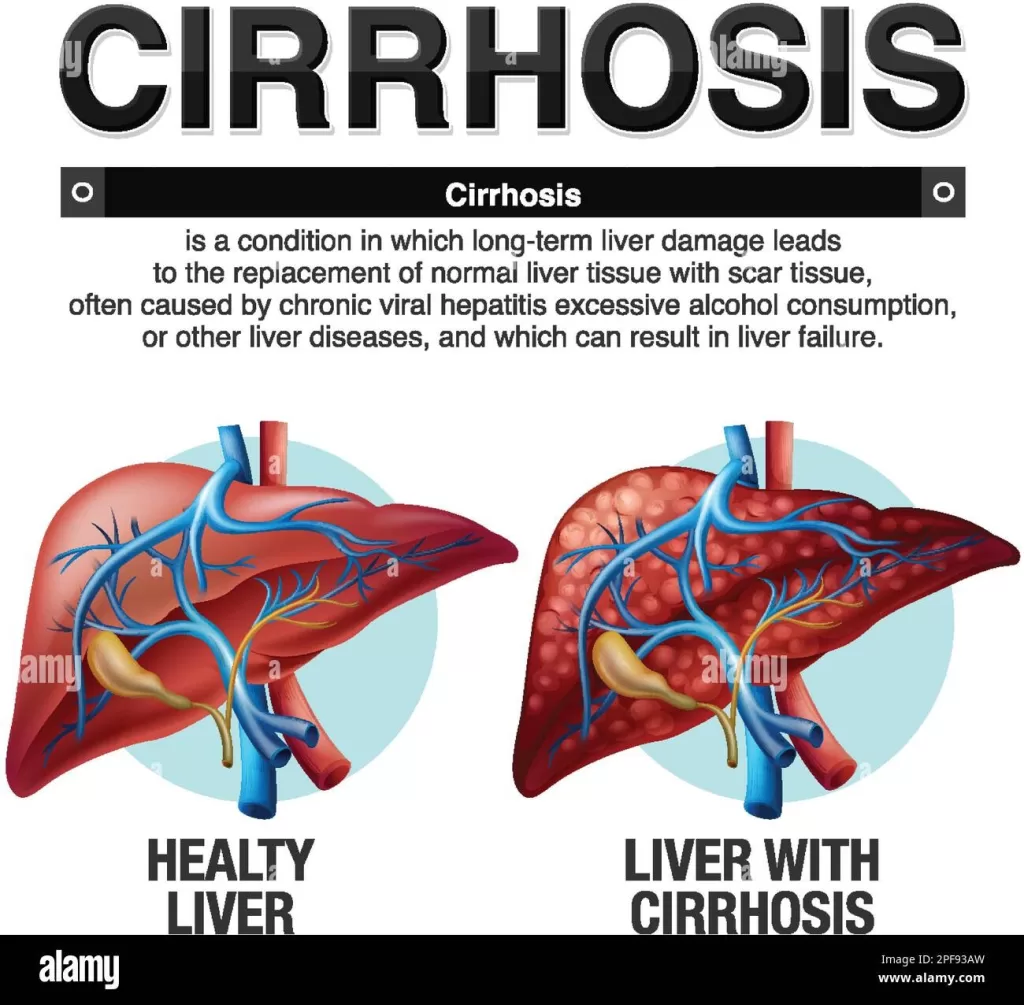
Cirrhosis is a severe liver condition marked by the progressive scarring of liver tissue, a critical process that disrupts normal liver function. This late-stage liver disease often stems from several underlying factors, including chronic alcohol use, obesity, and viral hepatitis. Patients suffering from cirrhosis may experience a range of symptoms, from fatigue to jaundice, which highlight the importance of liver health awareness. As this condition progresses, it can lead to serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer, necessitating effective cirrhosis treatment and management strategies. By understanding the causes and symptoms of cirrhosis, individuals can better navigate their health and seek appropriate support.
Also known as end-stage liver disease, cirrhosis represents a critical stage of liver dysfunction characterized by irreversible damage and fibrosis. This condition results from a variety of factors, including unhealthy lifestyle choices and viral infections, which contribute to the decline of liver health over time. When the liver is unable to function correctly due to extensive scarring, it may lead to severe health issues, such as portal hypertension and potential liver cancer. Survivors of liver disease must focus on cirrhosis management efforts that include lifestyle adjustments, medical intervention, and close monitoring of symptoms. Recognizing the early symptoms can be instrumental in preventing further complications and improving overall outcomes.
Identifying the Causes of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a progressive liver disease typically caused by chronic damage to liver tissue. The most common cause is chronic alcohol consumption, which leads to inflammation and eventual scarring of the liver. Over time, excessive alcohol intake can inhibit the liver’s ability to process toxins effectively, predisposing individuals to serious complications including liver failure and hepatitis. In addition to alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, particularly types B and C, are significant contributors to the development of cirrhosis. The prolonged immune response to these infections can cause severe inflammation and fibrosis of liver tissue.
Moreover, obesity is increasingly recognized as a causative factor in cirrhosis. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition characterized by excess fat in the liver, can progress to cirrhosis in individuals who are obese. The global rise in obesity rates presents a growing challenge in managing liver health. Other notable causes of cirrhosis include autoimmune diseases that target the liver, bile duct obstructions, and certain genetic conditions. Identifying these causes early is critical for preventing further liver damage through informed lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Cirrhosis
The symptoms of cirrhosis often remain unnoticed in the early stages, making early diagnosis quite challenging. As liver function deteriorates, patients may experience a range of symptoms. Fatigue and weakness are common initial signs due to the liver’s reduced ability to produce the necessary proteins that help maintain energy levels. As the condition progresses, jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, can become evident, indicating an accumulation of bilirubin due to impaired liver function.
