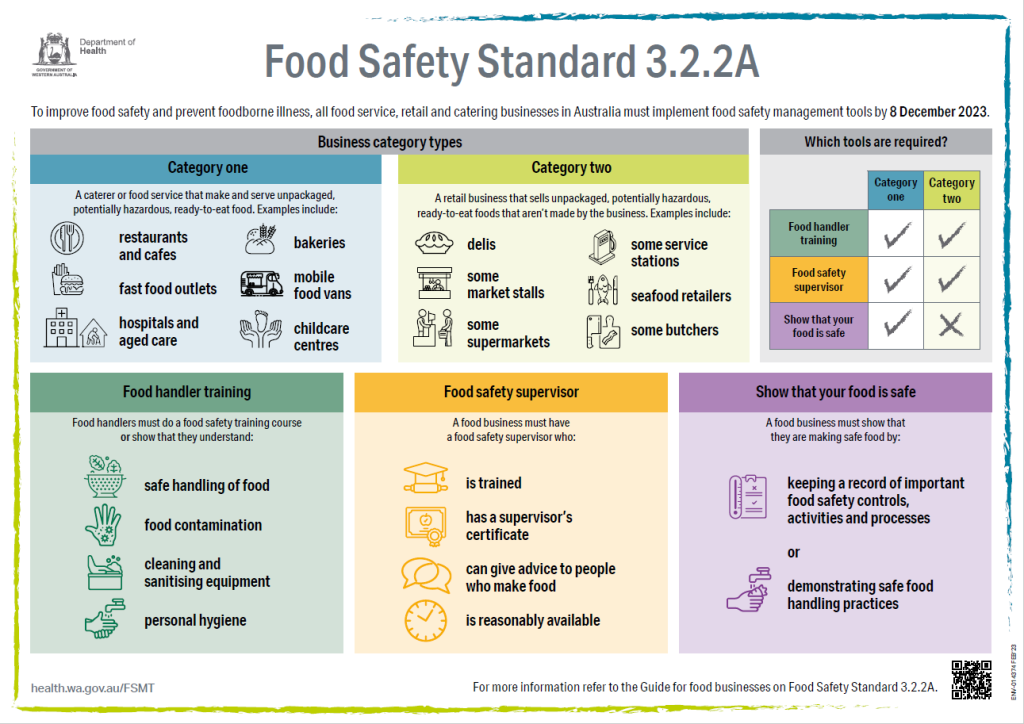
Food safety standards play a crucial role in protecting public health by ensuring that meat and poultry products are safe for consumption. The recent Government Accountability Office (GAO) report highlights the urgent need for the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) to finalize regulations addressing harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Campylobacter, which are known to cause foodborne illnesses. With thousands of cases reported annually, including outbreaks linked to Listeria in food, the importance of stringent food safety regulations cannot be overstated. The USDA’s ongoing challenges, as noted in the GAO report, emphasize the necessity for updated standards to mitigate risks associated with these pathogens. As the USDA navigates through these Salmonella regulations, the health and safety of consumers hang in the balance.
Standards for food safety encompass a broad range of regulations designed to safeguard the public from health risks associated with contaminated food products. The GAO’s recent findings underscore the urgent need for the USDA to address critical pathogens such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, which pose significant threats to consumer health. This need for enhanced oversight is further highlighted by the alarming statistics related to foodborne illnesses, including those caused by the presence of Listeria in food products. As the USDA grapples with the complexities of implementing these vital standards, the call for a more robust framework to address these challenges becomes increasingly pressing. Ensuring that food safety protocols are effectively established and maintained will ultimately protect millions of Americans from potential health hazards.
Understanding Food Safety Standards for Salmonella
Food safety standards are critical in preventing foodborne illnesses caused by bacteria like Salmonella. The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) has recognized the severity of Salmonella contamination, particularly in raw poultry and meat products. The recent GAO report emphasizes the need for the USDA to finalize these standards, which have been stalled since 2019. Implementing rigorous regulations will not only help in safeguarding public health but will also enhance consumer confidence in meat and poultry products. Without definitive standards, the risks associated with Salmonella remain high, leading to potential outbreaks and significant health implications.
Moreover, the establishment of clear Salmonella regulations is essential for meat processing facilities to implement effective control measures. The GAO report suggests that a prioritization plan is necessary to identify which meat products require immediate attention, highlighting the importance of establishing standards that can mitigate the risks associated with this pathogen. By focusing on high-risk products, the USDA can ensure that food safety protocols are tailored to the specific challenges posed by Salmonella, ultimately protecting consumers from foodborne illnesses.
The Importance of Campylobacter Standards
Campylobacter is another significant pathogen that poses a serious threat to food safety, particularly in poultry products. The GAO has pointed out that the USDA has not revised any standards for Campylobacter since 2018, which raises concerns about the effectiveness of current food safety measures. Given that Campylobacter is one of the leading causes of bacterial food poisoning in the United States, the need for updated regulations becomes increasingly urgent. The GAO report advocates for the development of specific standards for Campylobacter in turkey parts, which would help to mitigate the risks associated with this pathogen.
