Burkholderia thailandensis is emerging as a significant pathogen within various clinical scenarios, including cases of hypoxemic respiratory failure and septic shock. This previously underestimated bacterium has gained attention due to its ability to cause severe infections, even in patients without underlying health conditions, as demonstrated in a recent case study from China. Medical professionals must recognize the virulence of Burkholderia infections and adapt their diagnostic processes accordingly to prevent tragic outcomes. The case of acute respiratory failure linked to Burkholderia thailandensis underlines the need for heightened clinical awareness and prompt treatment interventions. With its potential to complicate patient outcomes, understanding the implications of Burkholderia thailandensis is crucial for improving public health responses to such infections.
The bacterium Burkholderia thailandensis, often overlooked in discussions about infectious diseases, is increasingly recognized for its role in severe clinical manifestations, particularly in cases of acute respiratory distress and systemic infections. Known primarily for its close relation to the more virulent Burkholderia pseudomallei, Burkholderia thailandensis has been documented in clinical settings, raising concerns about its pathogenic potential. Cases of hypoxemic respiratory failure associated with these pathogens have prompted researchers and healthcare professionals to reconsider the clinical implications and treatment protocols required to manage such infections effectively. This shift in perspective underscores the importance of advancing our understanding of Burkholderia infections, as timely interventions can be critical in preventing serious health complications, including septic shock.
Understanding Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
Acute hypoxemic respiratory failure is a severe condition characterized by a sudden inability to maintain adequate gas exchange in the lungs, leading to critically low levels of oxygen in the bloodstream. It can be triggered by various causes, including pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and infections such as those caused by Burkholderia thailandensis. This type of respiratory failure requires immediate intervention as it can rapidly progress to multi-organ failure if not addressed promptly.
The clinical presentation of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure typically involves symptoms such as shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and a drop in oxygen saturation levels. Diagnosis generally relies on imaging studies, such as chest X-rays or CT scans, which can reveal underlying lung infections or abnormalities. Given the critical nature of this condition, treatment strategies often include oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and addressing the underlying cause, which may involve broad-spectrum antibiotics in cases of infectious etiology.
Burkholderia thailandensis and Its Misdiagnosis Risks
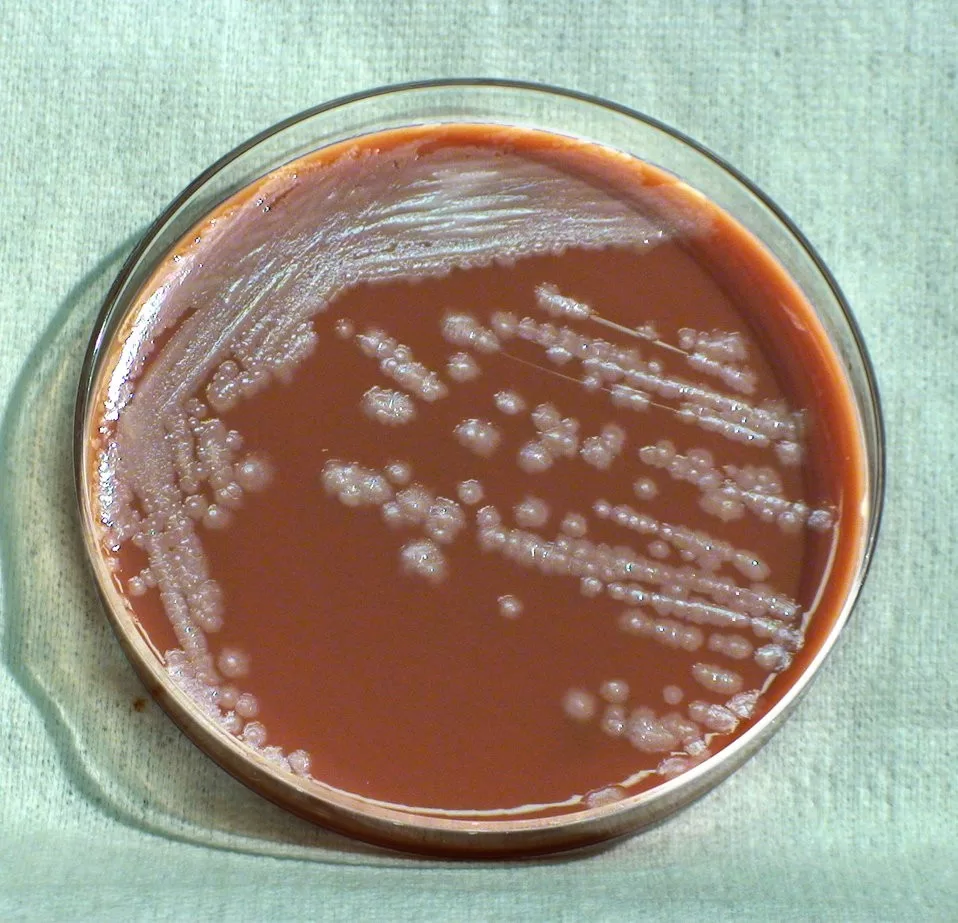
Burkholderia thailandensis is a gram-negative bacterium that is often underestimated in terms of its pathogenic potential. Traditionally viewed as non-pathogenic, recent cases—like the fatal instance of hypoxemic respiratory failure in China—shed light on its virulence, even in previously healthy individuals. The challenge lies in its misidentification, as clinicians may mistake it for its more virulent relative, Burkholderia pseudomallei, which is notorious for causing melioidosis.
