Understanding the birth control blood clot risk is essential for anyone considering hormonal contraceptives. While these methods offer relief and control over reproductive health, they come with potential hazards, such as an increased chance of developing blood clots. Notably, contraceptives that contain estrogen have been linked to this risk, which is something that potential users should not overlook. Recognizing the blood clot signs can be crucial for timely intervention, as early detection can make a significant difference. In this article, we will explore various birth control options, their link to estrogen and blood clots, and ways to minimize the risk of developing these serious complications.
When it comes to contraceptive methods, the term “birth control” encompasses a wide range of options, each with distinct implications for health. Many hormonal contraceptives, which include medications designed to manage fertility, can inadvertently heighten the risk of clot formation in the bloodstream. Users should familiarize themselves with the potential complications associated with these contraceptives, particularly concerning estrogen levels and the associated blood clot danger. Knowledge about the symptoms of blood clots can empower individuals to seek prompt medical advice if necessary. Selecting an appropriate birth control option may require a comprehensive understanding of safety and health risks, ensuring personal choices align with their lifestyle.
Understanding Blood Clot Risks Associated with Birth Control
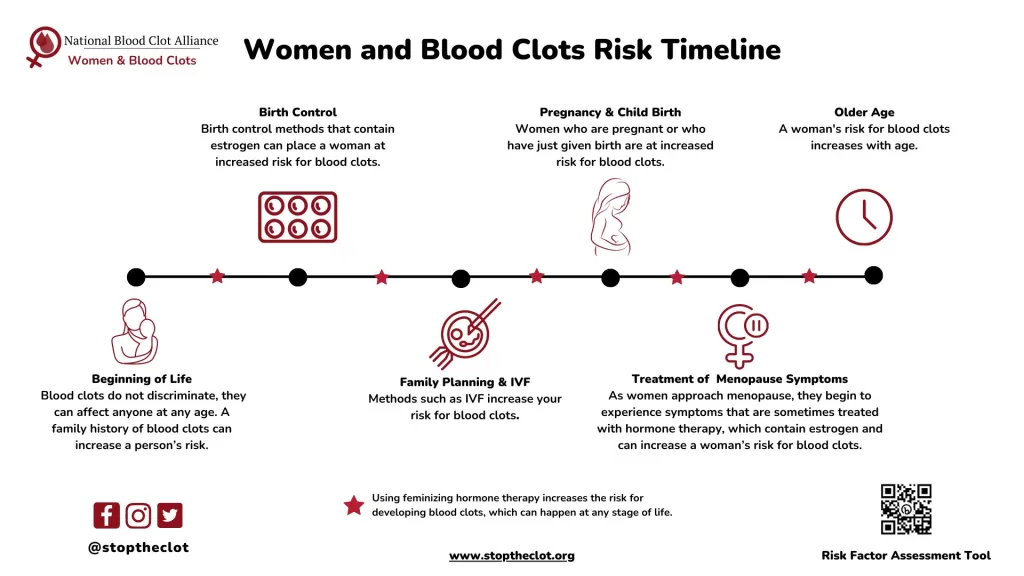
Birth control methods, particularly hormonal contraceptives containing estrogen, have a well-documented association with increased blood clot risk. This risk, although significant, is often overshadowed by the numerous advantages that contraceptives provide for those looking to avoid or delay pregnancy. According to medical professionals, the likelihood of developing a blood clot while on estrogen-based birth control is approximately ten per 10,000 women annually. Individuals who smoke or possess a personal or family history of clotting disorders are particularly at risk, as estrogen can elevate the levels of clotting factors in the blood.
While it’s essential to be aware of these risks, the overall incidence of blood clots remains relatively low compared to the number of users of hormonal contraception. Health practitioners emphasize the importance of regular check-ups and discussions with a healthcare provider about any concerns regarding blood clot signs. Users are encouraged to report any unusual symptoms promptly, allowing for early intervention if necessary. Ultimately, understanding the nuanced interplay between birth control and blood clot risk empowers individuals to make informed decisions.
How Estrogen in Birth Control Can Lead to Blood Clots
Estrogen is a key component in many popular hormonal contraceptives, and understanding its role provides insight into the associated blood clot risks. Hormonal contraceptives work by mimicking the hormonal environment of pregnancy, which inadvertently stimulates the synthesis of proteins responsible for blood coagulation. While this mechanism helps prevent excessive bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, it also means that users of these contraceptives may experience an increased likelihood of clot formation.
