Bartholin’s cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form near the vaginal opening when the Bartholin glands, responsible for lubrication, become obstructed. These cysts can vary in size, often going unnoticed, but sometimes they can cause significant discomfort or pain. Understanding Bartholin cyst symptoms is crucial, as they may indicate infection or other complications, prompting timely Bartholin cyst treatment. The causes of these cysts can range from infections to hormonal changes, making awareness of Bartholin cyst diagnosis essential for effective management. This article delves into the nature of Bartholin’s cysts, exploring their symptoms, causes, and the latest treatment options available.
Known colloquially as cysts of the Bartholin glands, these benign swellings can develop in the vicinity of the vaginal area, often resulting from duct blockages. The Bartholin glands play a vital role in female sexual health, and when their ducts are hindered, it can lead to the formation of these fluid-filled sacs. Recognizing the signs of a Bartholin gland cyst is important for women, as symptoms may include discomfort and potential infection. Understanding the factors that contribute to the development of these cysts can aid in their prevention and management. This overview will discuss the various aspects of these cysts, including their symptoms, underlying causes, and available treatment methods.
Understanding Bartholin’s Glands and Their Function
Bartholin’s glands are two small glands located on either side of the vaginal opening. They are responsible for producing a lubricating fluid that helps to ease sexual intercourse and maintain moisture in the vaginal area. Each gland has a duct that opens into the vaginal vestibule, allowing the secreted fluid to flow out. These glands are crucial for sexual health, as they ensure comfort and reduce friction during sexual activity. When functioning properly, the Bartholin glands play a significant role in a woman’s reproductive system.
However, when the ducts of the Bartholin glands become blocked, they can lead to the formation of Bartholin’s cysts. This blockage can occur due to various reasons such as infections, injuries, or hormonal changes. Understanding the function of these glands is essential, as it helps in recognizing the importance of maintaining their health and addressing any issues that may arise promptly.
Bartholin’s Cyst Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs
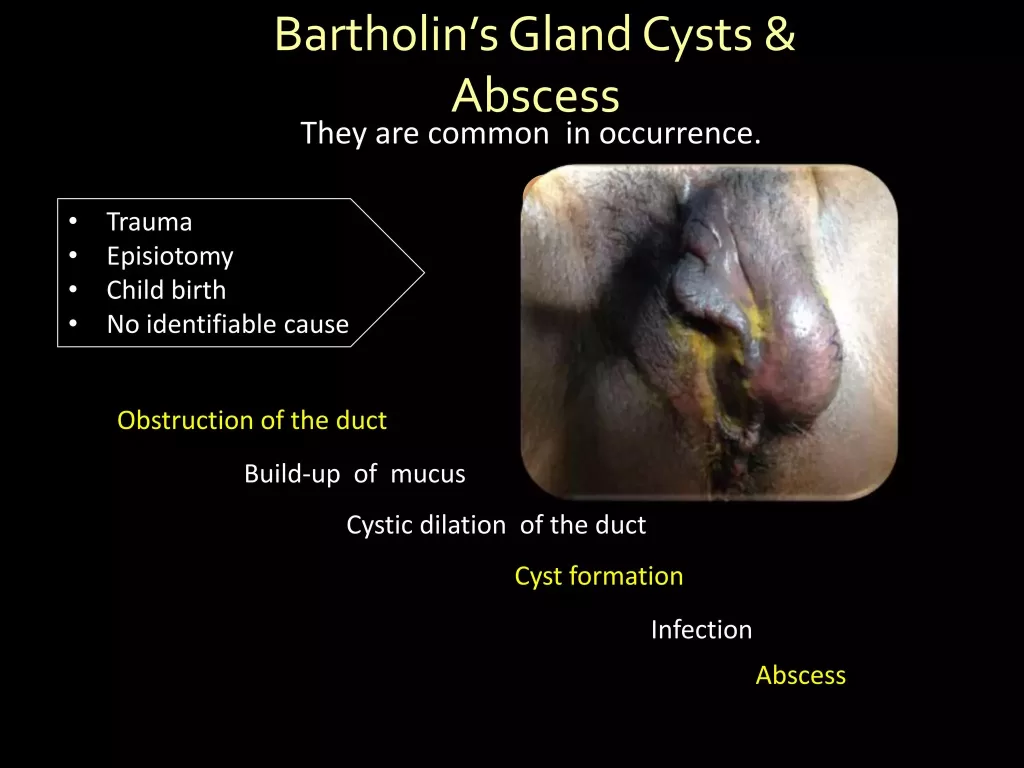
Bartholin’s cysts can often be asymptomatic, meaning that many individuals may not even realize they have one. However, when symptoms do arise, they can manifest as a noticeable lump near the vaginal opening. This lump may vary in size and can sometimes cause discomfort or pain, particularly if the cyst becomes infected. In more severe cases, symptoms can include fever, swelling, and pus formation, highlighting the necessity of monitoring any changes in the area.