This misdiagnosis can lead to delayed treatment, significantly affecting patient outcomes. The case reported from Hainan Province emphasizes the urgency for healthcare providers to remain vigilant regarding the possibility of *B. thailandensis* infections. Timely identification and correct diagnosis are crucial to implementing appropriate treatment measures, particularly in regions where such pathogens may be prevalent, thus mitigating the risks of severe complications like septic shock.
Septic Shock Cases Associated With Burkholderia Infections
Septic shock is a life-threatening condition that can arise from various infectious agents, including Burkholderia species. In the context of infections caused by Burkholderia thailandensis, septic shock may occur due to the rapid onset of systemic inflammation and multi-organ dysfunction. Patients presenting with symptoms of severe pneumonia or respiratory distress should be closely monitored for signs of septic shock, particularly in light of the organism’s potential to cause rapid clinical decline.
Healthcare providers must be equipped to recognize the clinical signs of septic shock, such as hypotension, tachycardia, and altered mental status. Early intervention is critical, typically involving the immediate administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics and intravenous fluids. Given that Burkholderia thailandensis can be misidentified, a heightened clinical suspicion is essential for appropriate management, as well as for implementing effective biosafety measures in healthcare settings.
Geographic Considerations: Burkholderia thailandensis in China
In recent years, reports of Burkholderia thailandensis infections have emerged from various regions, including China. The environmental prevalence of this organism poses a unique challenge for public health, especially in areas involved in agricultural activities like rice farming, as indicated by the case study of the 58-year-old male farmer from Hainan Province. Understanding the geographical distribution and local environmental factors is crucial for determining risk factors associated with infections.
The presence of Burkholderia species in the soil and water in endemic regions can lead to increased exposure among individuals. Thus, routine surveillance and awareness programs should be established to inform local communities about the risks associated with Burkholderia thailandensis. Implementing preventive measures, particularly in agricultural sectors, may help reduce the incidence of infections and enhance overall public health safety in China.
Clinical Management of Burkholderia thailandensis Infections
The clinical management of infections caused by Burkholderia thailandensis is complex and requires a multifaceted approach. Identification of the pathogen through cultures and molecular methods is essential to tailor antibiotic therapy effectively, especially since strains may exhibit resistance to standard treatments. In acute settings, where respiratory failure is present, rapid initiation of broad-spectrum antibiotics is crucial, ideally followed by adjustments based on susceptibility patterns.
Ongoing monitoring of the patient’s respiratory status and overall clinical picture is vital, as complications like pneumonitis and septic shock can arise unexpectedly. Multi-disciplinary care involving infectious disease specialists, pulmonologists, and critical care experts can enhance outcomes for affected patients by ensuring comprehensive treatment strategies that encompass infection control and supportive care measures.
