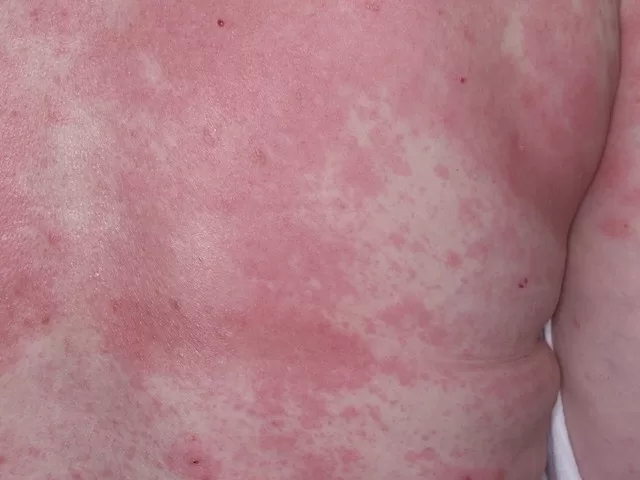
Cutaneous coccidioidomycosis is a fungal infection that can mimic common skin conditions such as rosacea, especially in patients with immunosuppressed skin conditions. This infection is caused by *Coccidioides* spp., fungi that thrive in the southwestern United States and can lead to complex dermatological presentations. For those undergoing treatments like vandetanib, the risk of cutaneous manifestations increases, raising concerns about potential side effects and diagnostic confusion. In many cases, timely coccidioidomycosis treatment is essential to prevent prolonged discomfort and complications, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. Addressing this condition early on can significantly improve patient outcomes and mitigate the persistent skin changes often seen following effective intervention.
Fungal infections endemic to certain regions can lead to skin lesions that closely resemble those of rosacea, particularly in immunocompromised patients. In areas like Arizona, where *Coccidioides* fungi are prevalent, cutaneous manifestations can pose diagnostic challenges. Factors such as recent immunosuppressive therapies may exacerbate these conditions, complicating treatment plans. Moreover, medications like vandetanib introduce their own spectrum of skin side effects, further blurring the lines in diagnosis. Continuous monitoring and prompt histopathological evaluations are vital to distinguish between these conditions and ensure appropriate coccidioidomycosis treatment.
Understanding Cutaneous Coccidioidomycosis
Cutaneous coccidioidomycosis, an infection caused by the *Coccidioides* fungi, often presents with skin lesions that can mimic various dermatological conditions, including rosacea. This fungal infection is a significant concern in immunocompromised patients, as their weakened immune systems are less capable of fighting off infections. Commonly found in the southwestern United States, particularly Arizona, the infection may arise from inhaled spores that eventually lead to cutaneous manifestations. Identifying cutaneous coccidioidomycosis is critical, especially among individuals undergoing treatments that compromise immune function.
Clinicians must be vigilant, as the presentation may vary significantly among patients. For instance, concomitant treatment with vandetanib in cancer therapy could complicate the clinical picture, as seen in the case of our patient, whose lesions closely resembled rosacea. Histological examinations are vital in distinguishing between these conditions, especially when serological tests yield inconclusive results. With adequate recognition, effective antifungal treatments like fluconazole can be administered promptly to manage the infection, underscoring the need for a thorough understanding of both immunosuppressed skin conditions and endemic fungal infections.
Diagnostic Challenges of Coccidioidomycosis in Immunosuppressed Patients
The diagnosis of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis in immunocompromised patients poses unique challenges due to the overlapping clinical features with other dermatological conditions. In patients with weakened immune systems, like those undergoing treatments for cancer, the misdiagnosis of coccidioidomycosis as rosacea can result in inappropriate management. IN this scenario, it becomes particularly crucial to utilize thorough histopathological evaluations to confirm the presence of the typical spherules associated with *Coccidioides* infection. Without accurate diagnosis, patients risk undergoing ineffective treatments that may fail to resolve their symptoms.
Moreover, the complexity of managing fungal infections in immunocompromised individuals amplifies this challenge. As seen with the patient in our study, despite aggressive antibiotic and corticosteroid regimens, significant improvement was only achieved with antifungal therapy. The healthcare team must also consider factors such as previous medications and ongoing treatment plans, which may have contributed to the presentation. Understanding the multifaceted nature of these infections can help healthcare providers tailor their approach more effectively towards the diagnosis and treatment of coccidioidomycosis.
