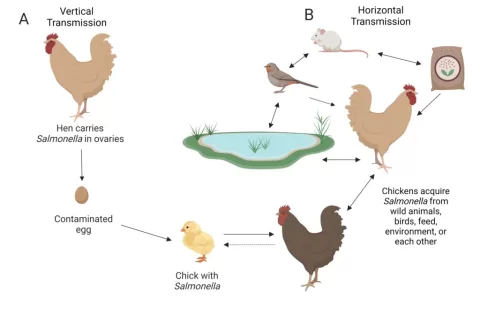
The FDA strategy for enteric viruses related to berries is a proactive initiative to enhance food safety and prevent outbreaks of illnesses such as hepatitis A and norovirus. Despite a long history of no domestic outbreaks linked to fresh or frozen berries, the agency recognizes the risks posed by imported products. Contamination can occur due to inadequate food safety practices, which makes the implementation of robust sanitary measures vital. By focusing on hygiene among field workers and the prevention of cross-contamination, the FDA aims to safeguard public health and bolster consumer confidence. This strategy underscores the importance of collaboration across the berry industry and regulatory bodies to address food safety outbreaks effectively.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has unveiled a comprehensive approach targeting viral contamination in berry products. This initiative aims to mitigate the risks of foodborne illnesses, including those caused by hepatitis A and norovirus. The strategy emphasizes the necessity for stringent sanitary practices throughout the berry supply chain, from harvesting to processing. By enhancing safety protocols and promoting preventive measures, the FDA seeks to ensure that both domestic and imported berries are safe for consumption. Collaboration among industry stakeholders and regulatory agencies is crucial to successfully implement these measures and reduce the threat of berry contamination.
Understanding the FDA Strategy for Enteric Viruses in Berries
The FDA’s strategy for tackling enteric viruses such as hepatitis A and norovirus focuses on the critical need for comprehensive food safety measures in the berry industry. Although no significant outbreaks have been reported from domestic sources in recent decades, the threat of contamination from imported berries remains a concern. By implementing rigorous sanitary practices, the FDA aims to mitigate risks associated with viral pathogens that can lead to foodborne illnesses.
This strategy emphasizes the importance of collaboration among various stakeholders, including regulatory bodies, the berry industry, and food safety experts. Through shared insights and collective action, the FDA is working to build a robust framework that fosters compliance with food safety standards and encourages the adoption of best practices across the supply chain. Ensuring that both domestic and international operations adhere to these guidelines is crucial for maintaining the integrity of berry products.
Key Measures for Hepatitis A Prevention in the Berry Industry
Preventing hepatitis A outbreaks linked to berries requires a multifaceted approach that addresses potential sources of contamination. The FDA’s strategy highlights the importance of implementing effective pre- and post-harvest sanitary practices. These include thorough training for field workers on hygiene and sanitation, as well as regular monitoring of sanitary facilities to ensure compliance with established safety standards.
Furthermore, the strategy advocates for the use of root-cause analysis in the event of food safety failures. This systematic approach allows the industry to identify the underlying causes of contamination and develop targeted solutions. By fostering a culture of accountability and continuous improvement, the berry industry can significantly reduce the risk of hepatitis A transmission through its products.
Norovirus Control: A Priority for Berry Safety
Norovirus is a highly contagious pathogen that poses a significant threat to food safety, particularly in fresh produce like berries. The FDA’s strategy underscores the need for rigorous controls to prevent norovirus contamination throughout the berry supply chain. This includes establishing stringent hygiene protocols for workers, as even asymptomatic individuals can harbor and transmit the virus.
In addition to preventive measures, the FDA encourages the berry industry to engage in scientific research aimed at understanding the persistence and detection of norovirus in agricultural environments. By expanding knowledge in this area, the industry can develop better strategies for monitoring and controlling potential outbreaks, ultimately protecting public health.
Implementing a Berry Contamination Strategy
The FDA’s contamination strategy for berries revolves around enhancing food safety protocols to prevent outbreaks. By focusing on both pre-harvest and post-harvest practices, the initiative aims to close gaps that could lead to foodborne illnesses. This includes rigorous training for farm workers, ensuring proper sanitation of facilities, and preventing cross-contamination during processing.
Additionally, the FDA stresses the importance of continuous monitoring for viral presence among farm workers and within processing environments. This level of vigilance not only helps identify potential contamination sources but also fosters a proactive rather than reactive approach to food safety in the berry industry.
Sanitary Practices for Berry Producers
Sanitary practices are at the core of the FDA’s strategy to ensure berry safety. Producers are encouraged to implement comprehensive sanitation protocols that cover all aspects of berry production, from field cultivation to packaging. This includes ensuring that all equipment and surfaces are properly sanitized and that workers follow strict hygiene practices to avoid cross-contamination.
By prioritizing sanitary practices, berry producers can significantly reduce the risk of enteric virus outbreaks. The FDA’s emphasis on education and compliance serves to reinforce the message that food safety is a shared responsibility among all players in the berry supply chain.
The Role of Collaboration in Food Safety
Collaboration is vital in addressing food safety challenges associated with enteric viruses in berries. The FDA has recognized that effective strategies require input and cooperation from various stakeholders, including government agencies, industry leaders, and food safety researchers. By working together, these groups can share valuable insights and develop comprehensive solutions to mitigate risks.
This collaborative approach not only enhances the understanding of food safety dynamics but also leads to the implementation of innovative practices that benefit the entire industry. Through partnerships, stakeholders can pool resources and knowledge, ultimately contributing to a safer environment for berry production and consumption.
Promoting Worker Vaccination to Prevent Outbreaks
One of the key recommendations from the FDA’s strategy is to promote worker vaccination as a preventive measure against hepatitis A and norovirus. Vaccination can significantly reduce the risk of transmission among workers, especially in environments where food is handled. By incentivizing vaccinations, the FDA aims to create safer working conditions that directly benefit food safety.