The Importance of Timely Diagnosis for Burkholderia Infections
Timely diagnosis of Burkholderia infections, particularly those caused by Burkholderia thailandensis, is paramount in preventing severe complications such as acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and septic shock. Clinicians must maintain a high index of suspicion for patients who present with respiratory symptoms and have potential exposure history. Advanced diagnostic techniques, including PCR and next-generation sequencing, can aid in rapid identification.
The earlier a diagnosis is made, the sooner treatment can be initiated, which can dramatically improve survival rates and outcomes. It is critical for healthcare systems to implement training and awareness programs for medical personnel concerning potential Burkholderia infections, emphasizing the effective use of diagnostic tools and appropriate clinical pathways to follow in suspected cases.
Biosafety Measures in Managing Burkholderia thailandensis
Biosafety measures are crucial in managing and preventing the spread of Burkholderia thailandensis within healthcare settings and the community at large. Healthcare institutions must establish strict protocols for handling suspected infections to protect healthcare workers and patients. This may involve personal protective equipment (PPE), diligent sterilization practices, and isolation procedures during the management of confirmed cases.
Community awareness programs can also play a significant role in educating the public about the potential risks associated with Burkholderia infections, particularly in rural areas with high exposure potential. Emphasizing biosafety in agriculture and water management practices can mitigate environmental transmission of this pathogen, ultimately reducing the incidence of infections among high-risk populations.
Public Health Implications of Burkholderia Infections
The public health implications of Burkholderia thailandensis infections extend beyond individual cases, affecting overall community health dynamics. Increased incidence of infections calls for rigorous epidemiological studies and public health strategies focused on monitoring and controlling environmental factors contributing to the spread. Enhanced surveillance systems can aid in early detection and outbreak response, which is particularly important in endemic regions.
Furthermore, public health initiatives should aim to educate at-risk populations about the signs and symptoms of Burkholderia infections, promoting early medical evaluation. Collaboration between public health entities, agricultural sectors, and healthcare systems is vital to strengthen responses to potential outbreaks and reduce overall morbidity associated with these infections.
Research Advancements in Burkholderia Pathogen Understanding
Research on Burkholderia thailandensis and its relatives has made significant strides in elucidating the genetic and pathogenic profiles of these organisms. Genomic sequencing tools and bioinformatics have provided insights into the evolutionary relationships among Burkholderia species, fostering a better understanding of virulence mechanisms. Such advancements are essential for developing targeted therapeutic interventions and improving diagnostic protocols.
Additionally, ongoing research efforts focusing on vaccine development and immunological responses to Burkholderia infections hold promise for future preventative strategies. By harnessing new technologies and methodologies, researchers aim to develop effective treatments and preventive measures against these infections, ultimately reducing the burden of disease caused by Burkholderia thailandensis and related species.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Burkholderia thailandensis and why is it important in medical research?
Burkholderia thailandensis is a bacterium that has gained attention in medical research due to its association with severe infections, including cases of fatal acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. While traditionally viewed as non-pathogenic, recent evidence, such as a fatal case in China, demonstrates its potential virulence, especially in previously healthy individuals, which emphasizes the need for increased clinical awareness and timely diagnosis.
How can Burkholderia thailandensis lead to septic shock?
Burkholderia thailandensis can lead to septic shock when it causes severe infections that rapidly progress. In a reported case, a patient developed septic shock after being diagnosed with an infection, highlighting that even individuals without pre-existing health conditions can be at risk. This underscores the critical need for healthcare professionals to recognize and respond to infections caused by this organism swiftly.
What were the symptoms of the patient with Burkholderia thailandensis infection in the 2019 case reported from China?
In the 2019 case from China, the patient exhibited symptoms including unexplained cough, sputum production, chest tightness, and shortness of breath over the course of eight days. These symptoms, along with significant lab abnormalities, ultimately led to the diagnosis of Burkholderia thailandensis and demonstrate the diverse respiratory manifestations of this bacterial infection.
What treatment options are available for infections caused by Burkholderia thailandensis?
