As the world continues to grapple with the impact of COVID-19, the relationship between COVID-19 vaccination and heart health has become a focal point of discussion. Exciting new research highlights that the incidence of heart attacks and strokes was notably reduced in individuals following their COVID-19 vaccination, emphasizing the cardiovascular safety of these vaccines. Studies reveal substantial COVID-19 vaccine benefits, indicating a decrease in heart attack incidence by 27% and stroke incidence post-vaccine by up to 20%. These findings suggest that the effects of the COVID-19 vaccine offer protective benefits against severe health risks, including cardiovascular diseases. This compelling evidence reinforces the importance of vaccination in safeguarding heart health and preventing serious complications during the pandemic.
In light of ongoing health concerns linked to the pandemic, understanding the intersection of COVID-19 immunization and cardiovascular well-being is critical. Recent investigations have shown a significant reduction in cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarctions and cerebrovascular accidents among those who have received their COVID-19 shots. This phenomenon raises important questions about the overall safety profile of vaccines and their role in mitigating serious heart-related issues. By exploring how doses of the COVID-19 vaccine influence cardiovascular outcomes, researchers aim to provide clarity on the safety and efficacy of these public health measures. Such insights are essential for informing patients and healthcare providers about the critical benefits of vaccination against both COVID-19 and its associated cardiovascular risks.
Understanding the Impact of COVID-19 Vaccination on Heart Health
Recent studies have illustrated a promising correlation between COVID-19 vaccinations and improved heart health outcomes. Specifically, research from multiple institutions analyzed data from almost 46 million adults in England, revealing that the incidence of heart attacks and strokes declined significantly post-vaccination. This finding highlights the importance of vaccines not just in preventing severe cases of COVID-19 but also in promoting cardiovascular health. The data indicated a 10% reduction in cardiovascular events in the weeks following the first vaccine dose, reaffirming the broader benefits of vaccination.
These findings are particularly significant when considering the increased risk of cardiovascular complications associated with severe COVID-19 infections. With vaccination, individuals demonstrate enhanced protection against both the virus and its associated cardiovascular impacts, leading to lower incidences of heart disease events. Understanding that vaccinations may contribute to better heart health can encourage more people to receive their shots, bolstering community immunity and reducing overall health risks.
COVID-19 Vaccine Benefits: A Closer Look at Cardiovascular Safety
The safety of COVID-19 vaccines, particularly concerning cardiovascular health, has been a topic of extensive research. The latest findings suggest that, after receiving vaccines like AstraZeneca and Pfizer/Biotech, individuals experienced lower rates of arterial thromboses. These doses correlated with reductions in heart attack incidence by up to 27% and stroke incidence by 20%. Such statistics not only demonstrate the vaccines’ effectiveness but also provide assurance regarding their cardiovascular safety profile.
While previous studies noted the occurrence of rare side effects like myocarditis and pericarditis following some mRNA vaccines, the overall data from the England study emphasize the favorable outcomes of vaccination compared to unvaccinated populations. Individuals who received the vaccine had fewer serious cardiovascular impacts than those who contracted the virus without vaccination. The findings reaffirm the notion that the benefits of receiving the COVID-19 vaccine substantially outweigh the risks, making it a critical public health measure.
The Role of Post-Vaccination Health Monitoring
As vaccination campaigns continue globally, monitoring the long-term health outcomes following COVID-19 vaccination becomes imperative. Research indicates that post-vaccine, the incidence of common cardiovascular conditions is lower than expected, putting forth the argument that vaccination may serve as a protective factor against severe health complications related to both COVID-19 and cardiovascular diseases. Continuous tracking of patients and community health statistics will further enhance understandings of these dynamics.
Ongoing studies and follow-up research will help document the long-term cardiovascular effects of vaccinations, allowing health officials to analyze any emerging patterns over time. By maintaining a database of health records from vaccinated individuals, specialists can evaluate the safety and performance of various COVID-19 vaccines in preventing heart-related complications, paving the way for better-informed public health decisions.
Stroke Incidence Post-Vaccine: Analyzing the Data
Studies indicate a marked reduction in the incidence of strokes in individuals vaccinated against COVID-19. The extensive research conducted, which analyzed health records across the adult population of England, showed a consistent reduction in stroke rates following vaccination. This is paramount, particularly as stroke is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The data suggests that with vaccinations ramping up, adverse cardiovascular events such as strokes are becoming less frequent.
This positive trend can largely be attributed to the protective measures afforded by the COVID-19 vaccines. By mitigating the severity of infection and potentially reducing the inflammation associated with viral infections, vaccines help safeguard against complications that can lead to strokes. This evidence reinforces the critical message that COVID-19 vaccinations not only help in controlling the pandemic but also serve a vital role in promoting better heart health and overall well-being.
