Early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis represents a significant breakthrough in oncology, especially given the challenges associated with detecting this aggressive disease. A new blood test, known as the PAC-MANN test, is showing promise by accurately diagnosing pancreatic cancer at its nascent stages, boasting an impressive sensitivity of 85%. This innovative approach leverages a biomarker for pancreatic cancer, allowing for early cancer screening that could revolutionize patient outcomes. With pancreatic cancer often remaining asymptomatic until it progresses, such advancements in pancreatic cancer detection are crucial. As we continue to seek better methods for diagnosing this formidable illness, the PAC-MANN test could become a vital tool in changing the grim statistics surrounding this disease, which currently has a mere 13% five-year survival rate.
The early identification of pancreatic malignancies remains an elusive challenge, particularly due to the insidious nature of the symptoms that often go unnoticed in patients. New developments, such as innovative blood assays, are paving the way for enhanced detection strategies tailored for this type of cancer. These tests, including methods targeting specific biomarkers, not only promise higher accuracy but also offer a less invasive alternative to traditional diagnostic techniques. Furthermore, they facilitate timely interventions that could significantly improve patient prognoses. By integrating these advanced testing methodologies into regular health assessments, we could effectively shift the paradigm for patients at risk of pancreatic diseases.
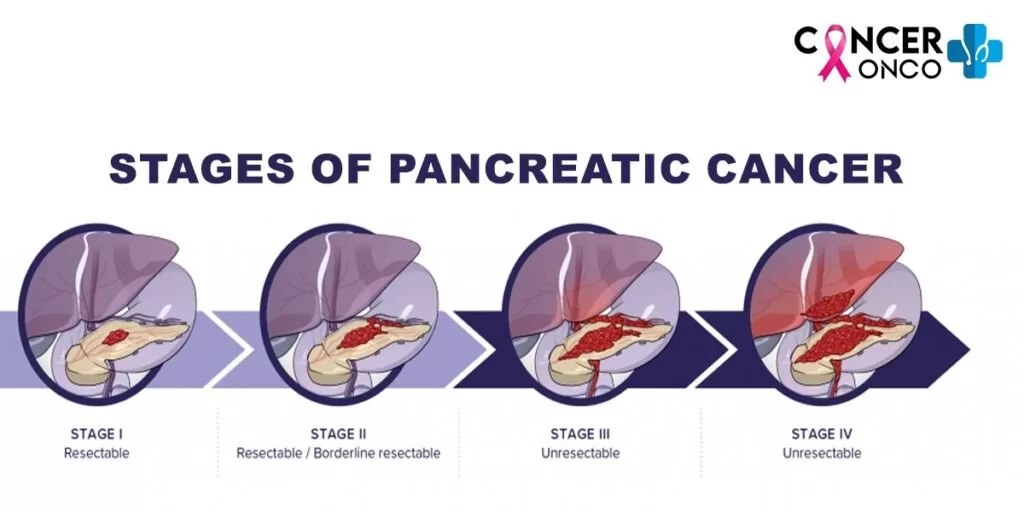
Understanding Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis
Early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis is critical for improving patient outcomes. This form of cancer, often asymptomatic in its initial stages, can progress rapidly, making early detection essential. Innovative approaches, such as the recently developed PAC-MANN blood test, offer new hope by diagnosing pancreatic cancer with remarkable accuracy, reaching up to 85%. Researchers emphasize the importance of such breakthroughs, as traditional diagnostic methods often fail to identify the disease until it has advanced significantly.
The PAC-MANN test, utilizing advanced nanosensor technology, has shown great promise in identifying elevated levels of specific biomarkers linked to pancreatic cancer. By focusing on the presence of proteases in the blood, this test strengthens the diagnostic landscape for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis provided by PAC-MANN could mean the difference between a manageable condition and a life-threatening situation, underlining the need for ongoing research and development in the field.
The Role of the PAC-MANN Test in Pancreatic Cancer Detection
The introduction of the PAC-MANN test significantly enhances pancreatic cancer detection capabilities. Unlike existing screening methods, which often provide limited sensitivity, PAC-MANN boasts an impressive ability to identify 73% of PDAC cases across various stages. This development represents a pivotal advancement in diagnostic accuracy, as early detection is paramount for effective treatment and better prognosis.