Treatment Considerations for Cutaneous Coccidioidomycosis
Effective treatment of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis requires a comprehensive understanding of the disease’s pathophysiology, particularly in immunocompromised patients. In the presented case, fluconazole therapy was the key to resolving the skin lesions associated with coccidioidomycosis, illustrating the importance of targeted antifungal treatments. However, it is crucial to recognize that the management does not end with antifungal administration; considerations around potential side effects from concurrent medications, such as vandetanib, must also be evaluated. The emergence of blue-gray hyperpigmentation in this patient signals the need for diligent monitoring of skin changes during and following treatment.
The timing and choice of coccidioidomycosis treatment can significantly influence recovery outcomes. Continuous assessment of the skin’s response to interventions is essential as some secondary effects, like drug-induced hyperpigmentation, may persist. Furthermore, understanding how immunosuppression can lead to a relapse of fungal infections emphasizes the necessity for ongoing patient education and regular follow-ups. By prioritizing comprehensive care and management strategies, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of life for patients afflicted by this complex fungal infection.
Preventing Misdiagnosis in Fungal Infections
Preventing misdiagnosis in cases of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis requires a heightened awareness among healthcare professionals regarding the complexities of dermatological presentations, especially among immunosuppressed individuals. Rosacea-like symptoms can be deceptively similar to those seen in coccidioidomycosis, particularly in patients receiving immunomodulating therapies. This emphasizes the importance of a thorough clinical assessment and consideration of patient history when establishing a differential diagnosis. Recognizing the specific risk factors associated with endemic fungal infections can support practitioners in developing a diagnostic framework to differentiate between conditions.
Additionally, education for both healthcare providers and patients is vital for raising awareness about the potential for coccidioidomycosis to mimic other skin disorders. Understanding the geographical distribution of *Coccidioides* and the population at risk can guide timely intervention and improve outcomes. Providing information about the signs and symptoms that warrant further investigation can empower patients to seek care earlier, reducing the likelihood of delayed diagnosis and treatment, which is especially critical in immunosuppressed patients.
Risks and Management of Vandetanib Therapy
The use of vandetanib, an oral therapy for advanced thyroid cancer, introduces various risks and side effects, especially in immunocompromised patients. This drug has been associated with skin reactions, including hyperpigmentation and other dermatological conditions that may obscure underlying fungal infections like coccidioidomycosis. The case profile illustrates a classic example of how treatment for one condition might unintentionally complicate the diagnosis and management of another. It raises critical concerns about monitoring skin conditions in patients receiving such therapies, emphasizing the need for careful observation of any emerging symptoms.
Healthcare providers should establish a thorough management plan that includes counseling on potential side effects of vandetanib and the importance of skin evaluations. This proactive approach not only aids in early detection of adverse reactions but also facilitates timely adjustments in therapy. Optimizing management of side effects while addressing the underlying conditions will contribute to better outcomes for patients facing dual challenges of cancer and fungal infections, aiding prevention and minimizing long-term complications from treatment.
Recognizing Histopathological Signs in Coccidioidomycosis
Histopathological examination serves a crucial role in accurately diagnosing cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. The identification of granulomatous inflammation and PAS-positive spherules in tissue specimens is definitive for this fungal infection. Such examinations can be especially vital in ambiguous cases, where clinical symptoms closely mimic those of other dermatoses like rosacea. Physicians must maintain awareness of these specific histological features to ensure that misdiagnoses do not occur, ultimately leading to proper treatment and intervention for immunosuppressed patients.
Furthermore, understanding the histological landscape of fungal infections can enhance the diagnostic skills of healthcare professionals, enabling them to differentiate between various infectious and inflammatory skin conditions. Continued education on histopathological modalities and their application in dermatology can help streamline the diagnostic pathway for patients with complex presentations. This understanding is particularly essential in endemic areas where such infections are prevalent, ensuring effective management and optimized outcomes for affected individuals.
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring Post-Treatment
After the treatment of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis, ongoing monitoring becomes imperative, especially for patients with underlying health issues such as immunosuppression. The potential for relapse of fungal infections necessitates a structured follow-up routine to assess for re-emergence of symptoms or development of new lesions. Regular skin evaluations can help healthcare providers identify any concerning changes early and initiate appropriate interventions to address them.
