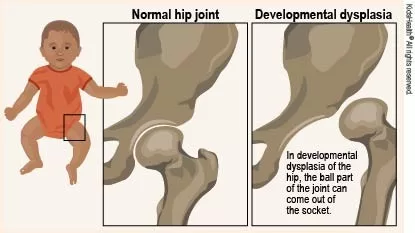
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) is a prevalent condition that affects an infant’s hip joint, causing it to form improperly. If left untreated, DDH can lead to debilitating issues such as early-onset arthritis and significant mobility challenges as the child grows. Therefore, timely diagnosis and intervention are crucial for optimal hip joint development. Among various treatment options, the Pavlik harness is a common orthopedic intervention that assists in aligning the hip joint effectively. The goal of such treatments is to ensure a healthy and functional hip, minimizing the chances of long-term complications associated with pediatric hip dysplasia.
Commonly referred to as hip dysplasia in children, Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) occurs when there is a disruption in the formation or alignment of the hip joint in very young patients. This condition is significant because improper hip development can pave the way for future mobility issues if not addressed early. The management of this condition requires careful monitoring and may involve non-surgical options such as specialized braces or, in some cases, surgical procedures for more severe cases. Utilizing tools like the Pavlik harness can facilitate the hip’s stabilization, fostering proper joint development. With advancements in orthopedic care, the emphasis on early intervention continues to grow, ensuring better outcomes for children with hip dysplasia.
Understanding the Importance of Early Diagnosis in Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
Early diagnosis of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) is crucial for effective treatment outcomes. Pediatric hip dysplasia can often go unnoticed especially in newborns, where subtle signs might be misinterpreted as normal variance in infant movement. Routine screenings, combined with clinical assessments by healthcare providers, play a pivotal role in catching this condition without delay. Around 1-2 out of every 1,000 infants are diagnosed with DDH, underscoring the necessity of awareness among parents and clinicians. By identifying DDH at an early age, healthcare professionals can recommend appropriate interventions such as the Pavlik harness, which holds the hip in a safe position, promoting optimal hip joint development during these formative months of life.
As research indicates, infants diagnosed with DDH prior to the six-month mark generally exhibit more favorable outcomes than those diagnosed later. The earlier the intervention begins, the better the chances of achieving a normal range of motion in the hip joint, minimizing long-term complications that could arise from neglecting this condition. Awareness programs targeting both parents and medical professionals can empower families to seek immediate evaluation if they notice any hip irregularities, such as limited leg movement or differences in leg length. Thus, prioritizing early diagnosis sets the foundation for successful management and improves the quality of life for affected children.
Exploring Non-Surgical Treatments for Pediatric Hip Dysplasia
Non-surgical treatments are foundational in managing Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip and are often the first line of defense for infants diagnosed with this condition. The Pavlik harness, a common non-invasive method, allows infants’ hip joints to develop properly by maintaining a position that favors stability. This method has shown to have a high success rate when applied before the age of six months, aligning with the critical window for hip joint development. The brace holds the hips in flexion and abduction, enabling the acetabulum to mold around the femoral head correctly, thus avoiding the need for more invasive procedures later on.
Other than the Pavlik harness, there are various bracing techniques that orthopedic specialists may recommend based on the specific presentation of DDH in the child. These braces not only assist in maintaining hip joint stability but also ensure room for continued growth and development. Monitoring progress through regular follow-up appointments is crucial; adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary as the child grows and their needs evolve. Overall, these non-surgical interventions are integral in achieving positive results without subjecting young patients to the risks associated with surgical interventions.
Recent advancements in orthopedics have also introduced dynamic bracing options, designed to support flexibility while ensuring the optimal alignment of the hip joint. Such innovations further assure parents of the effectiveness of non-surgical management, alleviating concerns regarding intervention protocols. The overarching goal remains clear: to provide children with the best chance for normal hip joint function and to prevent complications associated with untreated DDH.
Surgical Options for Untreated Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
In situations where non-surgical approaches have proven ineffective, surgical options may be necessary to correct Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Surgical intervention typically involves more invasive procedures, with open reduction being a primary method. This technique entails repositioning the femoral head securely within the acetabulum, thereby ensuring appropriate joint stability. Open reduction surgeries generally have a high success rate and can significantly improve mobility and function for affected children. Protective measures and physical therapy follow-up are critical to ensure long-term success and help facilitate normal hip joint function.