Furthermore, the PAC-MANN test’s technology enables it to differentiate between pancreatic cancer and other non-cancerous pancreatic diseases with unprecedented precision. Its ability to rule out 98% of patients without cancer and provide accurate results for early-stage cases positions PAC-MANN as a revolutionary tool in oncology. These features could streamline the screening process, making early cancer screening more accessible and effective for high-risk populations.
Emerging Biomarkers and Techniques for Pancreatic Cancer
In the pursuit of early cancer detection, researchers are continually exploring new biomarkers that could assist in diagnosing pancreatic cancer. Beyond the PAC-MANN test, other emerging strategies involve analyzing urine and bacterial microbiomes. These novel approaches promise to reveal additional insights into the pathology of pancreatic cancer, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses and improved patient care.
Biomarkers play a crucial role in disease identification, with proteins such as CA 19-9 historically leading traditional tests. However, as tests like PAC-MANN demonstrate higher sensitivity and specificity, the emphasis is shifting towards discovering and utilizing more reliable biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. This trend towards precision medicine in detecting pancreatic cancer can dramatically improve early detection rates and, ultimately, patient outcomes.
The Importance of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer Screening
Biomarkers are essential in the development of reliable screening tests for pancreatic cancer. The detection of specific proteins, such as those targeted by the PAC-MANN test, provides a clearer understanding of the disease at its onset. Elevated biomarker levels in the blood can be a critical indicator of the presence of pancreatic cancer, which is indispensable given the disease’s notoriously low visibility in its early stages.
The potential of using a biomarker like CA 19-9 alongside PAC-MANN underscores the importance of comprehensive screening approaches. As researchers identify additional biomarkers for pancreatic cancer, the goal becomes clearer: to create a multi-faceted detection strategy that enables clinicians to identify the disease both accurately and early, ultimately improving survival rates for patients.
How PAC-MANN Innovates Early Cancer Screening
PAC-MANN revolutionizes early cancer screening by providing a highly sensitive and affordable test that can be administered with minimal blood volume. With just 8 microliters required for the test, it is a less invasive option compared to traditional methods like endoscopic ultrasounds. This convenience can encourage more frequent screenings, particularly in high-risk populations, promoting early detection.
Additionally, the test’s affordability—costing less than a penny per sample—could make it accessible in rural and underserved communities, where advanced medical testing is often unavailable. By overcoming these barriers, the PAC-MANN test could significantly increase the number of individuals screened for early-stage pancreatic cancer, ultimately aiding in timely diagnosis and intervention.
Advantages of Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Blood Tests
Early-stage pancreatic cancer blood tests, such as the PAC-MANN, offer numerous advantages over traditional screening methods. Their high sensitivity and ability to detect cancer-specific biomarkers allow for quicker and more reliable results. Early detection of pancreatic cancer, known for its aggressive nature, profoundly impacts treatment options, enabling patients to begin therapy sooner, which can lead to better outcomes.
Moreover, being less invasive and more cost-effective than conventional methods makes blood tests like PAC-MANN appealing to both patients and healthcare providers. By increasing the accessibility of early cancer screenings, these blood tests might encourage more individuals to seek diagnostic evaluations, thereby enhancing early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis rates that are currently alarmingly low.
Research Advancements in Pancreatic Cancer Detection
Research advancements in pancreatic cancer detection are crucial in facing a disease that is notoriously difficult to diagnose early. The recent development of the PAC-MANN test exemplifies innovative research aimed at improving survival rates through better screening techniques. These advancements not only provide immediate benefits through early detection but also pave the way for future research into other potential biomarkers.
By continuing to refine diagnostic processes, researchers contribute to a growing body of knowledge that could ultimately lead to breakthroughs in pancreatic cancer treatment and management. The interplay between emerging technologies and comprehensive biomarker analysis reinforces the urgent need for targeted research in this area to enhance early detection strategies.
The Future of Pancreatic Cancer Screening Methods
The future of pancreatic cancer screening methods is promising, with technologies like the PAC-MANN blood test leading the way. As new research emerges, integrating various diagnostic tools will be essential to providing comprehensive screening approaches. The focus on increasing sensitivity and specificity will likely shape the next generation of tests, ensuring the early detection of pancreatic cancer becomes a standard practice.
