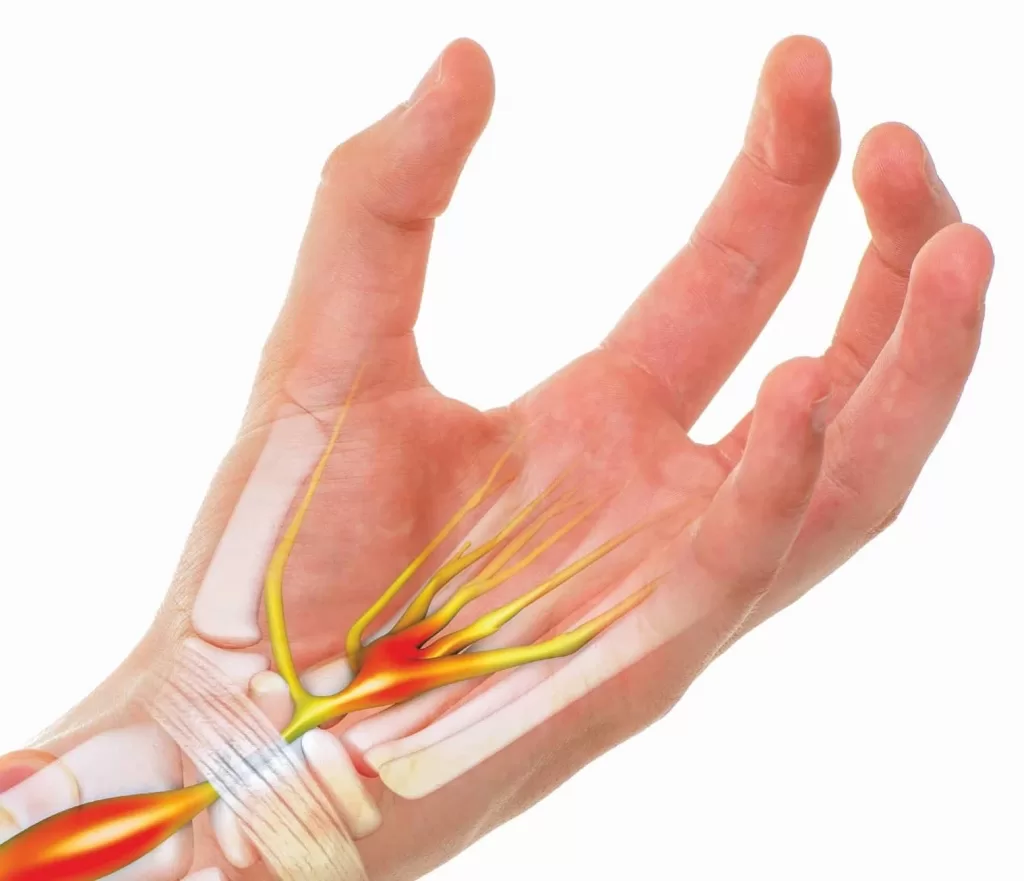
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a prevalent condition that results from increased pressure on the median nerve within the wrist, often causing discomfort and functional impairment in the affected hand. This syndrome is particularly common among individuals who perform repetitive tasks, leading to various carpal tunnel symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and pain. Understanding the causes of carpal tunnel is essential for prevention and management, especially as it can often be linked to factors like health conditions, anatomical peculiarities, and genetics. Fortunately, several CTS treatment options are available, ranging from lifestyle modifications and conservative measures to surgical interventions. Early recognition and treatment can greatly enhance carpal tunnel relief, allowing individuals to regain control over their daily activities.
Often referred to as median nerve compression syndrome, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome manifests itself through a variety of discomforting symptoms affecting the wrist and hand. This condition is frequently encountered by those whose activities involve repetitive wrist motions, leading to inflammation and irritation of the median nerve. By recognizing the underlying causes of carpal tunnel syndrome, individuals can proactively seek solutions for effective management. With various pathways to alleviate symptoms, including ergonomic adjustments and targeted treatments, finding relief from this condition is both attainable and essential for maintaining a healthy, functional lifestyle. Whether through non-invasive measures or surgical options, understanding the nuances of median nerve compression is vital for anyone dealing with the challenges it presents.
What Are the Primary Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) can arise from various factors that lead to increased pressure on the median nerve. Commonly, repetitive hand movements are a significant contributor, as seen in individuals engaged in typing or assembly line work. These activities require constant wrist flexion and can cause inflammation of the tendon sheath, resulting in swelling that compresses the median nerve. Notably, even leisure activities such as knitting or crafting can exacerbate the risk of developing CTS, highlighting the impact of daily activities on wrist health.
Health conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and hypothyroidism also play a critical role in the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. Diabetes affects the body’s nerve health, which increases vulnerability, while rheumatoid arthritis can lead to joint swelling that limits nerve space in the wrist. Additionally, hormonal changes experienced during menopause may contribute to fluid retention and increased pressure on the median nerve, further complicating the condition. Understanding these causes can empower individuals to implement preventive measures effectively.