Another significant surgical procedure for DDH is pelvic osteotomy, which modifies the structure of the pelvis to improve the fit of the femoral head within the socket. Minimally invasive surgical approaches are increasingly being adopted, as they result in reduced recovery times and fewer complications for young patients. Advancements in technology and surgical techniques are continually enhancing the success rates of these interventions, enabling orthopedic specialists to offer informed guidance to parents and caregivers regarding the best course of action for their child’s health and quality of life.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Care in Managing DDH
Managing Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip requires a comprehensive approach involving multiple healthcare disciplines. Collaborative care between pediatricians, orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, and family caregivers ensures that children with DDH receive the most effective treatment options tailored to their individual needs. The multifaceted nature of this condition means that different specialists can provide valuable insights on various aspects of treatment, from diagnosis to rehabilitation. For instance, pediatricians play a key role in identifying signs and symptoms of hip dysplasia early on, while orthopedic specialists can recommend specific interventions based on radiological assessments.
Physical therapists are also integral to the management of DDH post-treatment, helping ensure a smooth transition from non-surgical methods like bracing to active remodeling of functional movements. Engaging in a multidisciplinary approach fosters a supportive network for families, empowering them with the knowledge and resources necessary to navigate their child’s care journey. This cooperation not only enhances treatment effectiveness but also leads to better outcomes, as specialists can share data and continually refine treatment methodologies, thus promoting the child’s healthy hip development over time.
Current Trends and Research in Orthopedic Interventions for DDH
Recent research developments underscore the importance of early intervention in the treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Studies demonstrate that children who undergo treatment within the first six months present significantly improved outcomes, including full hip function and fewer long-term complications. These findings have spurred ongoing advancements in non-surgical treatments, as parents and healthcare providers are increasingly advocating for timely screenings and prompt responses to any signs of hip dysplasia.
Moreover, technological advancements in imaging modalities enhance the ability of orthopedic professionals to monitor the hip joint’s development closely. This improvement allows for better evaluation and adjustment of treatment protocols, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes. Research continues to explore innovative solutions, specifically within the realm of less invasive surgical techniques that could further improve recovery times and minimize operational risks. The continuous evolution of orthopedic practices surrounding DDH heralds a brighter, more effective future for managing this common pediatric condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) and how is it diagnosed?
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) is a condition where the hip joint doesn’t form properly, often leading to instability or dislocation. Diagnosis typically involves physical examinations and imaging studies like ultrasounds or X-rays to assess the hip joint development.
How does the Pavlik harness work in treating Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip?
The Pavlik harness is a primary non-surgical treatment for infants with Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH). It holds the hips in a position that promotes normal development, ensuring the femoral head stays correctly positioned within the acetabulum.
What are the potential long-term outcomes of untreated Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip?
Untreated Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) can lead to severe complications, including early-onset arthritis, chronic pain, and significant mobility challenges. Early intervention is essential for better long-term hip joint function.
What orthopedic interventions are available for more severe cases of DDH?
For severe cases of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) where non-surgical methods fail, surgical options such as open reduction and pelvic osteotomy may be required. These procedures help reposition the femoral head and improve hip joint stability.
What role does early detection play in the treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip?
Early detection of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) is crucial because it allows for timely intervention, often resulting in better outcomes. Infants diagnosed before six months typically respond well to non-surgical treatments like the Pavlik harness.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip occurs when the hip socket (acetabulum) does not fully cover the femoral head, leading to instability or dislocation. |
| Diagnosis | Diagnosis usually involves physical exams and imaging techniques like ultrasound or X-rays, emphasizing the importance of early detection. |
| Non-Surgical Treatments | Pavlik harness is used to maintain proper hip position for infants, with high success rates when applied early. |
| Surgical Interventions | If non-surgical treatments fail, options include Open Reduction to reposition the femoral head and Pelvic Osteotomy to reshape the pelvis. |
| Long-term Prognosis | Children treated early typically achieve good functionality, while late treatment can lead to severe complications. |
| Guidelines for Care | The AAP recommends routine screening for high-risk infants, and emphasizes a multidisciplinary approach in treatment. |
Summary
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip is a condition that highlights the vital role of orthopedic intervention in pediatric health. Early identification and treatment significantly affect long-term outcomes, including mobility and pain. Effective management through non-surgical options such as the Pavlik harness, followed by timely surgical interventions when necessary, can lead to improved hip function and quality of life for affected children. As research progresses, orthopedic specialists are better equipped to tailor treatment plans that optimize recovery and ensure healthy development.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.