individuals with gout to discuss their medications with healthcare providers to ensure their regimen supports their overall health.
When managing gout, it’s essential to recognize that not all medications will lead to increased uric acid levels. There are medications specifically designed to lower uric acid and prevent flare-ups. Learning more about these options and consulting with a healthcare provider about the best treatments available can significantly impact the quality of life for those suffering from gout.
Dehydration: A Hidden Gout Trigger
Dehydration is often an overlooked factor that can contribute to increased uric acid levels and subsequent gout flare-ups. When the body is dehydrated, uric acid is less effectively eliminated through urine, leading to heightened concentrations in the bloodstream. This accumulation can result in the formation of painful crystals in the joints, which is the hallmark of a gout attack. Adequate hydration is crucial, especially for individuals who are prone to this condition.
Being aware of hydration status and ensuring adequate fluid intake can make a significant difference in gout management. Individuals are encouraged to drink ample water throughout the day, particularly if they are in hot conditions or have been engaging in physical activities. Staying hydrated not only aids in uric acid elimination but also supports overall joint health, potentially reducing the frequency of gout flare-ups.
Gout and Weight Management: A Delicate Balance
Maintaining a healthy weight is critical for individuals dealing with gout, as being overweight or obese significantly increases the risk of developing this painful condition. Excess body weight can lead to higher production of uric acid and decreased elimination from the body, creating a perfect storm for gout flare-ups. Therefore, managing weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential for those with or at risk of gout.
Effective weight management requires a multifaceted approach, combining dietary changes with physical activity. It’s beneficial to focus on a gout diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, while avoiding purine-rich foods. Gradual weight loss rather than extreme dieting is preferable, as rapid weight reduction can also spike uric acid levels, potentially triggering flare-ups.
Stress Management as a Gout Prevention Strategy
Stress is another factor that may contribute to elevated uric acid levels and subsequent gout flare-ups. While the exact relationship between stress and gout is still being studied, it is generally understood that prolonged stress can affect body physiology, potentially leading to increased uric acid production. Managing stress effectively through techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and physical activity may assist in reducing the likelihood of gout attacks.
Incorporating stress-relief strategies into daily routines can also improve overall well-being, which is essential for anyone managing a chronic condition like gout. By prioritizing mental health alongside physical health, individuals may find it easier to navigate the complexities of their diet, lifestyle, and medication management, ultimately reducing the stress associated with living with gout.
Temperature Changes and Their Effects on Gout
Temperature fluctuations can significantly impact the body’s uric acid levels and contribute to gout flare-ups. For instance, warm temperatures can lead to dehydration, which in turn increases uric acid concentrations in the bloodstream. People living in very hot climates or during summer months might find themselves more susceptible to gout attacks due to these temperature-related changes.
To mitigate the impact of temperature changes, individuals should remain vigilant about staying hydrated, particularly when temperatures rise. Wearing breathable clothing and avoiding excessive heat exposure can also help maintain a stable internal environment, reducing the risk of uric acid build-up and preventing painful gout flare-ups.
Keeping Track of Gout Triggers with a Journal
Keeping a detailed journal of dietary intake, activities, and any accompanying symptoms can be an invaluable tool for individuals with gout. By meticulously noting what foods, medications, or lifestyle changes coincide with flare-ups, individuals can begin to identify patterns and specific triggers that lead to increased uric acid levels and subsequent attacks. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed choices regarding their diets and lifestyle.
Additionally, recording your experience can help establish a dialogue with healthcare professionals, enabling more tailored management strategies. The insight gained from tracking triggers can assist in modifying diets to avoid certain high-purine foods and understanding which habits may need adjusting to improve overall health outcomes and minimize the risk of gout flare-ups.
A Comprehensive Review of Gout Management Strategies
In conclusion, effectively managing gout requires a multifaceted approach that considers dietary choices, medications, hydration, weight management, and stress levels. By prioritizing low-purine foods, staying hydrated, and monitoring body weight, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of gout flare-ups. Being aware of personal triggers, whether they are food-related, environmental, or related to lifestyle factors, is crucial for effective management.