Updating Campylobacter standards is not just about compliance; it also involves understanding the broader implications for public health. The GAO report emphasizes the need for a comprehensive assessment of the public health impacts of delaying these standards. By establishing stringent regulations and guidelines, the USDA can help to reduce the incidence of Campylobacter-related illnesses, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for consumers. In conclusion, prioritizing the development of Campylobacter standards is a crucial step towards enhancing food safety and protecting public health.
Listeria in Food: Addressing the Risks
Listeria is a particularly dangerous bacterium that can thrive in refrigerated foods and poses a significant risk to vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women and the elderly. The recent outbreak linked to Listeria-contaminated Boar’s Head deli meat serves as a stark reminder of the potential dangers present in our food supply. The GAO report highlights that harmful bacteria affect one in six Americans each year, leading to thousands of deaths. This alarming statistic underscores the need for robust food safety standards to address the risks associated with Listeria and protect consumers from foodborne illnesses.
To combat the threat of Listeria, the USDA must prioritize the development and implementation of effective food safety regulations. This includes creating educational materials for food processing facilities to reduce the spread of Listeria and other pathogens. By enhancing compliance with food safety standards, the USDA can play a pivotal role in minimizing the risks associated with Listeria in food products. Addressing this issue is vital not only for safeguarding public health but also for ensuring the integrity of the food supply chain.
Food Safety Oversight: Challenges and Solutions
The GAO report has identified the improvement of federal oversight of food safety as a high-risk area. Since 2007, there has been increasing concern over the ability of the USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) to effectively manage food safety standards for pathogens like Salmonella and Campylobacter. The lack of a clear prioritization plan and timeline for resuming work on these crucial standards has resulted in oversight gaps that could jeopardize public health. Addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring the safety of meat and poultry products in the market.
To enhance food safety oversight, the GAO recommends that FSIS develop a comprehensive plan that outlines the necessary steps to finalize standards for Salmonella and Campylobacter. Additionally, updating the memorandum of understanding (MOU) with APHIS is critical for clarifying the respective responsibilities of each agency in managing foodborne pathogens. By fostering better coordination and communication between these agencies, the USDA can create a more effective food safety framework that addresses the challenges posed by harmful bacteria in the food supply.
Recommendations for Enhancing Food Safety Protocols
The GAO report outlines several recommendations aimed at improving food safety protocols within the USDA. One key recommendation is for FSIS to develop a prioritization plan that identifies which food products require immediate attention to mitigate the risks associated with Salmonella and Campylobacter. By systematically documenting the necessary policies and actions, the USDA can better allocate resources and focus on high-risk areas that need urgent regulatory attention. This strategic approach will help in reducing foodborne illnesses and enhancing overall food safety.
Furthermore, the GAO emphasizes the importance of assessing the public health impacts of delaying proposed standards for harmful pathogens. Understanding these implications will allow the USDA to make informed decisions regarding food safety priorities. Additionally, providing educational materials to regulated facilities is essential for improving compliance with food safety regulations. By equipping meat and poultry processing plants with the necessary knowledge and resources, the USDA can foster a culture of safety that prioritizes the health and well-being of consumers.
The Role of the USDA in Food Safety
The USDA plays a crucial role in ensuring food safety standards are upheld in the meat and poultry industry. As highlighted in the GAO report, the USDA’s FSIS is responsible for establishing and enforcing regulations that protect consumers from foodborne pathogens like Salmonella and Campylobacter. However, the lack of finalized standards since 2018 has raised concerns about the effectiveness of current oversight mechanisms. It is imperative for the USDA to take decisive action in updating and implementing these standards to safeguard public health.
In addition to regulatory functions, the USDA also collaborates with other agencies, such as APHIS, to address food safety concerns comprehensively. The GAO report recommends updating the MOU between these agencies to clarify their responsibilities regarding pathogen management from farms to processing plants. By enhancing inter-agency coordination, the USDA can create a more robust food safety system that effectively tackles the challenges posed by various foodborne pathogens.
Impact of Foodborne Illness Outbreaks on Public Health
Foodborne illness outbreaks have significant implications for public health, as evidenced by the GAO report highlighting the annual impact of harmful bacteria in food. The report notes that one in six Americans is affected by foodborne illnesses each year, resulting in thousands of hospitalizations and deaths. These statistics underscore the critical need for effective food safety standards that can prevent such outbreaks and protect the health of consumers. The recent Listeria outbreak linked to deli meat serves as a reminder of the devastating consequences of inadequate food safety measures.
To mitigate the impact of foodborne illnesses, it is essential for regulatory agencies to establish and enforce stringent food safety standards. The GAO report advocates for the USDA to prioritize the completion of proposed standards for Salmonella and Campylobacter, which are prevalent in meat and poultry products. By addressing these pathogens through updated regulations, the USDA can significantly reduce the likelihood of future outbreaks and enhance overall public health outcomes.
