Benign prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a prevalent condition that affects a significant number of men, particularly those over the age of 40. As the prostate gland enlarges, it can lead to a variety of uncomfortable prostate symptoms, including frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, and a weak urine stream. Understanding BPH is crucial for men to recognize these symptoms early and explore available prostate treatment options. This guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for benign prostate enlargement, helping men navigate their health concerns effectively. Distinguishing between prostate cancer vs BPH is equally important, as both conditions may present similar symptoms but require different approaches for treatment.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is often referred to as prostate enlargement, a condition that becomes increasingly common as men age. This non-cancerous condition results in the increased size of the prostate gland, leading to various urinary challenges. Men may experience symptoms that disrupt their daily lives, such as urgency and difficulty in urination. Understanding the implications of prostate enlargement is essential for men, as it can affect their overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore the nuances of managing this condition, including distinguishing it from prostate cancer and discussing the spectrum of treatment options available.
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
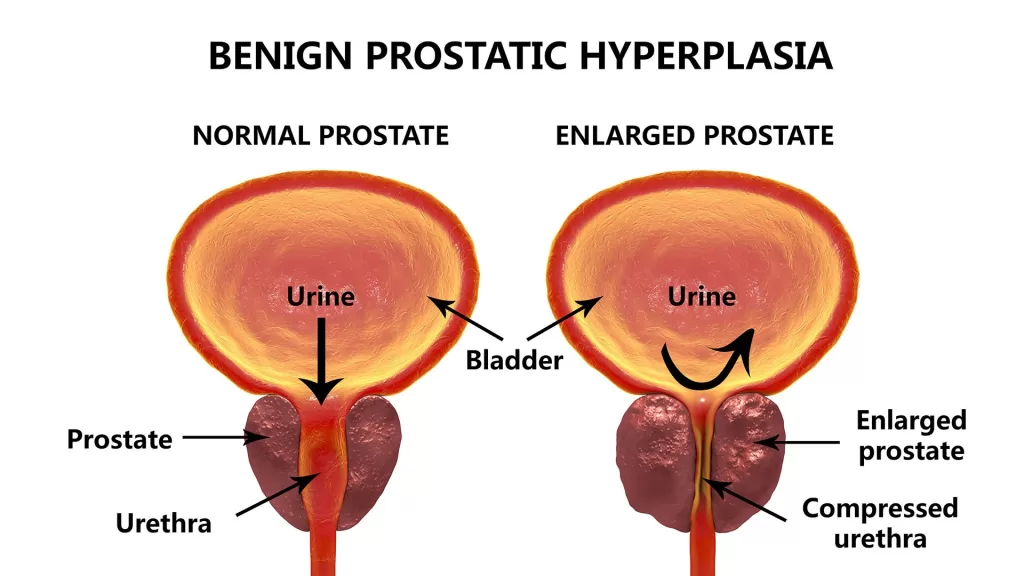
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), or benign prostate enlargement, is a condition that affects a significant number of men, particularly as they age. The prostate gland, which is crucial for male reproductive health, can grow larger and begin to obstruct normal urinary flow. This enlargement is not cancerous, but it can lead to discomfort and various urinary symptoms that can impact quality of life. Understanding BPH is essential for men to recognize their symptoms and seek timely medical advice.
The growth of the prostate is often associated with hormonal changes that occur as men enter middle age. Testosterone levels decrease while estrogen levels can rise, leading to an increase in prostate cell growth. This can cause the prostate to press against the urethra, resulting in common symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, and a weak urine stream. Awareness of these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and management of BPH.
Common Symptoms of Benign Prostate Enlargement
Men experiencing benign prostate enlargement often report a range of symptoms that can significantly affect their daily lives. Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia), is one of the most common complaints. This can lead to sleep disturbances and fatigue, making it imperative for individuals to seek medical advice. Other symptoms include difficulty starting urination, a weak urine stream, and a sense of incomplete bladder emptying, which can lead to feelings of urgency and discomfort.