Recognizing the symptoms of Bartholin’s cysts is crucial for timely intervention. If you notice any unusual lumps or experience pain, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and ensure proper management of the cyst, making awareness of symptoms a vital part of women’s health.
Causes of Bartholin’s Cyst: What You Need to Know
The primary cause of Bartholin’s cysts is the obstruction of the ducts that drain the Bartholin glands. This obstruction can occur due to a variety of factors. One significant cause is infections, especially sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can inflame the ducts and lead to blockage. Additionally, trauma or injury to the area can cause scarring or swelling, resulting in the same duct obstruction.
Hormonal changes can also play a role in the formation of Bartholin’s cysts. Fluctuations in hormone levels—often linked to menstrual cycles—can affect how the Bartholin glands function. Maintaining overall health and well-being, alongside managing stress and lifestyle factors, can be essential in preventing the conditions that lead to cyst formation.
Bartholin’s Cyst Treatment: Options Available
Treatment for Bartholin’s cysts typically depends on the severity of symptoms. In many cases, no treatment is necessary, especially if the cyst is asymptomatic. However, if the cyst causes pain or discomfort, several treatment options are available. One common recommendation is the use of sitz baths, which involve soaking in warm water to soothe the area and encourage drainage. This method is often the first line of management for symptomatic cysts.
For larger cysts or those that have become infected, more invasive treatments may be required. Surgical drainage is a common procedure, where a healthcare provider makes an incision to relieve pressure and allow the cyst to drain. In certain cases, antibiotics may also be prescribed to address any underlying infections. Understanding the available treatment options can empower individuals to seek appropriate care and alleviate symptoms effectively.
Diagnosing Bartholin’s Cyst: Understanding the Process
Diagnosing a Bartholin’s cyst typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. During this examination, the doctor will assess any lumps or swelling near the vaginal opening and inquire about symptoms. If there are signs of infection or complications, additional tests, such as a culture or imaging studies, may be necessary to determine the nature of the cyst and guide treatment.
In recent years, advancements in imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, have enhanced the ability to diagnose Bartholin’s cysts accurately. These non-invasive methods can help evaluate the size and characteristics of the cyst, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively. Early diagnosis is crucial to manage symptoms and avoid potential complications, making it essential for individuals to seek medical advice when experiencing unusual signs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Bartholin’s cyst?
Bartholin’s cyst symptoms can vary, but many are asymptomatic. When symptoms do occur, they may include a noticeable lump near the vaginal opening, pain or tenderness, and in severe cases, fever and pus formation, especially if the cyst becomes infected.
What causes a Bartholin’s cyst to develop?
The primary cause of Bartholin’s cysts is the obstruction of the gland’s duct, which can result from infections (like STIs), trauma to the area, or hormonal changes. Understanding these Bartholin cyst causes is essential for prevention.
How is a Bartholin’s cyst diagnosed by healthcare providers?
Bartholin’s cyst diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. In some cases, ultrasound imaging may be used to determine the size and nature of the cyst, helping to decide on the best treatment option.
What treatment options are available for Bartholin’s cyst?
Bartholin’s cyst treatment may include sitz baths to relieve discomfort, surgical drainage for larger cysts or abscesses, and antibiotics if an infection is present. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and cyst size.
How can I prevent Bartholin’s cysts from recurring?
To help prevent Bartholin’s cysts from recurring, it’s important to maintain good overall health, manage stress, and seek prompt treatment for any infections. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also aid in early detection and management.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A noncancerous swelling caused by obstruction of the Bartholin glands, leading to fluid accumulation. |
| Symptoms | May be asymptomatic; can include a lump, pain, tenderness, fever, and pus if infected. |
| Causes | Infections (e.g., STIs), injury, and hormonal changes. |
| Treatment Options | Sitz baths, drainage, antibiotics, and possible catheter placement for recurrent cases. |
| Recent Developments | Increased awareness of infection risks and advancements in ultrasound imaging for diagnosis. |
Summary
Bartholin’s cyst is a common condition that can cause discomfort but is generally manageable with proper care. These fluid-filled lumps can arise from blockages in the Bartholin glands, leading to various symptoms, including pain and swelling. Understanding the causes, such as infections or hormonal changes, and recognizing the symptoms are crucial for effective treatment. Options like sitz baths and surgical drainage can alleviate discomfort, while recent advances in ultrasound imaging have enhanced diagnosis and management strategies. Awareness and proactive health management are key in addressing Bartholin’s cysts effectively.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.