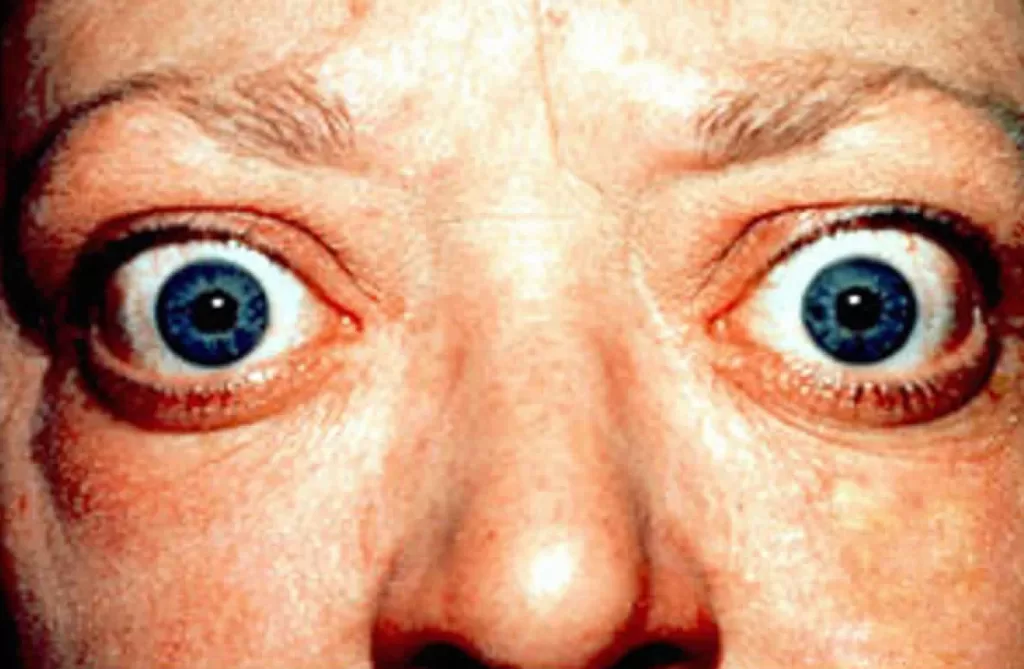
Exophthalmos, often known as proptosis, is a condition characterized by the abnormal bulging of one or both eyes, leading to noticeable changes in appearance and potential health concerns. This eye disorder is most frequently linked to Graves’ disease, a type of hyperthyroidism that triggers inflammation and swelling behind the eyeballs. The resulting bulging eyes can impact not only aesthetics but also eye health, causing discomfort and vision problems if left unaddressed. Understanding exophthalmos is vital for effective early diagnosis and management, helping those affected to seek appropriate treatment. If you notice signs of this condition, knowing that it may be associated with serious health issues emphasizes the importance of prompt medical action.
The term exophthalmos describes a protrusion of the eyeball, which can also be referred to as proptosis or bulging eyes. This phenomenon often signals underlying medical issues, such as Graves’ disease, which is linked to thyroid dysfunction, notably hyperthyroidism and its associated symptoms. Besides the cosmetic implications, individuals suffering from this condition may experience significant discomfort and vision alterations. Various other factors, including tumors or infections, can also lead to similar outcomes. By exploring the different terminologies and associations tied to exophthalmos, we can better understand its implications for overall health and the urgency of addressing such concerns.
Understanding Exophthalmos and Its Symptoms
Exophthalmos, often known as proptosis, is a significant medical condition characterized by the abnormal protrusion of one or both eyes. This dilation can be alarming for those affected and may change the appearance of the face dramatically. The condition is most frequently associated with Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder that results in an overactive thyroid gland. As the eyes bulge forward, this can cause various symptoms, including heightened sensitivity to light, difficulty closing the eyelids, and an overwhelming sense of discomfort and irritation in the eyes.
Beyond mere aesthetics, exophthalmos can lead to more severe health implications if left untreated. Patients may experience changes in vision, such as blurred vision or double vision, which can be distressing and affect daily activities. Additionally, the protruding eyes can leave the cornea exposed, leading to dryness or even serious complications like corneal ulceration. It is essential for individuals exhibiting these symptoms to seek medical advice promptly, as early intervention can significantly alter health outcomes.
The Link Between Exophthalmos and Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is the leading cause of exophthalmos and is classified as a form of hyperthyroidism. In patients with Graves’ disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to an overproduction of thyroid hormones. This hormonal imbalance causes inflammation and swelling of the eye muscles and orbital tissues, pushing the eyeballs forward and resulting in the characteristic bulging associated with exophthalmos. Understanding this link is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of those experiencing symptoms.
The treatment of exophthalmos linked to Graves’ disease often focuses on managing thyroid hormone levels through various interventions, including medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. These treatments aim to reduce the inflammation and pressure that contribute to eye protrusion. Moreover, learning about the association between thyroid health and eye health can empower patients to take proactive steps toward monitoring and managing their conditions effectively.
