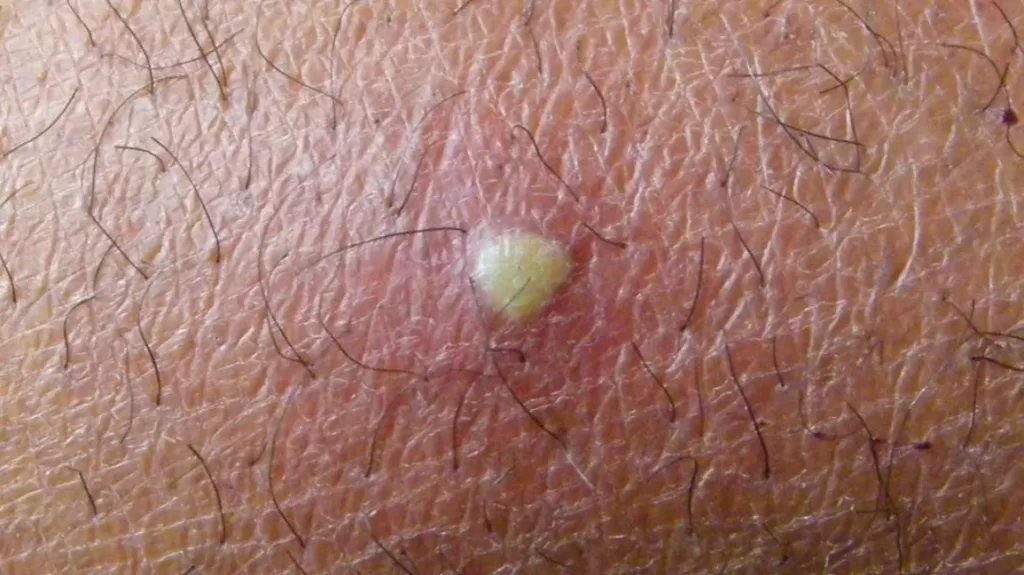
Boils, also known as furuncles, are painful, pus-filled lumps that develop under the skin as a result of bacterial infections. These uncomfortable swellings often occur when hair follicles or oil glands become infected, predominantly due to *Staphylococcus aureus*, a common bacteria found on the skin. Recognizing the symptoms of boils, understanding their causes, and exploring effective treatment options is essential for anyone affected by this condition. In addition, learning about preventing boils can help reduce the likelihood of future occurrences. By gaining insights into how to treat boils and their underlying factors, individuals can take proactive steps toward better skin health.
Furuncles are an unfortunate yet common skin condition characterized by painful lumps filled with pus. Often arising from infected hair follicles, these lumps can lead to significant discomfort and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling and redness. Understanding the various factors that contribute to the formation of these skin infections, along with the signs to watch for, is crucial in effectively managing them. Additionally, exploring different treatment methods and preventive measures can empower individuals to maintain healthier skin and minimize the recurrence of similar conditions. Whether referred to as boils, furuncles, or skin abscesses, addressing these issues promptly can lead to improved outcomes.
Understanding the Symptoms of Boils
Boils often manifest with distinct symptoms that can help individuals identify them early. The initial sign is usually a red, swollen bump that may feel tender and painful to the touch. As the boil develops, it can grow larger and become filled with pus, which may create a noticeable head or pustule. This progression is essential to recognize, as it indicates the boil is maturing and may soon require treatment. Additionally, one might notice warmth around the affected area, signaling an active infection.
Other symptoms can include systemic signs such as fever, particularly if the boil is severe or if multiple boils are present. Pain and discomfort can worsen as the boil expands, leading to difficulty in movement if located in areas that undergo friction, such as the inner thighs or underarms. Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for prompt treatment and preventing further complications.
Common Causes of Boils
The primary cause of boils is a bacterial infection, particularly from *Staphylococcus aureus*, which can enter the skin through small cuts or abrasions. This bacteria is commonly found on the skin’s surface and usually does not cause harm unless it breaches the skin barrier. Once inside, it can infect hair follicles or oil glands, leading to the development of painful lumps filled with pus.
In addition to bacterial infection, other factors can contribute to the formation of boils. Blocked hair follicles, often due to excessive oil, dead skin, or other debris, provide a fertile environment for bacteria. Moreover, skin friction and irritation, especially in moist areas, can exacerbate the risk of boils. Individuals with underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or those with compromised immune systems are also at a greater risk, as their bodies may struggle to fend off infections effectively.
