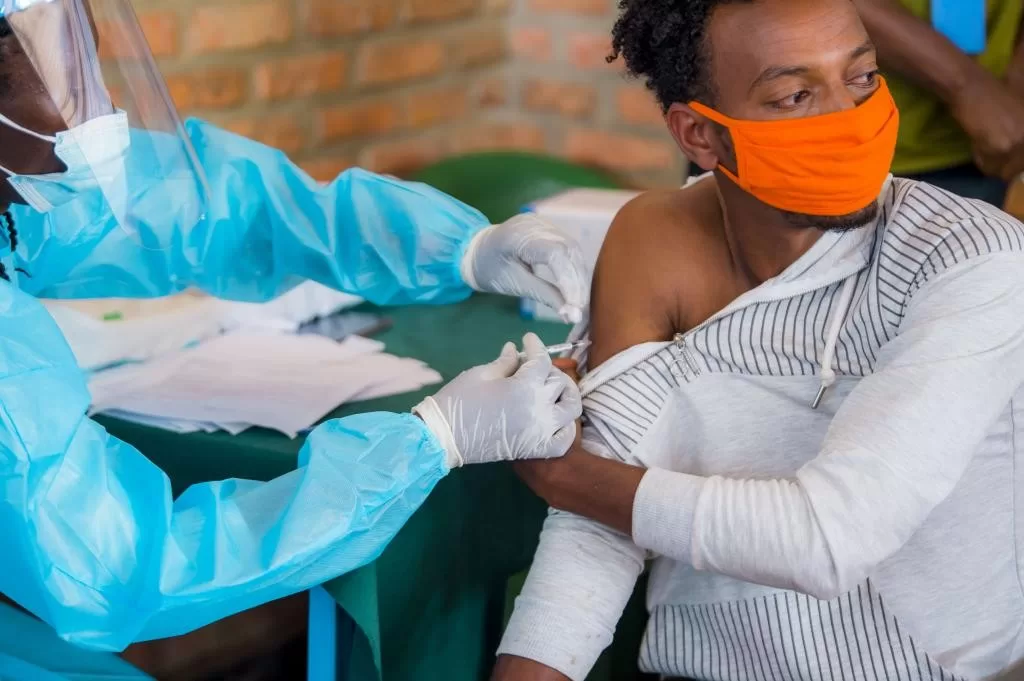
COVID-19 testing and vaccination refugees present a critical aspect of public health during the pandemic era, particularly concerning refugee health. As thousands sought resettlement in the US, the challenges of ensuring proper COVID-19 test results and vaccination coverage became more pronounced. Between November 2020 and June 2022, a staggering number of refugees were tested, revealing a positivity rate of 2.6% amidst rising vaccination statistics that climbed to 71% for adult refugees. The ongoing pandemic significantly impacted refugee resettlement processes, introducing delays and complicating access to health services. Understanding these dynamics not only highlights the pandemic’s impact on refugees but also underscores the importance of health initiatives aimed at facilitating seamless integration into resettlement programs.
The phenomenon of refugees navigating COVID-19 testing and vaccination underscores the urgent need to address health disparities within refugee populations. Many individuals fleeing conflict and instability face unique barriers to healthcare access, particularly during the pandemic. The statistics surrounding COVID-19 vaccination rates among migrants and the implications of test result positivity become vital in shaping effective resettlement strategies. Moreover, examining how the public health crisis has disrupted traditional refugee resettlement in the US can reveal significant insights into improving health outcomes. Thus, ensuring comprehensive care and timely vaccinations for these vulnerable groups is more crucial than ever.
Impact of COVID-19 on Refugee Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has had profound implications for refugee health, highlighting vulnerabilities in this already marginalized group. Refugees often arrive in the host country with pre-existing health issues that complicate their care during public health crises. Addressing these needs became paramount as the pandemic exacerbated barriers to healthcare access, including language, cultural differences, and logistical challenges. Ensuring that refugees receive adequate medical attention is critical, especially as they navigate the complexities of COVID-19 testing and vaccination.
Furthermore, the disruption caused by COVID-19 has revealed inequities among refugee populations across different regions. Studies have shown that certain demographics, including those from Asian countries, experienced higher positivity rates during predeparture testing, raising alarms about their overall health status. This highlights the need for tailored health interventions to test, track, and treat COVID-19 among refugees, ensuring that they are not left behind during health emergencies.
