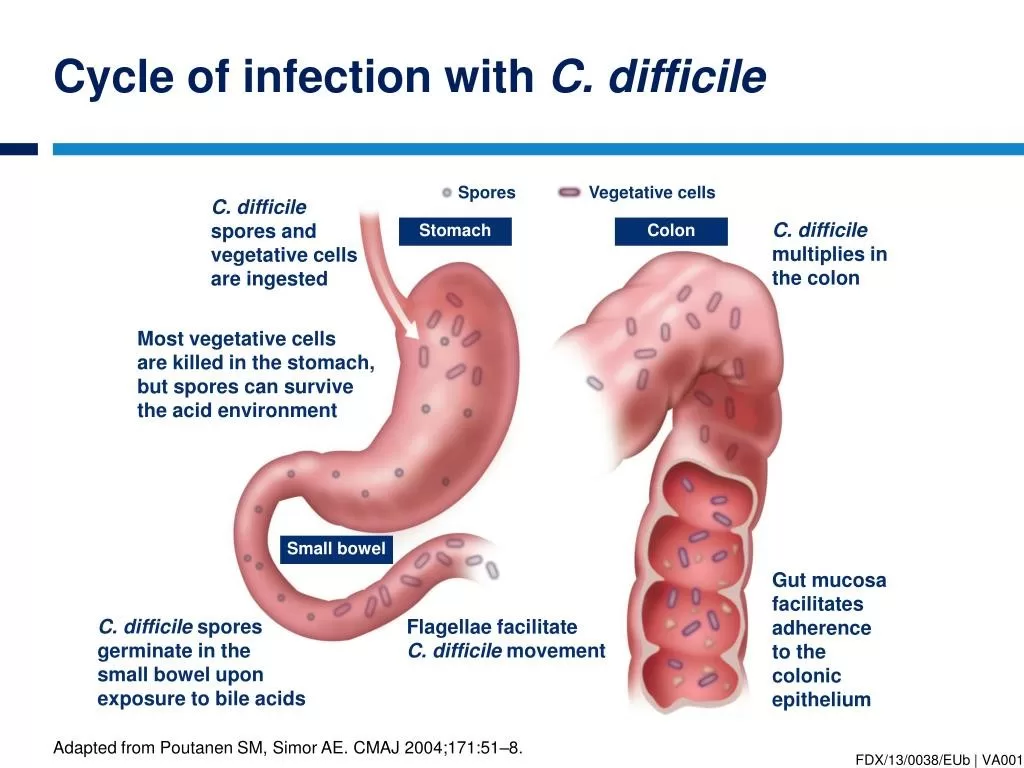
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) has rapidly become a major concern within healthcare settings, affecting nearly 500,000 individuals annually in the United States alone. This dangerous infection arises when the natural balance of gut bacteria is disrupted, often due to antibiotic use, allowing the C. difficile bacterium to proliferate and lead to severe gastrointestinal symptoms. Understanding Clostridium difficile symptoms is essential for early detection and effective intervention. Moreover, knowing how to prevent C. diff can significantly reduce transmission rates in vulnerable populations. In this article, we will explore the risks, symptoms, and prevention strategies associated with C. diff infection to foster a safer health environment for all.
C. diff infection, a serious intestinal issue caused by the Clostridium difficile bacterium, poses significant health risks, particularly in healthcare facilities. This infection can lead to severe cases of diarrhea and colitis, primarily affecting individuals whose gut flora is compromised, often by antibiotics or underlying health conditions. Understanding the manifestation of Clostridium difficile symptoms is critical to effectively address and manage the condition. Preventive measures play a vital role in curbing the spread of C. difficile, ensuring that both patients and healthcare providers remain vigilant. In this exploration, we’ll discuss various aspects of C. diff treatment options and how to prevent C. diff infections to enhance public awareness.
Understanding Clostridium Difficile Symptoms: Identifying Signs Early
Clostridium difficile symptoms often manifest as a significant disturbance in gastrointestinal function, prominently featured by severe diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever. Patients might notice that the frequency of their bowel movements increases dramatically, often characterized by an unusually foul-smelling stool. These symptoms can escalate, leading to dehydration and colitis if left untreated, making it critical for individuals, particularly those in high-risk categories, to recognize these early warning signs. Additionally, losses in appetite and associated nausea may appear, contributing to a general sense of unwellness.
Early identification of Clostridium difficile symptoms is essential in preventing progression to more severe health outcomes. It is particularly imperative for vulnerable groups such as older adults and those with weakened immune systems to be vigilant. If someone has recently taken antibiotics and exhibits these symptoms, immediate medical evaluation is advised. Prompt diagnosis and intervention can lead to more effective treatment, reduce the risk of complications, and help in curbing the spread of infection within community and healthcare settings.
Clostridium Difficile Prevention: Effective Strategies to Avoid Infection
Preventing Clostridium difficile infection begins with diligent hygiene practices. In healthcare environments, thorough cleaning of surfaces using bleach-based disinfectants can kill C. diff spores that might linger on frequently touched areas. Hand hygiene plays a critical role as well; healthcare workers are urged to wash their hands with soap and water rather than relying on alcohol-based sanitizers, which are less effective against these spores. Educating staff on proper handwashing techniques and adherence to cleaning protocols is crucial in high-risk areas, such as hospitals and nursing homes.