The impact of these symptoms on a man’s quality of life cannot be overstated. Many men may hesitate to discuss these issues due to embarrassment, but recognizing and addressing the symptoms of BPH is crucial. Lifestyle changes, medications, or surgical options can provide relief, but timely intervention is key to managing these prostate symptoms effectively.
Diagnosis and Distinction Between BPH and Prostate Cancer
Diagnosing benign prostatic hyperplasia typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms and medical history. Physicians may perform a digital rectal exam (DRE) to assess the size of the prostate and may also use symptom assessment tools like the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS). It is essential to differentiate BPH from prostate cancer, as both conditions can present similar urinary symptoms but require different treatment approaches.
Prostate cancer poses a significant health risk and can have serious implications if not caught early. Unlike BPH, which is benign and does not increase cancer risk, prostate cancer requires a different diagnostic strategy, often involving blood tests for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, imaging studies, and potentially a biopsy. Understanding these distinctions is vital for men to ensure they receive appropriate care and treatment.
Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Treatment for benign prostate enlargement varies depending on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s overall health. For many men, lifestyle changes such as fluid management, dietary adjustments, and bladder training techniques may alleviate mild symptoms. When lifestyle modifications are insufficient, medications such as alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are commonly prescribed to relax bladder neck muscles and reduce prostate size, respectively.
In cases where symptoms are severe or do not respond to medication, minimally invasive procedures or surgery may be necessary. Options like the Optilume BPH device and transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) are available for those with significant obstruction. Each treatment plan should be tailored to the individual’s needs, taking into account the impact on sexual health and quality of life.
Recent Research Advances in BPH Treatment and Understanding
Recent studies have shed light on the underlying mechanisms of benign prostatic hyperplasia, particularly regarding inflammation and oxidative stress. Research published in January 2025 has identified correlations between metabolic health, inflammation, and BPH progression, suggesting that addressing metabolic syndrome could open new avenues for treatment. These findings emphasize the importance of an integrated approach to managing prostate health.
In addition, ongoing research is exploring novel treatment modalities that may better target the underlying causes of BPH while minimizing side effects. As our understanding of the condition evolves, it is essential for men to stay informed about the latest developments, ensuring they can make educated decisions about their prostate treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of benign prostate enlargement (BPH)?
Common symptoms of benign prostate enlargement, or BPH, include frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia), difficulty starting urination, a weak urine stream, and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. These prostate symptoms can significantly impact daily life and may worsen over time.
How is benign prostatic hyperplasia diagnosed?
Diagnosing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) typically involves a review of medical history, a physical exam including a digital rectal exam (DRE), symptom questionnaires like the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), urinary flow studies, and sometimes ultrasound to assess prostate size.
What treatment options are available for benign prostate enlargement?
Treatment options for benign prostate enlargement include lifestyle changes, medications such as alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical options like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), depending on the severity of symptoms.
Is benign prostatic hyperplasia a risk factor for prostate cancer?
No, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is not a precursor to prostate cancer. While both conditions share some similar prostate symptoms, BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate and does not increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
What causes benign prostate enlargement in men?
The exact cause of benign prostate enlargement (BPH) is not fully understood, but factors such as hormonal changes, chronic inflammation, and genetics are believed to contribute to the condition as men age, leading to prostate cell growth.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), or benign prostate enlargement, is the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, common in older men. |
| Symptoms | Frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, weak urine stream, inability to empty bladder, intermittent stream. |
| Causes | Hormonal changes, inflammation, and genetics may contribute to BPH. |
| Diagnosis | Includes medical history, physical exam, symptom questionnaires, urinary flow studies, and ultrasound. |
| Treatment Options | Lifestyle changes, medications (alpha-blockers, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors), minimally invasive procedures, and surgical options like TURP. |
| Recent Research | Studies indicate potential links between oxidative stress, inflammation, and BPH progression. |
Summary
Benign prostate enlargement is a significant health concern for many men, particularly as they age. This condition, known medically as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), can lead to various urinary symptoms that impact daily life. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for effective management. Timely diagnosis and appropriate care can mitigate the effects of BPH, ensuring a better quality of life for affected individuals. Proactive measures and regular consultations with healthcare professionals are recommended for optimal prostate health.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.