COVID-19 Testing Statistics Among Refugees
Between November 2020 and June 2022, the International Organization for Migration documented testing data suggesting that 23,972 refugees underwent 28,465 COVID-19 tests, with a positivity rate of just 2.6%. This statistic is particularly relevant when considering the global context of the pandemic and its influence on refugee resettlement in the US. Understanding these testing statistics is crucial for shaping future health policies that include robust screening protocols, tailored to the needs of immigrants and refugees.
The low positivity rate among refugees indicates effective predeparture public health measures, yet it also raises questions about access to testing and the impact of health education within refugee communities. As refugees prepare to arrive in the U.S., bolstering their understanding and access to COVID-19 testing is imperative. By fostering an environment of trust and education, health authorities can ensure that refugees are well-informed, further reducing the incidence of COVID-19 in this vulnerable population.
Vaccination Coverage Trends in Refugee Populations
As vaccinations increased globally during the pandemic, refugee vaccination coverage also saw significant growth, rising from 0% to 71% among adult refugees by the end of 2022. Notably, the provision of vaccines to refugees requires strategic planning and resources, as barriers to healthcare access can hinder efforts. Vaccination outreach programs specifically targeting refugee populations have been essential in addressing these challenges, helping to reduce the transmission of COVID-19 within these communities.
This surge in vaccination rates among refugees reflects the importance of inclusivity in health campaigns. Successful vaccination programs not only aid in protecting individual health but also contribute to community-level immunity, ultimately supporting broader public health goals. Continuous efforts to improve refugee vaccination uptake will ensure their role in moving toward recovery from the pandemic, thus paving the way for healthier futures for these populations.
The Role of Refugee Health in Pandemic Preparedness
The COVID-19 pandemic has underlined the importance of integrating refugee health into broader pandemic preparedness frameworks. Refugees often face unique health challenges that necessitate distinct considerations in emergency response strategies. The lessons learned from the pandemic provide an opportunity to reevaluate how refugee health is prioritized within public health systems, ensuring that resettlement agencies and health authorities work hand-in-hand to deliver adequate resources and support.
Implementing effective health monitoring systems for refugees can enhance their resilience against future pandemics. By ensuring accessible testing and vaccination services, and fostering community engagement in health initiatives, recovery efforts can be more comprehensive. Furthermore, structuring these responses around the specific health needs of refugees can lead to overall improvements in public health outcomes within the host country, highlighting the necessity of equitable healthcare access.
Regional Disparities in COVID-19 Testing
The data from the COVID-19 predeparture testing among refugees reveals significant regional disparities in positivity rates, with Asia facing a high rate of 4.1% compared to 1.8% in Europe. Such variations emphasize the need for region-specific strategies to bolster public health responses tailored to the specific circumstances and healthcare infrastructures of those areas. Understanding these differences is crucial for global health policymakers aiming to improve health outcomes among refugees.
Addressing the high rates of COVID-19 positivity in certain regions is vital for historical context in refugee health. Testing rates should be coupled with education campaigns in regions with high transmission rates to mitigate further spread. By collaborating with local health authorities in these regions, targeted approaches can be employed to improve health outcomes for refugees and the communities in which they settle, ultimately fostering a healthier environment for all.
Challenges Faced by Refugees During the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced numerous challenges for refugees, complicating their already precarious situations. Many refugees encountered significant delays in resettlement processes due to travel restrictions and testing requirements, prolonging their period of uncertainty and hardship. This disruption has psychological implications, as prolonged waiting periods can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and distress among individuals seeking stability.
Moreover, access to adequate healthcare services has been compromised for many refugees, particularly those without stable resettlement status. Barriers to obtaining COVID-19 testing and vaccination, such as transportation issues and language barriers, have hindered their ability to protect themselves adequately. Providing robust support systems and ensuring equitable access to healthcare during pandemics is essential for safeguarding the health and well-being of refugee populations.
The Importance of Refugee Resettlement in Public Health Policy
Refugee resettlement policies must be aligned with public health goals, especially during emergencies such as the COVID-19 pandemic. It is essential to understand how medical interventions, including testing and vaccination coverage, can be strategically integrated into resettlement processes. Strong public health frameworks that prioritize the specific needs of refugees are crucial to safeguarding against potential outbreaks and ensuring the health of the broader community.