Effective Home Remedies for Boils
For those dealing with boils, several home remedies can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing. One of the most effective methods is the application of warm compresses to the affected area. This approach encourages drainage of the pus from the boil, reduces swelling, and helps relieve pain. It is advisable to repeat this process several times throughout the day for optimal results.
In addition to warm compresses, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation associated with boils. It’s crucial to avoid squeezing or picking at the boil, as this can worsen the infection or lead to scarring. By utilizing these home remedies, many individuals can effectively manage their symptoms while waiting for the boil to resolve.
Medical Treatment Options for Persistent Boils
If home remedies do not yield improvement, or if a boil becomes particularly large or painful, seeking medical intervention is essential. Healthcare providers can perform a procedure known as incision and drainage, where they make a small cut to release the pus and relieve pressure. This not only alleviates discomfort but also accelerates the healing process.
In some cases, especially if the infection is widespread, doctors may prescribe antibiotics to combat the bacteria causing the boil. It’s important to follow the prescribed course of antibiotics fully to ensure the infection is eradicated and to prevent recurrence. Consulting a healthcare professional for persistent boils can provide tailored treatment options and guidance on managing this condition effectively.
Preventing Future Boils: Key Strategies
Preventing boils is often more effective than treating them after they occur. Maintaining good hygiene is paramount; this includes regularly washing the skin with soap and water to reduce bacterial load. Special attention should be paid to areas that are prone to boils, such as the armpits and thighs, where moisture can accumulate.
Another essential strategy is to avoid sharing personal items, such as towels, razors, or clothing, as these can easily transmit the bacteria that cause boils. Additionally, individuals should manage underlying health conditions like diabetes, as these can increase susceptibility to infections. Wearing loose-fitting clothing can also reduce friction and irritation, further minimizing the risk of developing boils.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of boils?
Symptoms of boils typically include red, swollen bumps that are painful to touch. As the boil develops, it may fill with pus, becoming larger and warmer. In some cases, systemic symptoms like fever can occur, indicating a more severe infection.
What causes boils to form on the skin?
Boils are primarily caused by bacterial infections, particularly from *Staphylococcus aureus*. They can form when hair follicles or oil glands become blocked or irritated, often exacerbated by skin friction, underlying medical conditions, or broken skin that allows bacteria to enter.
How can I treat boils at home effectively?
To treat boils at home, apply warm compresses to the affected area several times a day to encourage drainage. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort. It’s important to avoid squeezing the boil, as this can worsen the infection.
What are some effective strategies for preventing boils?
Preventing boils involves maintaining good hygiene, such as regularly washing the affected areas and avoiding sharing personal items like towels and razors. Wearing loose-fitting clothing can also reduce skin friction, which lowers the risk of boils.
When should I seek medical treatment for boils?
You should seek medical treatment for boils if they are particularly large, persistent, or accompanied by fever. A healthcare provider may need to perform an incision and drainage procedure or prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection effectively.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| What Are Boils? | Boils are painful, pus-filled lumps that develop under the skin due to infections, usually from Staphylococcus aureus. |
| Symptoms of Boils | Common symptoms include red swollen bumps, pain, tenderness, warmth in the area, and sometimes fever. |
| Causes of Boils | Bacterial infection, blocked hair follicles, skin friction, and underlying medical conditions like diabetes. |
| Treatment Options | Home remedies include warm compresses and pain relievers; medical treatments include incision and drainage or antibiotics if necessary. |
| Prevention Strategies | Maintain good hygiene, avoid sharing personal items, manage underlying conditions, and wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction. |
Summary
Boils are painful skin infections that can significantly affect your comfort and well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for boils is essential for effective management. These pus-filled lumps often occur due to bacterial infections, especially from Staphylococcus aureus, and are characterized by red, swollen bumps that can be quite tender. Treatment ranges from home remedies like warm compresses to medical interventions such as drainage and antibiotics for more severe cases. To prevent boils, maintaining good hygiene and avoiding skin irritation are key strategies. If you notice persistent symptoms or severe discomfort, it is wise to consult a healthcare professional for tailored advice.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.