Heart Attack Incidence: A Decrease in Rates Following Vaccination
The occurrence of heart attacks has significantly decreased in populations following administration of COVID-19 vaccines. The study’s findings reveal a decrease of up to 27% in heart attack incidents shortly after vaccination, providing an encouraging outlook for public health. The data aligns with observations that vaccines may help lower the risk of severe cardiovascular outcomes, particularly among vulnerable populations.
This trend of reduced heart attack incidence highlights the vaccines’ key role in addressing not only COVID-19-related health issues but also in alleviating broader cardiovascular concerns. As researchers continue to investigate the long-lasting effects of vaccination on heart health, this data fosters hope for improving overall health outcomes for millions across the globe.
Exploring COVID-19 Vaccine Effects on Cardiovascular Events
The effects of COVID-19 vaccines on cardiovascular events have garnered significant attention from medical researchers and public health officials alike. With compelling evidence pointing to a reduction in serious cardiovascular issues such as heart attacks and strokes among vaccinated individuals, it becomes increasingly vital to communicate these advantages to the public. The study conducted in England not only indicates a decrease in the incidence of these events post-vaccination but also reaffirms the vaccines’ essential role in protecting against severe COVID-19.
As nations continue rolling out vaccines, understanding the broader implications of immunization against COVID-19 is paramount. Data revealing lower cardiovascular risks can help alleviate vaccine hesitancy and encourage more individuals to receive their vaccinations, ultimately leading to healthier communities. This information could be a driving force in public health initiatives aimed at increasing vaccination rates to combat both the ongoing pandemic and potential cardiovascular risks associated with the virus.
The Importance of Continued Research on COVID-19 Vaccination
As research surrounding COVID-19 vaccinations and health outcomes evolves, it is essential to focus on the ongoing study of vaccine-induced effects, particularly concerning cardiovascular health. With the continuous collection of health data and analysis of post-vaccination health, researchers can uncover patterns that may inform future vaccine development and public health strategies. This extensive monitoring allows health professionals to ascertain the reliability of vaccines in reducing incidents of heart-related issues.
The commitment to studying the effects of COVID-19 vaccination extends beyond immediate benefits, also encompassing potential long-term health implications. By generating extensive databases and enabling collaborative research efforts, countries can more effectively track health trends and provide robust information regarding the vaccines’ safety and efficacy in the context of cardiovascular disease, subsequently reinforcing public health policies.
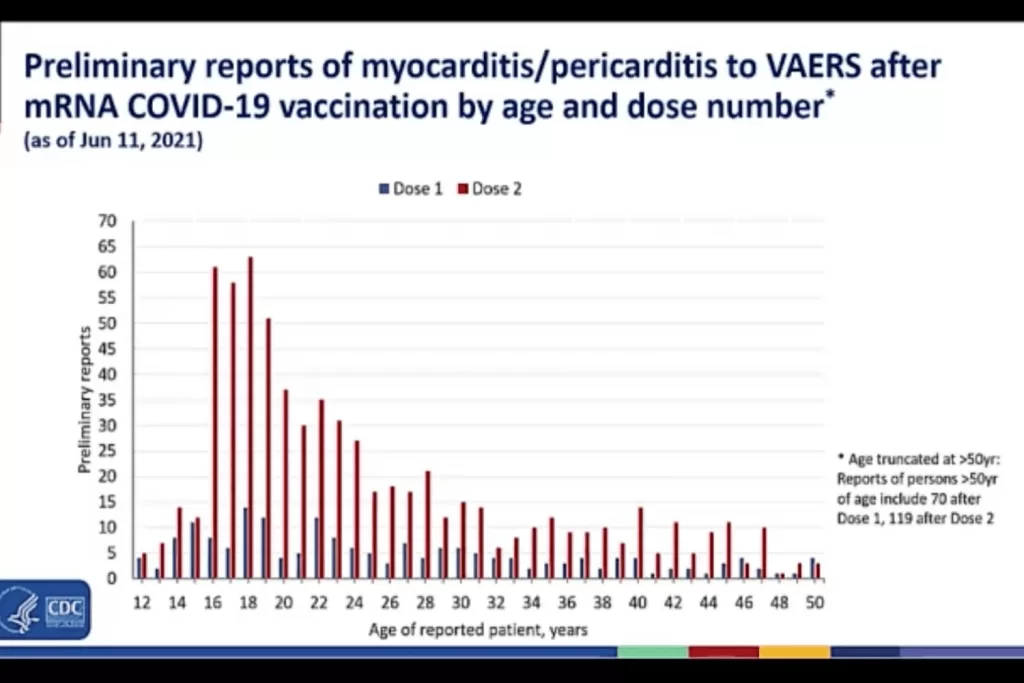
Myocarditis and Pericarditis: Understanding Rare Complications
While research has established the overall cardiovascular safety of COVID-19 vaccines, attention must also be given to rare complications such as myocarditis and pericarditis. These conditions have been observed following certain mRNA-based vaccines, prompting health authorities to recommend monitoring patients who experience symptoms following vaccination. Despite these occurrences, comparative data shows that the incidence of such complications remains low when viewed against the backdrop of the catastrophic health risks posed by COVID-19.