Treatment for Burkholderia thailandensis infections typically involves antibiotics such as tigecycline and imipenem. In the case reported from China, despite initial treatment, the patient experienced deterioration, which suggests that effective management of these infections may require prompt identification and careful selection of antibiotics based on susceptibility.
Why is there concern about Burkholderia thailandensis being misidentified?
There is concern about Burkholderia thailandensis being misidentified as Burkholderia pseudomallei, the latter being the primary cause of melioidosis. This misidentification can lead to inadequate treatment regimens and worsen patient outcomes. The reported case emphasizes the importance of accurate laboratory diagnostics to distinguish between these two closely related species.
What factors may contribute to the virulence of Burkholderia thailandensis in healthy individuals?
The virulence of Burkholderia thailandensis in healthy individuals might be influenced by factors such as strain variability, host immune response, and environmental exposure. The recent fatal case in China illustrates that while the organism is often deemed non-lethal, it can indeed cause severe and life-threatening infections under certain circumstances.
What lessons can be learned from the fatal case of Burkholderia thailandensis in China?
The fatal case of Burkholderia thailandensis in China teaches us the importance of heightened clinical awareness and the need for rapid diagnosis and treatment. It challenges the assumption that this bacterium is non-lethal, emphasizing the necessity for improved biosafety measures and education among healthcare professionals regarding the potential dangers associated with Burkholderia infections.
How does Burkholderia thailandensis cause acute respiratory failure?
Burkholderia thailandensis can cause acute respiratory failure by leading to severe lung infections that result in significant respiratory distress and complications, such as pneumonia. In the reported case, the patient experienced acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, indicating that the bacterium can impact lung function markedly, especially when treatment is delayed or inadequate.
What are the implications of Burkholderia thailandensis infections in tropical regions?
In tropical regions, Burkholderia thailandensis infections pose a significant health risk, as environmental conditions may favor the growth of this organism. The case from China shows that healthcare systems need to prepare for potential outbreaks and ensure they have the diagnostic capabilities to handle such infections effectively, particularly in areas where the bacterium may be endemic.
What further research is needed regarding Burkholderia thailandensis?
Further research on Burkholderia thailandensis is crucial to understand its pathogenic mechanisms, environmental reservoirs, and potential therapeutic options. Studies should focus on improving diagnostic methods, mapping virulence factors, and developing effective treatment guidelines to manage infections caused by this opportunistic pathogen.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Letter | Fatal Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure Caused by Burkholderia thailandensis in China |
| Authors | Pei Zhang, Dai Kuang, Shaowen Chen, Wei Liu, Xuehan Duan, Yang Chen, Xuming Wang, Qianfeng Xia, Hua Wu |
| Affiliations | Hainan General Hospital, NHC Key Laboratory of Tropical Disease Control, Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Linyi Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital, China |
| Published In | Emerging Infectious Diseases, Volume 31, Number 7—July 2025 |
| Abstract | A fatal case of infection caused by Burkholderia thailandensis in a healthy individual. |
| Significant Findings | The case indicates a potential virulence of B. thailandensis, which is usually considered non-pathogenic. |
| Patient Details | 58-year-old male rice farmer with acute respiratory failure; treated but eventually succumbed to the infection. |
| Diagnosis and Treatment | Confirmed through culture and sequencing; initial treatment with tigecycline, then with imipenem was administered. |
| Conclusion | Emphasis on the need for heightened awareness regarding B. thailandensis and its potential risks. |
Summary
Burkholderia thailandensis is recognized for its potential pathogenicity, as illustrated by a recent case in Hainan Province, China, where a previously healthy 58-year-old male developed severe respiratory failure and subsequently died from an infection caused by this bacterium. This case challenges existing notions about the low virulence of B. thailandensis, emphasizing the need for increased clinical awareness to prevent fatal outcomes. Medical professionals should remain vigilant in diagnosing and treating infections caused by this pathogen, particularly given its similarities to the more virulent Burkholderia pseudomallei. The findings from this research underscore the importance of prompt intervention and improved understanding of Burkholderia thailandensis’s risks in clinical settings.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.