Additionally, the persistence of side effects, such as hyperpigmentation from therapies like vandetanib, warrants monitoring to improve the patient’s cosmetic outcomes and overall well-being. Providers should actively communicate with patients about their post-treatment experiences while fostering an environment where they feel comfortable reporting any concerning changes. By integrating thorough monitoring practices into patient care, healthcare teams can enhance recovery trajectories and support long-term health in immunocompromised patients following fungal infections.
Key Takeaways on Coccidioidomycosis Management
In summary, effective management of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis, particularly in immunosuppressed patients, hinges on accurate diagnosis, timely treatment, and ongoing evaluation of patient outcomes. The mimicry of symptoms with conditions such as rosacea requires an astute clinical eye and a solid understanding of both histopathological indicators and treatment side effects. Adequate education for clinicians about this endemic fungal infection will prepare them to address the nuanced challenges these patients often face.
Moreover, incorporating interdisciplinary collaboration among dermatologists, infectious disease specialists, and oncology teams can improve management strategies for complex cases involving multiple conditions. Having a robust support network and ongoing patient engagement can enhance the overall efficacy of treatment protocols while promoting better health outcomes for individuals dealing with cutaneous coccidioidomycosis in the context of immunosuppression.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cutaneous coccidioidomycosis and how does it mimic rosacea?
Cutaneous coccidioidomycosis is a skin infection caused by the *Coccidioides* fungus, which can manifest as itchy, inflammatory lesions that resemble rosacea-like dermatitis, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. This similarity can lead to diagnostic challenges, necessitating histopathological examinations for accurate identification.
What is the relationship between immunosuppressed skin conditions and cutaneous coccidioidomycosis?
Immunosuppressed patients are at a higher risk for developing cutaneous coccidioidomycosis due to their weakened immune systems, making them susceptible to fungal infections that can exhibit symptoms mimicking common skin conditions like rosacea.
How is cutaneous coccidioidomycosis treated, especially in patients undergoing vandetanib therapy?
Treatment for cutaneous coccidioidomycosis often involves antifungal medications such as fluconazole, which can effectively reduce lesions. In patients receiving vandetanib, care must be taken as this drug can lead to side effects such as hyperpigmentation, complicating the treatment process.
What are the common signs of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis in immunocompromised patients?
Common symptoms of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis in immunocompromised individuals include itchy, inflammatory papules and pustules on the skin, which can mimic the appearance of rosacea. These manifestations may require a punch biopsy for accurate diagnosis.
What are the potential side effects of vandetanib in patients with cutaneous fungal infections like coccidioidomycosis?
Vandetanib can cause side effects including blue-gray hyperpigmentation at the treatment sites of fungal infections like cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. This side effect complicates the clinical picture and may persist even after successful treatment of the fungal infection.
How can histopathological examinations aid in diagnosing cutaneous coccidioidomycosis?
Histopathological examinations are crucial for diagnosing cutaneous coccidioidomycosis, especially when lesions mimic rosacea. These examinations reveal granulomatous inflammation and periodic acid–Schiff-positive spherules, confirming the presence of the *Coccidioides* fungus.
Why is it important to consider the risk of relapse in cutaneous coccidioidomycosis among immunosuppressed patients?
Immunosuppressed patients, such as those undergoing treatment for conditions like cancer, face a heightened risk of relapse with cutaneous coccidioidomycosis due to their compromised immune systems. Vigilant monitoring is essential to manage potential recurrences effectively.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Case study of cutaneous coccidioidomycosis mimicking rosacea in an immunocompromised patient, Arizona, USA, 2024 |
| A 70-year-old woman with stage IV medullary thyroid cancer presented with inflammatory skin lesions on her forehead and cheeks, itchy for 8 months. |
| Histopathological examination confirmed cutaneous coccidioidomycosis through granulomatous inflammation and identification of *Coccidioides* spp. spherules. |
| Initial treatments like doxycycline and metronidazole were ineffective; fluconazole ultimately led to lesion resolution but left hyperpigmentation. |
| Complications from immunosuppression considered; the potential for relapse emphasizes the need for continuous monitoring in affected patients. |
Summary
Cutaneous coccidioidomycosis presents unique diagnostic challenges, especially in immunocompromised patients where the symptoms may mimic conditions like rosacea. This case highlights the complexities of diagnosing this endemic fungal infection in Arizona, underscoring the importance of timely histological evaluations for accurate treatment. Patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy should be closely monitored for signs of coccidioidomycosis, given the potential for skin manifestations that can easily be mistaken for other dermatological conditions.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.