Diagnosis and Assessment of Exophthalmos
Diagnosing exophthalmos typically involves a series of assessments conducted by an eye care professional. Initial evaluation often includes vision tests to measure how well the eyes function collectively and individual assessments of visual acuity. Imaging tests such as CT and MRI scans are also instrumental in identifying underlying causes of eye protrusion, including tumors or areas of swelling surrounding the eyes.
Furthermore, blood tests are crucial in identifying thyroid function levels, providing insight into whether a thyroid disorder like hyperthyroidism is at play. Accurate diagnosis not only aids in determining the appropriate treatment approach but also helps in addressing the various complications associated with exophthalmos, ensuring patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their specific needs.
Treatment Modalities for Exophthalmos
The treatment approach for exophthalmos primarily depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For cases linked with Graves’ disease, antithyroid medications are often prescribed to inhibit the production of excess thyroid hormones, thereby lowering inflammation rates. In more severe instances, radioactive iodine therapy may be warranted to decrease thyroid gland activity steadily. In addition to these medical treatments, corticosteroids may be utilized to reduce swelling and inflammation around the eyes.
Surgical interventions may also be considered, particularly in cases where vision is compromised or for cosmetic corrections. For instance, procedures to reposition the eyes may restore a more natural appearance while also mitigating the risk of subsequent complications such as optic nerve damage or chronic eye discomfort. Overall, the goal of treatment is not only to alleviate physical symptoms but to improve overall quality of life for those affected.
Recent Advances in Understanding Exophthalmos
Recent research has significantly expanded our understanding of exophthalmos and its relationship with thyroid conditions like Graves’ disease. Advances in medical science are now focusing on targeted therapies specifically designed for managing thyroid eye disease. Such innovative approaches aim to address the inflammatory processes responsible for the condition effectively, promising more efficient management strategies for affected individuals.
As our comprehension of the pathophysiology of exophthalmos evolves, patient care may become more multidimensional. The development of new treatment modalities offers fresh hope, minimizing the impact on a patient’s appearance and eye health. Furthermore, ongoing clinical trials and studies continue to demonstrate the potential for personalized medicine in treating conditions that lead to exophthalmos, highlighting the importance of seeking specialized care for appropriate intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Exophthalmos and how does it relate to Proptosis?
Exophthalmos, also known as proptosis, is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal protrusion or bulging of one or both eyes. This condition can result from various factors such as Graves’ disease, tumors, infections, and inflammatory conditions affecting the eye region.
How does Graves’ disease lead to Exophthalmos?
Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder, is the most common cause of exophthalmos. It leads to inflammation and swelling of the eye muscles and surrounding tissues, which pushes the eyeballs outward, creating the prominent appearance often associated with bulging eyes.
What are the main symptoms of Exophthalmos?
Symptoms of exophthalmos include noticeable bulging of the eyes, discomfort, dryness or excessive tearing, changes in vision such as double or blurred vision, and pain around the eyes due to pressure from swelling.
Can hyperthyroidism cause Exophthalmos?
Yes, hyperthyroidism can lead to exophthalmos as it involves an overproduction of thyroid hormones, which may cause various symptoms including the characteristic bulging of the eyes. This connection is particularly pronounced in thyroid-related eye diseases.
What treatment options are available for Exophthalmos?
Treatment for exophthalmos varies based on the underlying cause. For Graves’ disease, options may include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine treatment, and surgical intervention to relieve pressure or correct the appearance of the eyes. Corticosteroids may also be used to address inflammation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Exophthalmos (or proptosis) is the abnormal bulging of one or both eyes. |
| Causes | 1. Graves’ Disease 2. Hyperthyroidism 3. Tumors (e.g., neuroblastoma) 4. Infections (e.g., orbital cellulitis) 5. Vascular Issues |
| Symptoms | – Prominent Eyes – Eye Discomfort – Changes in Vision – Pain around the eyes |
| Diagnosis | Involves vision tests, imaging tests (CT, MRI), and blood tests to evaluate thyroid function. |
| Treatment Options | – Management of Graves’ Disease via medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery – Surgical interventions for cosmetic or vision issues – Corticosteroids for inflammation |
| Prognosis | If diagnosed and treated early, complications can be managed effectively. Left untreated, it may lead to permanent vision loss. |
Summary
Exophthalmos is a serious medical condition characterized by the abnormal bulging of the eyes, which can significantly affect both appearance and overall health. This condition is primarily linked to Graves’ disease, a disorder that impacts the thyroid, but it can also occur due to tumors, infections, and other vascular issues. Recognizing the causes and symptoms of exophthalmos is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Affected individuals may experience prominent eyes, discomfort, vision changes, and in severe cases, pain. Diagnosis typically involves comprehensive eye examinations and imaging studies, while treatment varies from medication and surgery based on the underlying cause. Early intervention can substantially improve a patient’s quality of life and prevent potential complications, making education on exophthalmos vital for both patients and healthcare providers.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.