Other symptoms may include swelling in the legs, abdomen, or feet, known as edema, which results from poor protein synthesis and fluid retention caused by cirrhosis. Patients can also experience skin itchiness, nausea, and easy bruising, alongside changes in mental state due to toxins accumulating in the bloodstream. Recognizing these symptoms early lets individuals seek timely medical care, enabling better management of cirrhosis and potentially slowing its progression.
Complications Associated with Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis can lead to various severe complications that significantly impact a patient’s health and quality of life. One of the most alarming risks associated with advanced cirrhosis is the development of liver cancer. Research has shown that individuals with cirrhosis have an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma due to ongoing liver cell damage. The transformation of healthy liver cells into cancerous ones is often a consequence of chronic inflammation and scarring.
Another significant complication is liver failure, where the liver can no longer perform its essential functions. This end-stage liver disease may necessitate a liver transplant as the only viable treatment option. Additionally, portal hypertension, an increase in blood pressure in the portal vein, can result in esophageal varices, which are enlarged veins that pose a risk of severe bleeding. Therefore, understanding the possible complications of cirrhosis is essential for proactive management and ongoing monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Effective Management Strategies for Cirrhosis
Managing cirrhosis effectively requires a multi-faceted approach that targets the underlying cause while also addressing symptoms. Lifestyle modification is a cornerstone of treatment; patients are often advised to abstain from alcohol, maintain a balanced diet, and achieve a healthy weight. Such changes can help slow the progression of the disease and enhance liver health. Regular exercise has also been shown to benefit those with liver disease by promoting overall health and physical function.
In addition to lifestyle changes, medication may play a vital role in treating the underlying causes of cirrhosis, such as antiviral treatments for hepatitis infections. Routine health check-ups and blood tests are crucial for monitoring liver function and detecting any complications early. Furthermore, connecting with support networks can provide emotional and practical resources, empowering patients in their health journey and improving their overall management of cirrhosis.
Patient Resources and Support Networks for Cirrhosis
Navigating the complexities of living with cirrhosis can be daunting, but numerous resources and support networks are available for patients and their families. Organizations such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs provide comprehensive information on cirrhosis, including causes, treatment options, and how to live a healthier lifestyle with the condition. They offer detailed guides that address common concerns and frequently asked questions about liver disease management.
Additionally, local support groups can connect patients with others facing similar challenges, creating a sense of community and shared understanding. Engaging with healthcare providers can also lead to personalized support tailored to individual needs. This holistic approach helps patients to not just manage their cirrhosis but also to enhance their quality of life while dealing with this serious liver condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis can be caused by several factors, with chronic alcohol use, obesity, and viral hepatitis being the most common. Heavy alcohol consumption leads to liver damage, while obesity increases the risk of fatty liver disease that can progress to cirrhosis. Chronic hepatitis infections (particularly types B and C) contribute significantly to liver health decline, often resulting in cirrhosis.
What are the early symptoms of cirrhosis I should watch for?
In the early stages, cirrhosis may not present symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, individuals may experience fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), swelling in the abdomen or legs, itchy skin, and easy bruising. Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for effective liver disease management and intervention.
How is cirrhosis treated and managed?
Cirrhosis treatment focuses on managing its underlying causes and preventing complications. This may include lifestyle changes such as abstaining from alcohol, maintaining a balanced diet, and achieving a healthy weight. Medication may be prescribed to address viral hepatitis or other liver issues, alongside regular check-ups to monitor liver health and assess for potential complications.
What complications can arise from cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis can lead to serious complications, such as liver cancer, liver failure, and portal hypertension, which can cause dangerous varices that may bleed. Monitoring for these complications is essential for those diagnosed with cirrhosis, as timely intervention can be critical in managing these severe risks.
How can I support liver health if I have cirrhosis?
To support liver health while living with cirrhosis, it is important to adopt a holistic approach. This includes making essential lifestyle changes like avoiding alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity. Regular medical check-ups and utilizing patient resources can also provide critical support in managing your condition.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Cirrhosis is the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, disrupting liver function. |
| Causes | 1. Chronic Alcohol Use 2. Obesity 3. Viral Hepatitis (Hepatitis B and C) |
| Symptoms | – Fatigue and weakness – Jaundice – Swelling in legs and abdomen (edema) – Itchy skin – Nausea and vomiting – Easy bruising |
| Complications | 1. Liver Cancer 2. Liver Failure (end-stage liver disease) 3. Portal Hypertension (varices) |
| Management | 1. Lifestyle changes (avoid alcohol, balanced diet) 2. Medications for underlying causes 3. Regular check-ups 4. Support services |
Summary
Cirrhosis is a serious liver condition that can have life-altering consequences for patients. This chronic disease results in extensive scarring of the liver, which leads to significant impairments in liver function. Understanding cirrhosis is crucial for early detection and effective management. Patients must recognize the various causes and risk factors, including heavy alcohol use, obesity, and viral hepatitis, which contribute to the development of this condition. Symptoms may not be apparent initially, but as cirrhosis progresses, they can become severe, potentially resulting in complications like liver cancer and liver failure. Effective management strategies involve lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and regular health monitoring to improve patient outcomes. Educating yourself about cirrhosis is vital, empowering individuals to proactively manage their health.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.