Encouraging vaccination not only protects workers but also enhances consumer confidence in berry products. When consumers know that stringent measures are in place to protect against viral contamination, they are more likely to trust and purchase these products, bolstering the economic viability of the berry industry.
Research and Innovation in Virus Detection
The FDA’s strategy places a strong emphasis on supporting research into improved methods for detecting enteric viruses in berries. This includes developing advanced laboratory techniques that can accurately identify and characterize viruses within various sample types. Enhanced detection methods are crucial for timely intervention and outbreak prevention.
By investing in research and fostering innovation, the FDA aims to equip the berry industry with the tools needed to proactively address contamination risks. This commitment to scientific advancement will not only protect public health but also ensure the sustainability and growth of the berry industry.
Understanding the Historical Context of Food Safety Outbreaks
An understanding of past food safety outbreaks is essential for developing effective prevention strategies. The FDA’s strategy is informed by historical data, which highlights the types of enteric viruses associated with berries and the circumstances that contributed to outbreaks. This historical perspective allows for a more targeted approach in addressing current risks.
By analyzing previous outbreaks, the FDA can identify patterns and vulnerabilities in the berry supply chain. This knowledge is invaluable in shaping policies and practices that enhance food safety, ensuring that the industry learns from the past to prevent future incidents.
The Importance of Compliance with Food Safety Standards
Compliance with FDA food safety standards is non-negotiable for ensuring the safety of berry products. The agency’s strategy encourages all stakeholders in the berry industry to adhere to these standards rigorously. This compliance is essential not only for protecting public health but also for maintaining the integrity of the berry supply chain.
Regular audits and assessments of compliance levels can help identify areas for improvement and reinforce the importance of food safety practices. By fostering a culture of accountability, the berry industry can significantly reduce the risk of contamination and enhance consumer trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the FDA strategy for preventing enteric viruses in berries?
The FDA strategy for preventing enteric viruses, such as hepatitis A and norovirus, in berries focuses on enhancing food safety standards and promoting sanitary practices throughout the berry production chain. This includes monitoring virus carriage among workers, ensuring proper hygiene in field operations, and preventing cross-contamination during processing.
How does the FDA address food safety outbreaks related to berries?
The FDA addresses food safety outbreaks related to berries by implementing a comprehensive strategy that emphasizes compliance with food safety standards, encourages effective sanitary practices, and promotes research on virus detection and mitigation in both fresh and frozen berries.
What preventive measures are recommended for hepatitis A prevention in the berry industry?
For hepatitis A prevention in the berry industry, the FDA recommends proper hygienic practices among field workers, management of sanitary facilities, and monitoring of workers for virus carriage to safeguard against potential contamination.
What role do sanitary practices play in the FDA berry contamination strategy?
Sanitary practices are crucial in the FDA berry contamination strategy as they help prevent the spread of enteric viruses. Consistent application of these practices among workers and in processing environments is essential to ensure the safety of both domestic and imported berries.
How can the berry industry control norovirus outbreaks according to the FDA?
The berry industry can control norovirus outbreaks by implementing effective pre- and post-harvest sanitary practices, ensuring proper hygiene among workers, and following the FDA’s guidelines for food safety compliance and monitoring.
What is the significance of collaboration in the FDA strategy for berries and enteric viruses?
Collaboration among regulators, the global berry industry, and stakeholders is significant in the FDA strategy for berries and enteric viruses as it fosters shared knowledge and resources, enhancing the overall effectiveness of food safety measures and outbreak prevention.
What incentives does the FDA propose for promoting worker vaccination in the berry industry?
The FDA proposes introducing incentives for the berry industry and governments to promote worker vaccination as a critical measure to prevent the spread of enteric viruses, thereby enhancing overall food safety.
How does the FDA enhance scientific knowledge regarding viruses in berries?
The FDA enhances scientific knowledge regarding viruses in berries by supporting research on their viability, persistence, detection, and mitigation across pre- and post-harvest stages, as well as in agricultural water sources.
What historical data has informed the FDA’s strategy on berry contamination?
The FDA’s strategy on berry contamination has been informed by historical data from past outbreaks, consultations with food safety experts, and an analysis of potential risks associated with both domestic and imported berries.
What actions will the FDA take to ensure compliance with food safety standards in the berry industry?
To ensure compliance with food safety standards in the berry industry, the FDA will promote adherence to established guidelines, encourage the implementation of effective sanitary practices, and support research into advanced detection methods for enteric viruses.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| FDA Strategy Overview | The FDA has introduced a strategy to prevent outbreaks of enteric viruses like hepatitis A and norovirus linked to fresh and frozen berries. |
| Historical Context | No outbreaks linked to domestic berries in 35 years, but outbreaks have occurred with imported berries. |
| Contamination Sources | Contamination can occur from lapses in food safety, hygienic practices, and worker sanitary management. |
| Collaboration Importance | Collaboration among regulators, the berry industry, and stakeholders is key for strategy development. |
| Key Strategy Actions | 1. Promote compliance with FDA standards. 2. Encourage effective sanitary practices. 3. Expand scientific knowledge on viruses in berries. 4. Introduce incentives for worker vaccination. 5. Support research for better detection methods. |
Summary
The FDA strategy for entering viruses in berries is a comprehensive approach aimed at preventing outbreaks of illnesses caused by pathogens such as hepatitis A and norovirus. By emphasizing the importance of food safety standards, effective sanitary practices, and collaboration among stakeholders, the FDA seeks to ensure the safety of both domestic and imported berry products. This strategy not only addresses past concerns but also promotes ongoing research and worker health initiatives, positioning the berry industry for safer practices in the future.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.