At home, preventing C. diff infections involves maintaining a clean living environment and being cautious after antibiotic use. Families should incorporate regular cleaning routines and teach proper hand hygiene to all members, ensuring that everyone understands the significance of these actions in preventing infections. Awareness of the risks associated with antibiotic overuse can also empower individuals to advocate for appropriate antibiotic prescriptions, thereby safeguarding their gut health and reducing the likelihood of a C. difficile outbreak.
C. Diff Treatment Challenges: Understanding Recurrence and Management
Treating Clostridium difficile effectively poses unique challenges, particularly when dealing with recurrence rates that affect 20-30% of patients following initial antibiotic therapy. While first-line treatments include antibiotics like vancomycin or fidaxomicin, these do not always guarantee long-term success, as some individuals may experience repeat infections. Understanding the intricacies of C. diff treatment requires healthcare providers to be aware of patient history and to continuously monitor symptoms, intervening quickly if recurrence occurs.
Emerging therapies are making headway in addressing these treatment challenges. One promising solution is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), which involves transferring healthy gut bacteria to those who have suffered from multiple recurrences of C. diff. By restoring the balance of microbiota in the intestines, FMT has shown significant success in reducing recurrence rates. Additionally, monoclonal antibodies targeting specific toxins produced by C. difficile are being investigated as new avenues for management, providing hope for more effective treatment strategies.
The Role of Education in Clostridium Difficile Awareness
Raising public awareness about Clostridium difficile is crucial to preventing outbreaks and promoting better health outcomes. Organizations like the C Diff Foundation are actively working to educate both healthcare providers and the general public about the infection, its symptoms, and the importance of hygiene. Their campaigns often highlight how widespread misinformation can lead to severe consequences, underscoring the need for continuous education regarding prevention and early intervention.
Effective educational initiatives can significantly impact how communities respond to C. diff infections. By fostering an understanding of the infection’s risks and encouraging proactive measures, awareness programs empower individuals to seek timely medical attention and adhere to preventive practices at home and in healthcare settings. Community workshops, informational brochures, and digital resources are tools that can facilitate knowledge sharing, further creating a safety net against the Clostridium difficile threat.
Identifying At-Risk Populations for Clostridium Difficile Infection
Certain demographics are more vulnerable to Clostridium difficile infection (CDI), particularly older adults over 65, individuals on long-term antibiotic therapies, and those with compromised immune systems. This high-risk categorization emphasizes the need for targeted prevention strategies within these groups. A proactive approach, including regular screenings, education on the risks, and enhanced hygiene practices, can significantly mitigate the impact of CDI among at-risk populations.
Healthcare providers should prioritize education for these vulnerable groups, ensuring they are informed of the symptoms of CDI and the steps they can take to protect themselves. Furthermore, family members and caregivers play a vital role in supporting at-risk individuals by emphasizing hygiene measures and encouraging prompt medical consultations if symptoms arise. By fostering an environment of awareness and vigilance, we can collectively work towards reducing infection rates within these susceptible groups.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common Clostridium difficile symptoms to watch for?
Common Clostridium difficile symptoms include severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and loss of appetite. If you experience these symptoms, especially after antibiotic use, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
How can I practice Clostridium difficile prevention effectively?
Effective Clostridium difficile prevention involves maintaining good hand hygiene, regularly disinfecting surfaces with bleach-based cleaners, and educating yourself and others about the risks associated with CDI. Avoid unnecessary antibiotic use to help protect your gut flora.
What is the current standard for C. diff treatment?
The current standard for C. diff treatment includes antibiotics like vancomycin or fidaxomicin. It’s crucial to follow your doctor’s advice, as the recurrence of infection can be a significant challenge after initial treatment.
How does Clostridium difficile spread in healthcare settings?
Clostridium difficile spreads in healthcare settings primarily through contaminated surfaces and direct contact with infected individuals. Rigorous cleaning protocols and good personal hygiene are essential to prevent transmission in hospitals and nursing homes.
Can Clostridium difficile symptoms be mistaken for other conditions?
Yes, Clostridium difficile symptoms can often be mistaken for other gastrointestinal disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease or regular viral gastroenteritis. Early recognition and proper diagnosis by healthcare providers are vital for effective treatment.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is a significant cause of gastrointestinal disorders, primarily in healthcare environments. |
| Incidence and Impact | Nearly 500,000 CDI cases occur annually in the U.S., showing a dramatic increase in incidence and severity. |
| At-Risk Populations | Older adults, individuals on antibiotics, and those with weakened immune systems are particularly susceptible to CDI. |
| Transmission Mechanism | C. difficile spores survive on surfaces for long periods, spreading through contaminated surfaces and direct contact. |
| Prevention Strategies | Effective cleaning, hand hygiene, and public education are crucial to prevent CDI. |
| Treatment Challenges | Standard antibiotics face recurrence issues; new treatments like fecal microbiota transplantation are being researched. |
| Public Awareness | Early recognition of CDI symptoms can lead to better outcomes; organizations promote prevention and education. |
Summary
Clostridium Difficile Infection (CDI) is a multifaceted health concern that underscores the importance of awareness and preventive strategies, especially among vulnerable populations such as older adults and those with weakened immune systems. Understanding CDI is crucial, as it leads to severe gastrointestinal issues that can have serious implications for health. By adhering to rigorous hygiene practices, promptly identifying symptoms, and implementing effective treatment options, communities can work towards reducing the incidence of CDI. Ongoing education and research remain pivotal in combating this infection and improving public health outcomes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.