In light of the findings, ongoing medical education and outreach are vital to ensuring that potential vaccine recipients are well-informed about both vaccine benefits and risks. It is crucial for healthcare providers to communicate effectively about these rare conditions, emphasizing the overall favorable risk-to-benefit ratio of vaccination. Understanding the balance between potential risks and significant protective benefits can empower individuals to make informed health decisions.
COVID-19 Vaccination: A Key to Promoting Public Health
The findings surrounding COVID-19 vaccination and heart health emphasize its critical role in promoting public health on a global scale. Vaccination campaigns aimed at achieving high immunization rates can lead to a marked reduction in cardiovascular events among larger populations. Such public health initiatives are even more essential as recovery from the pandemic progresses, particularly in the face of ongoing emerging variants.
Investing in public health awareness while ensuring broader vaccination reach can significantly contribute to a healthier populace. Through informed educational campaigns about the benefits of COVID-19 vaccines in reducing severe health complications, including cardiovascular risks, community health is sure to flourish in the aftermath of the pandemic. Thus, prioritizing vaccination not only helps combat COVID-19-related health issues but also reinforces a commitment to minimizing future heart health risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the COVID-19 vaccine benefits for heart health?
The COVID-19 vaccines have been shown to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. A recent study indicated that after vaccination, the incidence of these events was up to 27% lower following the second dose, highlighting the significant COVID-19 vaccine benefits in promoting heart health.
Is there evidence of cardiovascular safety after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine?
Yes, extensive studies, including one involving nearly 46 million adults in England, have demonstrated the cardiovascular safety of COVID-19 vaccines. The research found lower rates of heart attacks and strokes after vaccination, suggesting strong support for the safety of the COVID-19 vaccination program concerning heart health.
What is the incidence of heart attacks and strokes post-COVID-19 vaccination?
The incidence of heart attacks and strokes has been reported to be lower after COVID-19 vaccination. Studies revealed up to a 27% decrease in these events in the weeks following the second vaccine dose, indicating positive outcomes for cardiovascular health after vaccination.
How do COVID-19 vaccines affect heart attack incidence?
Research indicates that the incidence of heart attacks is significantly lower in individuals who have received the COVID-19 vaccine compared to those who are unvaccinated. This decrease highlights the protective effects of the COVID-19 vaccine on heart health.
Are there risks of stroke incidence following COVID-19 vaccination?
While some rare complications have been reported post-vaccination, the overall risk of stroke incidence is lower among vaccinated individuals. A study found that the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination in reducing strokes outweigh the very rare cardiovascular risks associated with certain vaccines.
What can be said about the COVID-19 vaccine effects on cardiovascular diseases?
The COVID-19 vaccine effects include a reduction in the incidence of various cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes. Evidence from large-scale studies reveals that vaccinated individuals have experienced a significantly lower occurrence of these serious conditions compared to those who are unvaccinated.
What do studies reveal about cardiovascular complications from COVID-19 vaccines?
Studies indicate that while certain rare cardiovascular complications like myocarditis and thrombotic events have been associated with some COVID-19 vaccines, the comprehensive research shows overall lower rates of serious cardiovascular incidents post-vaccination, reaffirming the COVID-19 vaccination’s overall benefits.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Lower incidence of cardiovascular diseases after vaccination | Post-vaccination, the incidence of heart attacks and strokes was lower, with a 10% reduction in 13-24 weeks following the first dose and up to 27% after the second dose of AstraZeneca vaccine. 20% reduction observed with Pfizer/Biotech vaccine. |
| Study Scope | The study analyzed health records of nearly 46 million adults in England between December 2020 and January 2022, comparing cardiovascular incidents before and after vaccination. |
| Collaboration | Conducted by the Universities of Cambridge, Bristol, and Edinburgh, supported by the British Heart Foundation Data Science Centre. |
| Cardiovascular safety assurance | The study confirmed no new adverse cardiovascular conditions related to COVID-19 vaccinations, supporting the notion that benefits outweigh risks. |
| Contributions to public health | The findings reassure the public about the cardiovascular safety of COVID-19 vaccines and their protective role against severe disease. |
Summary
COVID-19 vaccination and heart health have been shown to exhibit a positive relationship, as recent studies indicate a lower incidence of heart attacks and strokes following vaccination. Evidence from a comprehensive study involving nearly 46 million adults in England reveals that individuals vaccinated against COVID-19 experienced up to a 27% reduction in cardiovascular events compared to their unvaccinated counterparts. As such, the research supports the ongoing COVID-19 vaccination program not only as a measure to prevent severe disease but also as a means of promoting heart health.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.