Moreover, as the healthcare industry embraces advancements in technology, accessibility to these new screening modalities will improve. This could democratize early cancer detection, extending life-saving screening provisions to communities previously underserved. As researchers continue to innovate, the goal remains clear: to enhance early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis through reliable and accessible screening tools.
Enhancing Patient Outcomes through Early Detection
Enhancing patient outcomes through early detection of pancreatic cancer is a pivotal concern in oncology. Early-stage diagnosis often correlates with a greater selection of treatment options and significantly improves the chances of survival. Blood tests like PAC-MANN that accurately identify pancreatic cancer at its earliest phase can empower patients and healthcare providers alike to act swiftly, potentially changing the trajectory of the disease.
Educational initiatives focusing on the importance of early screening and the availability of innovative tests are crucial. Encouraging awareness about the efficacy of tests like PAC-MANN can nurture a proactive approach to health management, especially among individuals at high risk. The intersection of education, technology, and timely intervention is vital to maximizing patient outcomes in the struggle against pancreatic cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the PAC-MANN test for early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis?
The PAC-MANN test is a novel blood test designed for the early detection of pancreatic cancer with up to 85% accuracy, specifically targeting biomarkers associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). It detects elevated levels of proteases, which serve as a key indicator of pancreatic cancer.
How effective is the blood test for pancreatic cancer detection?
The blood test developed by researchers at Oregon Health and Science University shows an impressive 85% sensitivity in diagnosing early-stage pancreatic cancer (PDAC) and can accurately rule out healthy individuals 96% of the time, making it a powerful tool for early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis.
What role do biomarkers play in early pancreatic cancer diagnosis?
Biomarkers, such as proteases detected by the PAC-MANN test, are critical for early pancreatic cancer diagnosis. They provide a measurable indication of the presence of pancreatic cancer, enabling healthcare providers to identify the disease at its earliest stages.
How does the PAC-MANN test differ from traditional pancreatic cancer blood tests?
Unlike traditional pancreatic cancer blood tests, which may require larger blood volumes and complex procedures, the PAC-MANN test only requires 8 microliters of blood and produces results in just 45 minutes. This efficiency facilitates more frequent testing, especially in high-risk populations.
Why is early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis important?
Early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis is vital because the disease often presents few symptoms and is typically diagnosed at advanced stages when survival rates are significantly lower. Techniques like the PAC-MANN test aim to improve early detection, thus enhancing treatment outcomes and survival rates.
What are the benefits of using the PAC-MANN test in rural areas for pancreatic cancer screening?
The PAC-MANN test’s low cost (under a penny per sample) and minimal blood requirement (8 microliters) make it an ideal screening tool for rural and underserved areas. It provides accessible early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis without the need for sophisticated medical infrastructure.
What is the potential impact of the PAC-MANN test on pancreatic cancer survival rates?
By enabling earlier detection of pancreatic cancer through tests like PAC-MANN, patients may have better treatment options and, consequently, increased survival rates, overcoming the historically low five-year survival rate of 13%.
What are other emerging methods for detecting pancreatic cancer early?
Other promising methods for early pancreatic cancer diagnosis include urine biomarker analysis and studying bacterial microbiomes. These innovations, alongside the PAC-MANN blood test, represent advancements in pancreatic cancer detection strategies.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| New Blood Test | PAC-MANN accurately detects early-stage pancreatic cancer. |
| Accuracy | The test shows up to 85% accuracy in diagnosing early pancreatic cancer. |
| Importance | Pancreatic cancer is often diagnosed late due to a lack of symptoms, resulting in a low survival rate. |
| Biomarker Detection | Elevated levels of proteases serve as biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). |
| Sensitivity and Specificity | PAC-MANN shows 85% sensitivity for stage 1 PDAC and rules out 96% of healthy controls. |
| Cost and Accessibility | Test requires only 8 microliters of blood and costs less than a penny per sample. |
| Potential Applications | Could be used for high-risk individuals in rural and underserved areas. |
| Research Publication | The study was published in Science Translational Medicine. |
Summary
Early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis is critical for improving survival rates. The innovative PAC-MANN blood test developed by researchers at Oregon Health and Science University demonstrates an impressive ability to identify pancreatic cancer early, boasting 85% accuracy. This advancement not only enhances early detection chances but also offers a convenient and cost-effective solution for screening, especially beneficial for high-risk populations and in resource-limited settings.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.