Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS), commonly referred to as Interstitial Cystitis (IC), is a complex and often debilitating condition that impacts the lives of millions worldwide. Characterized by chronic pelvic pain, urinary urgency, and frequent urination, BPS can severely disrupt daily activities and emotional well-being. Understanding this syndrome is essential for both patients and healthcare providers, as effective management relies on recognizing its symptoms and potential causes. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of Bladder Pain Syndrome, focusing on its diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of bladder health. From lifestyle changes to advanced therapies, we aim to provide valuable insights for those navigating the challenges of this chronic condition.
Bladder Pain Syndrome, also known as Interstitial Cystitis, is a chronic ailment that manifests as persistent pelvic discomfort and an overwhelming need to urinate. Often grouped under the umbrella of chronic pelvic pain disorders, this syndrome affects bladder health and quality of life significantly. Individuals experiencing this condition may find themselves grappling with urinary urgency and frequency that disrupts their everyday routines. Understanding the various treatment options available for managing IC symptoms is crucial for those affected, as personalized care can lead to improved outcomes and relief. By examining the nature of this condition through different lenses, we can better appreciate the complexities surrounding its diagnosis and management.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis in Bladder Pain Syndrome
Early diagnosis of Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS) is crucial for effective management and treatment. Patients often experience a range of symptoms including chronic pelvic pain, urinary urgency, and frequency, which can overlap with other urinary disorders. Recognizing these symptoms early allows healthcare providers to differentiate BPS from conditions like urinary tract infections or bladder infections. A comprehensive evaluation involving symptom assessment, urine tests, and possibly cystoscopy can lead to a more accurate diagnosis. This is important as early intervention can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.
Moreover, timely diagnosis can prevent the condition from worsening. Delayed diagnosis may result in increased pain and discomfort, leading to emotional distress and anxiety for patients. By understanding the nuances of BPS and the importance of early recognition, both patients and healthcare professionals can work together to create a management plan that addresses the unique challenges posed by this chronic condition. Education about the symptoms and available diagnostic tools is key in empowering patients to seek help sooner rather than later.
Understanding the Causes of Bladder Pain Syndrome
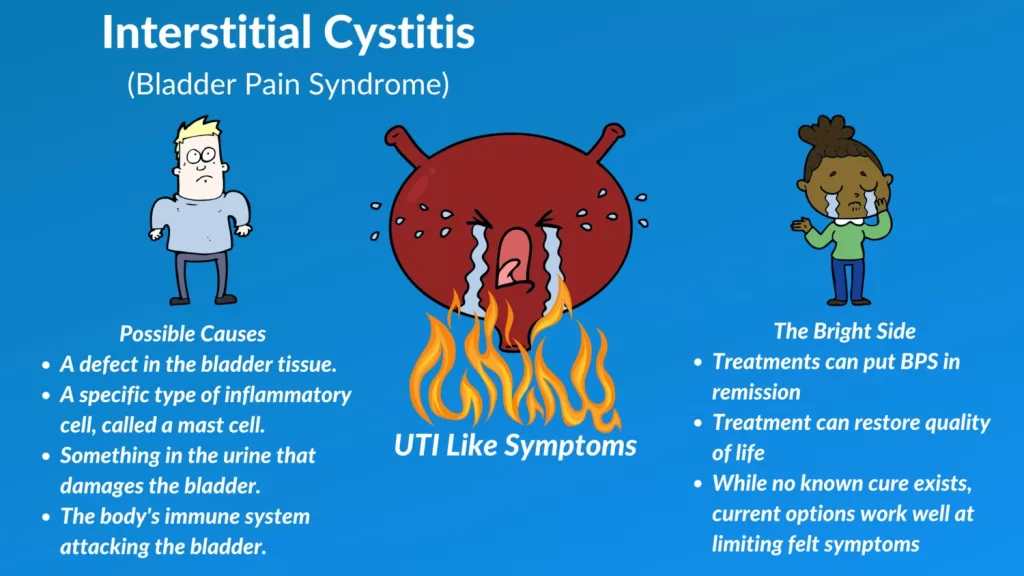
The causes of Bladder Pain Syndrome (Interstitial Cystitis) are complex and not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development. One prominent theory suggests that chronic inflammation could play a significant role, damaging the bladder lining and leading to increased sensitivity. This inflammation may stem from autoimmune responses or previous infections, which can leave lasting effects on bladder health. Understanding these potential causes is essential for effective treatment, as addressing underlying inflammation may alleviate symptoms for many patients.
Additionally, neurological factors may contribute to the heightened pain response often reported by individuals with BPS. Some studies suggest that the nervous system’s interpretation of pain signals can become altered in chronic conditions, making patients more sensitive to bladder stimuli. This highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to treatment, which may include pain management strategies and therapies aimed at retraining the nervous system. By exploring these diverse causes, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans that address the multifaceted nature of Bladder Pain Syndrome.
Treatment Strategies for Bladder Pain Syndrome
Treatment for Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS) is multifaceted and often requires a combination of approaches. Oral medications such as NSAIDs can provide relief from pain and inflammation, while antidepressants can help manage chronic pain symptoms associated with the condition. Additionally, bladder pain medications like pentosan polysulfate sodium specifically target and protect the bladder lining, offering hope to patients experiencing debilitating symptoms. It is crucial for patients to discuss their treatment options thoroughly with their healthcare providers to find the most effective regimen.