Medical experts state that the degree of clotting risk is closely tied to the amount of estrogen present in the contraceptive method. For instance, birth control pills containing higher doses of estrogen can significantly raise an individual’s propensity for blood clots. However, the benefits of hormonal birth control often outweigh the risks for most women, especially those without pre-existing conditions that predispose them to clotting issues. Ongoing research continues to shape our understanding of effective contraceptive options and associated health risks.
Identifying Warning Signs of Blood Clots for Birth Control Users
Users of birth control, especially those on estrogen-containing methods, must be vigilant about recognizing warning signs of blood clots. Typical symptoms might include sudden leg pain, swelling, or redness, indicating a potential deep vein thrombosis (DVT). For those experiencing sharp chest pain or shortness of breath, this could indicate a pulmonary embolism, which occurs when a clot travels to the lungs. Similarly, sudden severe headaches or changes in vision could suggest a brain clot, demanding immediate medical attention.
Awareness of these symptoms can lead to early detection and treatment, drastically improving outcomes. Women on hormonal contraceptives are encouraged to familiarize themselves with these signs and consult a healthcare professional whenever they notice something unusual. Prompt recognition and action can be life-saving, reinforcing the importance of understanding the balance between the benefits of birth control and its possible side effects.
Evaluating Birth Control Options with Respect to Blood Clot Risk
When considering contraception, individuals are faced with numerous options, each varying in efficacy and associated risks. It is crucial to evaluate which method might be the safest considering one’s personal health profile. For instance, estrogen-free options like progestin-only pills, hormonal IUDs, and non-hormonal methods such as copper IUDs tend to present a lower risk for blood clot formation. These choices can be particularly advantageous for women with a history of thrombosis or other risk factors.
Engaging in discussions with a healthcare provider to assess the most suitable birth control options is vital. Such conversations enable individuals to make informed decisions that align with their health needs and lifestyle. Furthermore, being proactive about contraceptive choices not only helps in managing pregnancy prevention but also mitigates potential health risks associated with certain methods.
Strategies for Preventing Blood Clots While Using Birth Control
Prevention is paramount in reducing the risk of blood clots among birth control users. Those on hormonal contraceptives, particularly those containing estrogen, can adopt several strategies to minimize their risk. Quitting smoking, for example, drastically decreases the chances of clot formation since smoking is a known risk factor. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can enhance overall circulation and reduce the likelihood of blood clots.
Moreover, opting for lower-dose estrogen contraceptives or transitioning to non-estrogen alternatives can be beneficial. Individuals should consult their healthcare provider to explore pregnancy prevention methods that may offer a more favorable risk profile. By being proactive and taking preventive measures, birth control users can significantly lower their chances of developing blood clots while still effectively managing their reproductive health.
The Role of Lifestyle Choices in Managing Blood Clot Risks
Lifestyle choices significantly influence the risk of blood clots, especially among individuals using hormonal birth control. Activities such as regular exercise, maintaining hydration, and adhering to a balanced diet can greatly enhance vascular health. Furthermore, awareness of one’s family health history, especially regarding clotting disorders, is essential in managing risk factors more effectively.
For those who are sedentary for long periods or have jobs that require prolonged sitting, taking breaks to move around can also prevent blood clots. Integrating movement into daily routines reinforces a proactive approach to health and wellbeing, particularly for those on hormonal contraceptives. Ultimately, a combination of awareness, lifestyle modifications, and regular healthcare consultations constitutes a comprehensive strategy for managing blood clot risks.
Alternatives to Hormonal Birth Control and Their Benefits
Not everyone needs to or should utilize hormonal birth control, especially individuals concerned about blood clot risks. Non-hormonal options, such as copper IUDs, offer effective contraception without the added risks associated with hormonal methods. Copper IUDs, for instance, prevent pregnancy by creating an environment hostile to sperm and can remain effective for up to ten years without hormonal interference.
Barrier methods, including condoms and diaphragms, also provide excellent choices for individuals aiming to prevent pregnancy while avoiding hormonal side effects. These options not only guard against unwanted pregnancies but may also protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). As such, understanding the variety of available birth control methods allows users to select safer alternatives that align with their health preferences and reproductive goals.