Incorporating regular consultations with healthcare providers ensures that individuals are receiving the best possible guidance on preventing and managing gout symptoms. By understanding and addressing various gout triggers, individuals can achieve a better quality of life and minimize the impact of this condition on their daily activities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What foods should I avoid to prevent gout flare-ups?
To prevent gout flare-ups, avoid foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats (like liver), shellfish (including shrimp and lobster), and anchovies. High-fructose foods and drinks, such as sugary beverages and certain desserts, should also be limited as they can raise uric acid levels.
How do alcohol consumption and gout flare-ups relate?
Alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits, can raise uric acid levels in the blood, increasing the risk of gout flare-ups. Even moderate alcohol intake has been linked to a significantly higher risk of gout attacks.
Can dehydration trigger gout symptoms?
Yes, dehydration contributes to higher uric acid levels in the body. Insufficient fluid intake reduces uric acid elimination through urine, making dehydration a significant trigger for gout symptoms and flare-ups.
What role do medications play in triggering gout attacks?
Certain medications, including low-dose aspirin and diuretics, can elevate uric acid levels, increasing the risk of gout attacks. It’s essential to consult your healthcare provider before altering any medications.
How does body weight affect gout flare-ups?
Being overweight or having a high body mass index (BMI) raises the risk of gout due to increased uric acid production. Weight loss through a proper diet and exercise may help lower uric acid levels and prevent future flare-ups.
Are there certain drinks that can trigger gout attacks?
Yes, drinks high in fructose, such as soft drinks and fruit juices, can elevate uric acid levels, increasing the risk of gout attacks. Limiting these beverages can help manage gout symptoms.
Can environmental factors trigger gout flare-ups?
Yes, temperature changes can trigger gout flare-ups as high heat often leads to dehydration, which raises uric acid levels. Maintaining proper hydration is crucial during extreme temperatures.
What should I track to identify personal gout triggers?
Keeping a journal of your food intake, activities, medications, and stress levels can help identify personal gout triggers. Noting what precedes flare-ups can assist in managing and preventing future attacks.
How does stress contribute to gout flare-ups?
While more research is needed, there is evidence that stress may raise uric acid levels, potentially triggering gout flare-ups. Managing stress through relaxation techniques may help in gout management.
What type of diet is best for managing gout and preventing flare-ups?
A gout diet should focus on low-purine foods, including low-fat dairy, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. It’s also beneficial to stay well-hydrated and limit intake of high-purine foods and sugary drinks to manage uric acid levels.
| Type of Trigger | Examples | Effect on Uric Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Food Triggers | – Red Meat (beef, lamb) – Organ Meats (liver, kidney) – Seafood (sardines, lobster, shrimp) | Raise uric acid levels significantly. |
| Alcohol | – Beer – Wine – Spirits | Increases uric acid levels; more consumption raises risk. |
| Fructose-rich Foods | – Soft Drinks – Fruit Juices – Sweets (cookies, candy) | Elevates uric acid in the bloodstream. |
| Health Conditions | – Cardiovascular Disease – Kidney Disease | Can elevate uric acid levels. |
| Dehydration | – Inadequate water intake | Leads to higher uric acid levels due to reduced elimination. |
| Medications | – Low-dose Aspirin – Diuretics | May raise uric acid levels and risk of attacks. |
| Weight Issues | – High Body Mass Index (BMI) | Being overweight increases uric acid levels. |
| Stress and Temperature Changes | – Stressful situations – High temperatures | May contribute to higher uric acid levels. |
Summary
Gout triggers can significantly impact those suffering from this form of arthritis, leading to painful flare-ups. Identifying various triggers such as certain foods, medications, and health conditions is crucial for effective management of gout. By staying aware of food choices and lifestyle factors, individuals can mitigate their risk of attacks, ensure a better quality of life, and reduce the frequency of gout flare-ups.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.