Incorporating lifestyle modifications and bladder training can also play a vital role in managing BPS. Dietary changes that avoid irritants such as caffeine and spicy foods can help reduce flare-ups. Bladder training, which involves gradually increasing the time between urinations, can help patients regain control over their bladder function. Furthermore, pelvic floor physical therapy can address muscle tension and improve overall bladder health. By implementing these diverse treatment strategies, patients can take proactive steps towards managing their symptoms and enhancing their quality of life.
The Role of Patient Support in Managing Bladder Pain Syndrome
Support from peers and healthcare professionals is vital for individuals dealing with Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS). Living with a chronic condition can be isolating, and patients often benefit from connecting with others who share similar experiences. Support groups provide a safe space for individuals to share their challenges and coping strategies, fostering a sense of community. Resources from organizations like the American Urological Association offer valuable information on symptom management, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments that can empower patients to take charge of their health.
Moreover, healthcare providers play a critical role in supporting their patients through education and personalized care. By maintaining open lines of communication, providers can ensure that patients feel heard and validated. This collaborative approach can help patients navigate the complexities of BPS, encouraging them to voice their concerns and preferences regarding treatment. Ultimately, a strong support system can significantly enhance the patient’s experience and promote better outcomes for those managing Bladder Pain Syndrome.
Exploring Advanced Treatment Options for Bladder Pain Syndrome
For patients with persistent or severe symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS), advanced treatment options may offer additional relief. Intravesical treatments, which involve delivering medication directly into the bladder, have shown promise in alleviating symptoms for some individuals. These treatments can target inflammation and promote healing of the bladder lining, thus improving overall bladder function. Healthcare providers may recommend this approach for patients who do not respond to standard oral medications.
In addition to intravesical treatments, neuromodulation techniques aim to regulate nerve signals that control bladder function. This innovative approach can provide significant relief for those suffering from chronic pelvic pain and urinary urgency. For the most severe cases, surgical options such as bladder augmentation may be considered when all other treatments fail. By exploring these advanced options, patients and their healthcare teams can work together to find effective solutions that address the unique challenges of Bladder Pain Syndrome.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome (Interstitial Cystitis)?
Common symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS), also known as Interstitial Cystitis (IC), include chronic pelvic pain, a persistent urge to urinate, and increased urinary frequency. Patients often report pelvic pressure that worsens when the bladder fills, and pain during sexual intercourse can also occur. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for effective diagnosis and management.
How is Bladder Pain Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosing Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS) typically involves a thorough symptom assessment, urine tests to rule out infections, and sometimes a cystoscopy to inspect the bladder. The diagnosis is confirmed when symptoms persist despite negative tests for urinary tract infections and other urological conditions, highlighting the need for specialized evaluation in suspected cases of Interstitial Cystitis (IC).
What are the treatment options for Bladder Pain Syndrome?
Treatment options for Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS) include oral medications such as NSAIDs and bladder pain medications, bladder training, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. For severe cases, advanced treatments like intravesical therapies and neuromodulation may be considered. A personalized treatment plan is essential for managing symptoms effectively and improving bladder health.
Can lifestyle changes help manage Bladder Pain Syndrome symptoms?
Yes, lifestyle changes can significantly help manage symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS). Patients are advised to identify and avoid trigger foods and beverages, practice stress management techniques, and engage in bladder training exercises. These adjustments can help reduce flare-ups and improve overall quality of life for those suffering from Interstitial Cystitis (IC).
Is there a connection between urinary urgency and Bladder Pain Syndrome?
Yes, urinary urgency is a hallmark symptom of Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS). Individuals with Interstitial Cystitis (IC) often experience a frequent and intense need to urinate, which can lead to anxiety and discomfort. Understanding this connection is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers in managing BPS effectively.
| Section | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | BPS is a chronic condition causing pelvic pain, urinary urgency, and frequency. |
| Defining BPS | Characterized by pelvic pain and frequent urination; symptoms vary. |
| Causes of BPS | Possible causes include inflammation, autoimmune disorders, neurological factors, and infections. |
| Diagnosis of BPS | Diagnosis involves symptom assessment, urine tests, and possibly cystoscopy. |
| Treatment Options | Includes oral medications, bladder training, lifestyle modifications, and advanced treatments. |
| Special Considerations for Men | Diagnosis can be complicated by conditions like prostatitis. |
| Patient Resources | Resources are available from organizations like the AUA for symptom management and support. |
Summary
Bladder Pain Syndrome (Interstitial Cystitis) represents a complex and often misunderstood condition that significantly impacts the lives of those affected. It is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to comprehend the multifaceted nature of this syndrome, which includes a variety of symptoms, potential causes, and treatment strategies. By fostering awareness and encouraging early diagnosis, individuals suffering from BPS can access appropriate care and support. The continuous evolution of treatment options and ongoing research into this condition offer hope for improved management and quality of life for those dealing with Bladder Pain Syndrome.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.