Incorporating refugee health frameworks into national health policies will lead to improved access to testing, vaccinations, and healthcare services for these vulnerable populations. By continually advocating for the inclusion of refugee perspectives in health policies, public health authorities can mobilize resources effectively and prepare comprehensive responses to future health crises.
Future Directions for Refugee Health Initiatives
Looking ahead, future refugee health initiatives should focus on creating sustainable systems that encompass mental health services, preventative care, and rapid response mechanisms for infectious diseases such as COVID-19. Establishing comprehensive health programs that address the diverse needs of refugees will bolster their resilience during public health emergencies. Emphasizing the importance of continuous healthcare access beyond immediate crises ensures that refugees remain supported long after the pandemic subsides.
Collaboration among global health organizations, NGOs, and governmental agencies is essential to strengthen the capacity of healthcare systems that serve refugee populations. By jointly developing strategies that include regular health assessments, education on available services, and pathways to mental health resources, the comprehensive needs of refugees can be met more effectively. This collaborative approach can ultimately create a healthier world for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the COVID-19 vaccination statistics for adult refugees resettling in the US?
COVID-19 vaccination statistics indicate that among adult refugees arriving in the US from November 2020 to June 2022, 41.8% had completed their primary vaccination series prior to departure, with numbers increasing significantly to 71.3% by December 2022. This highlights the growing emphasis on refugee health in vaccination efforts.
How has the pandemic impacted refugee resettlement processes?
The pandemic significantly impacted refugee resettlement processes, causing delays primarily for those testing positive for COVID-19. With a positivity rate of 2.6% among tested refugees, resettlement efforts faced disruptions due to health protocols designed to ensure safety during travel.
What types of COVID-19 tests are administered to refugees prior to resettlement?
Refugees are primarily administered reverse transcription PCR tests for COVID-19, which comprised 87% of all tests conducted. Other testing methods, such as antigen tests, may also be used, but PCR remains the standard for verifying COVID-19 status prior to resettlement.
What were the COVID-19 test results for refugees entering the US?
From November 2020 to June 2022, a total of 28,465 COVID-19 tests were conducted among refugees, with a positivity rate of 2.6%. The results varied regionally, with higher positivity in Asia at 4.1% and lower rates in Europe at 1.8%.
What challenges were faced in vaccinating refugees during the pandemic?
Vaccination efforts for refugees encountered significant challenges, particularly in low-income areas, affecting both accessibility and implementation. Barriers such as lack of information and healthcare access hindered successful vaccination outreach, underscoring the need for integrating refugee health into broader public health strategies.
How many refugees underwent COVID-19 testing before coming to the US?
A total of 23,972 refugees underwent COVID-19 testing before their arrival in the US from November 2020 to June 2022, supporting the need for effective public health measures in refugee health management during the pandemic.
Why is monitoring COVID-19 vaccination coverage among refugees important?
Monitoring COVID-19 vaccination coverage among refugees is crucial for ensuring community health safety, facilitating safe resettlement, and preventing outbreaks in host countries. This data helps public health officials develop strategies that address the specific health needs of refugee populations.
| Key Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | November 24, 2020 – June 11, 2022 |
| Testing Overview | 23,972 refugees underwent 28,465 COVID-19 tests, with a positivity rate of 2.6%. |
| Vaccination Coverage | Vaccination rates increased from 0% at the start to 71% by December 2022 among adult refugees. |
| Regional Positivity Rates | Highest positivity in Asia (4.1%), lowest in Europe (1.8%). |
| Challenges in Resettlement | Testing delays and barriers to vaccination in low-income areas impacted refugee resettlement efforts. |
Summary
COVID-19 testing and vaccination refugees were significantly impacted by the pandemic, as highlighted by the findings from November 2020 to June 2022. During this period, a total of 23,972 refugees were tested for COVID-19, with a modest positivity rate of 2.6%, indicating effective health measures among incoming populations. Furthermore, vaccination coverage surged from complete absence to 71% among adult refugees within the same timeframe. These results reflect the ongoing efforts to integrate public health strategies for refugees and address disparities faced in low-income areas, emphasizing the importance of access to health resources during crises.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.