Recognizing Carpal Tunnel Symptoms Early
Identifying the symptoms associated with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is essential for early intervention and management. Many individuals experience numbness or tingling sensations that primarily affect the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger. These symptoms often occur during sleep or after prolonged hand use, indicating that the median nerve is being compressed. Recognizing these early signs can lead to prompt assessment and treatment, preventing the condition from becoming more debilitating over time.
In addition to numbness, individuals suffering from CTS may experience pain that radiates from the wrist into the forearm. This pain can worsen at night or during daily activities that involve gripping or holding objects. Furthermore, weakness in grip strength is a common complaint, making routine tasks challenging and frustrating. Awareness of these symptoms is crucial, as it can motivate those affected to seek medical advice sooner rather than later.
Effective Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
When it comes to treating Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, a multifaceted approach often yields the best results. Initial treatments may include the use of wrist splints to keep the wrist in a neutral position, particularly during sleep. This simple intervention helps alleviate pressure on the median nerve and can lead to significant symptom relief. Furthermore, modifying activities to reduce repetitive wrist movements is crucial. For those whose work necessitates such tasks, employing ergonomic tools or taking regular breaks can provide substantial benefits.
In cases where conservative treatments prove insufficient, medical interventions such as corticosteroid injections can be considered. These injections are designed to reduce inflammation and swelling around the median nerve, often resulting in rapid symptom relief. Pain relief medications can also support management efforts by addressing pain and discomfort. For patients who continue to experience symptoms despite these interventions, surgical options like Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Adopting lifestyle changes is a proactive way to prevent or mitigate the impact of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace, such as monitor height, keyboard placement, and proper wrist positioning, can significantly reduce the risk of median nerve compression. Additionally, incorporating regular breaks into your routine allows the wrist to rest and recover from repetitive tasks, maintaining optimal nerve function and reducing inflammation.
Physical activity is also vital in preventing CTS. Engaging in exercises that strengthen the wrist and hand might prevent the onset of symptoms. Stretching exercises, in particular, can enhance flexibility and circulation, minimizing the risk of nerve compression. Overall, being aware of your body mechanics and making conscious changes in daily routines can greatly contribute to better wrist health and the prevention of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
The Role of Medical Professionals in Carpal Tunnel Management
Medical professionals play a key role in diagnosing and managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome effectively. If symptoms of CTS are suspected, seeking evaluation from a healthcare provider is critical. They may perform physical examinations and recommend diagnostic tests, such as nerve conduction studies, to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential conditions. Obtaining a clear diagnosis is essential for outlining a tailored treatment plan that addresses individual symptoms and lifestyle needs.
In addition to initial assessments, medical professionals can provide ongoing management strategies, including prescribing medications or recommending physical therapy. They can educate individuals about lifestyle adjustments and ergonomic practices that can help alleviate symptoms or prevent further episodes. When conservative measures fail, they can also guide patients through surgical options, ensuring comprehensive care that promotes recovery and long-term hand health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)?
Common symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) include numbness and tingling in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger, especially at night. Pain may radiate from the wrist into the forearm, and individuals often experience weakness in grip strength, making daily tasks difficult.
What are the primary causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The primary causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) include repetitive hand movements, certain health conditions like diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, anatomical factors such as a smaller carpal tunnel, and genetic predisposition. These factors can lead to median nerve compression, resulting in CTS symptoms.
What treatment options are available for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome relief?
Treatment options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) include wrist splinting to keep the wrist stable, activity modification to avoid repetitive strain, physical therapy to strengthen muscles, corticosteroid injections for inflammation, and oral medications. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
How does median nerve compression relate to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Median nerve compression is the primary issue in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS). When the median nerve, which travels through the carpal tunnel in the wrist, becomes compressed due to inflammation or anatomical factors, it leads to the characteristic symptoms of numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
To prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), consider making lifestyle changes such as taking regular breaks during repetitive tasks, using ergonomic tools while working, practicing wrist exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight. These adjustments can help reduce the risk of developing symptoms associated with median nerve compression.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome | Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is caused by increased pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, leading to discomfort and functional loss. |
| Causes of CTS | Includes repetitive hand movements, health conditions (like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis), anatomical factors, and genetics. |
| Symptoms of CTS | Common symptoms include numbness or tingling, pain radiating to the forearm, and weakness in grip strength. |
| Initial Treatment Options | Wrist splinting, activity modification, and physical therapy are effective initial treatments for CTS. |
| Medical and Surgical Treatments | Corticosteroid injections and oral medications can relieve symptoms; surgery may be necessary for persistent cases. |
Summary
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a prevalent condition that necessitates understanding and awareness about its symptoms and treatment options. This syndrome arises from the compression of the median nerve in the wrist, leading to significant discomfort and reduced hand function. Identifying the causes, such as repetitive hand activities, specific health conditions, anatomical factors, and genetic predisposition, is crucial in managing CTS effectively. Treatments often begin with conservative measures such as wrist splinting and activity modifications, and may escalate to medical interventions like corticosteroid injections or surgical options if symptoms persist. Understanding the comprehensive nature of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome allows individuals to seek appropriate help and improve their quality of life.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.