Consultation with Healthcare Providers for Personalized Advice
Consulting healthcare providers is an essential step for anyone considering or currently using birth control. These medical professionals can offer personalized advice based on individual health history, lifestyle factors, and specific concerns about blood clots. By discussing personal risk factors, users can make more informed choices regarding their contraceptive methods, ensuring both safety and efficacy.
Whether switching birth control methods or managing potential risks, ongoing communication with healthcare professionals can optimize reproductive health. Regular check-ups and open discussions about any emerging symptoms or concerns can lead to timely interventions, minimizing health risks associated with birth control. Thus, staying informed and actively engaging with healthcare providers is fundamental to ensuring a safe birth control experience.
The Importance of Monitoring Health While on Hormonal Contraceptives
Monitoring one’s health while using hormonal contraceptives is crucial for early detection of any associated risks, particularly blood clots. Regular self-examinations and awareness of bodily changes allow users to pick up on warning signs quickly. For instance, noting any sudden swelling, pain, or changes in usual patterns can expedite necessary medical consultations.
Healthcare providers recommend that individuals remain vigilant about their health, especially if they have other risk factors for blood clot formation. Engaging in regular health screenings and maintaining an open dialogue with healthcare providers can facilitate proactive management of any complications. Ultimately, being proactive about health while on hormonal birth control enhances safety and provides peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between birth control and blood clot risk?
Birth control, particularly hormonal contraceptives containing estrogen, is associated with an increased risk of blood clots. This is due to estrogen’s stimulating effect on blood clotting factors in the body. According to data, about 10 out of every 10,000 individuals on estrogen-based birth control may experience blood clots each year.
What are the warning signs of blood clots for users of hormonal birth control?
Users of hormonal birth control should be alert for warning signs of blood clots, including sudden leg pain or swelling, sharp chest pain, shortness of breath, severe headaches, or unexplained arm pain. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for prompt medical evaluation.
Which birth control options pose the highest risk for blood clots?
Birth control options that contain estrogen, such as combination pills, hormonal patches, and vaginal rings, carry the highest risk of blood clot formation. For those concerned about this risk, progestin-only methods or non-hormonal options may be safer alternatives.
How can I prevent blood clots while taking birth control?
To reduce the risk of blood clots while on birth control, you can choose lower-risk options like progestin-only pills or IUDs, stop smoking, and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Discussing your options with a healthcare provider is essential for personalized advice.
What are the dangers of estrogen and blood clots in contraception?
Estrogen in hormonal contraceptives increases blood coagulation factors, which can lead to a higher risk of blood clots. This is particularly evident in users with additional risk factors, such as a history of clotting disorders, obesity, or smoking.
Are there non-hormonal contraceptive options to consider if I’m worried about blood clot risks?
Yes, if you’re concerned about blood clot risks, you can consider non-hormonal contraceptive options such as copper IUDs, the Phexxi vaginal gel, or barrier methods like male and female condoms, which also reduce the risk of STIs.
What should I do if I notice symptoms of a blood clot while on birth control?
If you experience symptoms suggestive of a blood clot, such as leg swelling, chest pain, or severe headaches while on birth control, it’s critical to seek medical attention immediately to assess your condition.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Increased Blood Clot Risk | Birth control, especially those containing estrogen, increases the risk of blood clots. About 10 people per 10,000 may be affected annually. |
| FDA Concerns | The FDA continues to evaluate the safety of drospirenone-containing birth control pills due to potential higher risk of clots. |
| Risks with Types of Birth Control | Estrogen-containing methods, like combination pills and patches, carry the highest risk. Those with clotting disorders are at greater risk. |
| Warning Signs | Watch for symptoms like leg pain, chest pain, shortness of breath, or severe headaches as signs of potential clots. |
| Prevention Strategies | Consider non-estrogen methods, quit smoking, and look into barrier methods or IUDs to lower risk of blood clots. |
Summary
Birth control blood clot risk is an important consideration for anyone using hormonal contraceptives. While hormonal birth control methods can be effective, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks. This includes an increased likelihood of developing blood clots, especially with estrogen-containing methods. It is vital for users to monitor for warning signs and consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on safe contraceptive options.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.