Educating Consumers on Food Safety
Consumer education is a vital component of food safety that often goes overlooked. The GAO report emphasizes the need for educational materials that inform the public about safe food handling practices, particularly concerning meat and poultry products. By providing consumers with knowledge about proper cooking, storage, and preparation techniques, the USDA can empower individuals to take an active role in preventing foodborne illnesses. This proactive approach not only enhances public health but also fosters consumer confidence in the safety of the food supply.
Furthermore, educational initiatives can help to bridge the gap between regulatory standards and consumer practices. The USDA should consider implementing outreach programs that promote awareness of food safety regulations and the importance of compliance among food processing facilities. By encouraging a shared responsibility for food safety between regulators, industry stakeholders, and consumers, the USDA can create a more comprehensive strategy to combat foodborne pathogens and protect public health.
Future Directions for Food Safety Regulations
The future of food safety regulations in the United States hinges on the USDA’s ability to adapt and respond to emerging threats posed by foodborne pathogens. The GAO report outlines the critical need for the USDA to finalize standards for Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Listeria in meat and poultry products. As food safety challenges continue to evolve, it is imperative for the USDA to stay ahead of potential risks through proactive regulatory measures and continuous assessment of food safety protocols.
Additionally, the USDA should foster collaboration with industry stakeholders and public health organizations to develop innovative solutions to enhance food safety. The GAO report suggests that a collaborative approach will not only improve compliance with food safety standards but also drive advancements in food safety technology and practices. By embracing a forward-thinking mindset, the USDA can ensure that food safety regulations remain effective and relevant in the face of changing consumer needs and evolving food safety challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current USDA food safety standards for Salmonella in meat products?
As of now, the USDA has classified Salmonella as harmful when present in high levels in uncooked breaded stuffed chicken products. However, no new standards for Salmonella in raw ground beef, beef trimmings, or other meat products have been finalized since 2019. The USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) is working on developing a framework for Salmonella standards in raw poultry.
How does the GAO report address Campylobacter standards in food safety?
The GAO report highlights that FSIS has not established any updated standards for Campylobacter in meat and poultry products since 2018. It recommends that FSIS prioritize the development of policies to mitigate the risks of Campylobacter, specifically in turkey parts, to enhance food safety standards.
What role does the GAO play in food safety regulation for Listeria in food products?
The GAO monitors food safety regulations and reported on the need for the FSIS to create and revise standards for harmful bacteria like Listeria. The recent outbreak linked to Listeria-contaminated deli meat emphasizes the importance of establishing stricter food safety standards to protect public health.
Why are Salmonella regulations considered a high-risk area according to the GAO?
Salmonella regulations are classified as a high-risk area because the GAO has identified persistent gaps in federal oversight and the lack of finalized standards by FSIS. This indicates that without proper regulations, there is an increased risk of foodborne illnesses related to Salmonella, affecting public health.
What recommendations did the GAO provide for improving USDA food safety standards?
The GAO recommended that FSIS develop a prioritization plan for addressing food products at risk of Salmonella and Campylobacter contamination, assess the public health impacts of delayed standards, update its MOU with APHIS for better coordination, and provide educational materials to aid compliance with food safety regulations.
How often do foodborne illnesses occur due to bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria?
Foodborne illnesses, particularly from bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria, affect approximately one in six people in the United States annually, resulting in thousands of hospitalizations and deaths. This highlights the critical need for effective food safety standards.
What are the implications of paused work on food safety standards for Campylobacter?
The suspension of work on Campylobacter standards since 2019 raises concerns about the potential risks associated with this pathogen in meat products. The GAO report emphasizes the necessity for FSIS to resume efforts to finalize these standards to ensure better oversight and protection against foodborne illnesses.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| GAO Report Release | US GAO urged USDA to finalize food safety standards for Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Listeria. |
| Background on FSIS | FSIS has paused work on four standards since 2019 and has not updated standards for disease-causing pathogens recently. |
| Salmonella Classification | USDA classified Salmonella as harmful in high levels in uncooked breaded chicken, but no new standards have been finalized. |
| Regulatory Proposals | Proposed regulations for Salmonella and Campylobacter have been suspended or delayed since 2019. |
| High-Risk Area | GAO has listed food safety oversight as a high-risk area since 2007 due to ongoing challenges. |
| Jurisdiction Issues | FSIS’s jurisdiction is limited to meat processing; APHIS oversees pathogen contamination on farms. |
| Listeria Outbreak | A 2024 Listeria outbreak linked to deli meat affected 61 people and caused 10 deaths. |
| GAO Recommendations | GAO advised FSIS to create a prioritization plan, assess public health impacts, and update coordination agreements with APHIS. |
Summary
Food safety standards are critical for ensuring public health, and the recent GAO report highlights the pressing need for the USDA to finalize standards addressing Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Listeria in meat and poultry. With high-profile outbreaks and ongoing regulatory delays, it is essential for FSIS to establish clear guidelines and prioritize food safety to protect consumers from foodborne illnesses. The recommendations provided by the GAO aim to enhance coordination and response measures, ensuring that harmful pathogens are effectively managed throughout the food supply chain.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.