Bacterial vaginosis treatment is a crucial topic for many women, as this common condition disrupts the delicate balance of the vaginal microbiome. Recent studies highlight the significance of including male partner treatment in the therapeutic approach to combat recurring infections effectively. A groundbreaking trial suggests that when men receive antibiotic treatment alongside women, the recurrence of bacterial vaginosis drops significantly. In fact, by integrating a male partner’s involvement in the treatment plan, healthcare providers may pave the way for better recurrence prevention and overall health outcomes. This innovative strategy emphasizes the need to view bacterial vaginosis not just as a women’s issue but as a condition that involves both partners for optimal management.
The management of bacterial vaginosis, often referred to as BV, represents a growing field of interest in women’s health. Although traditionally viewed as a female-specific ailment, recent research focuses on the role of male partners in both treatment and prevention strategies. This condition is characterized by an imbalance in the vaginal flora, leading to various complications if left unchecked. New findings suggest that addressing bacterial vaginosis with a comprehensive approach, which includes antibiotic treatment for male partners, could significantly lower the chances of recurrence. By broadening our perspective on BV, we can foster a more collaborative treatment environment that emphasizes the importance of the sexual health of both partners.
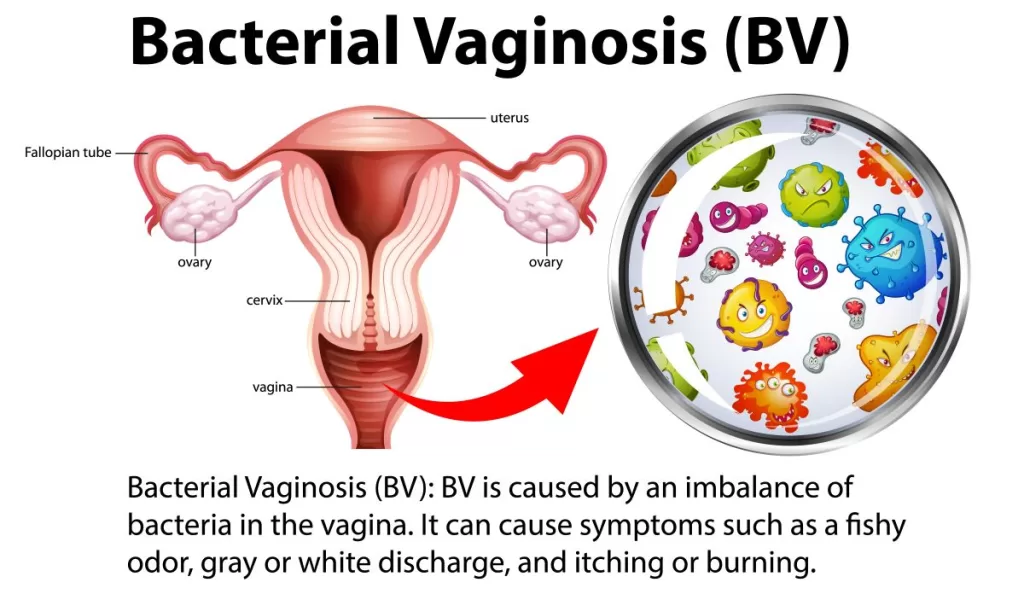
Understanding Bacterial Vaginosis and Its Implications
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection characterized by a disruption in the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina. This condition affects nearly one in three women globally, leading to a variety of symptoms such as unusual discharge, odor, and discomfort. The significance of BV extends beyond discomfort, as it can result in serious health complications including pelvic inflammatory disease, an increased risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Understanding the underlying causes of BV is crucial in managing and treating the condition effectively.
The vaginal microbiome plays a vital role in maintaining overall reproductive health, and any disturbances can lead to BV. Various factors contribute to this imbalance, including sexual activity, hormone changes, and use of antibiotics. It is noteworthy that more than 50% of women experience a recurrence of BV within three months following antibiotic treatment. Therefore, it is essential to explore comprehensive treatment strategies, including considerations for male partners, to reduce recurrence rates.
Bacterial Vaginosis Treatment: The Role of Male Partner Antibiotic Therapy
Recent trials have highlighted the effectiveness of male partner antibiotic treatment in reducing the recurrence of bacterial vaginosis (BV). In a groundbreaking study conducted in Australia, couples where one partner was diagnosed with BV received varying treatments. The results showed that women whose male partners were treated with a combination of oral and topical antibiotics had a significantly lower rate of recurrence—cut in half compared to the control group. This finding suggests that reinfection from male partners plays a crucial role in BV recurrence, reinforcing the need for a dual approach to treatment.
Integrating male partner treatment in the management of BV not only improves women’s health outcomes but also opens up new avenues for understanding the sexual transmission dynamics of this condition. As BV is often misunderstood and under-discussed, educating both men and women about the implications of bacterial vaginosis and the necessity of combined antibiotic treatments can foster better health practices. This innovative approach aligns with emerging research trends that recognize the intricacies of the vaginal microbiome and its interactions with male partners.
Reducing Bacterial Vaginosis Recurrence: Effective Strategies
To effectively reduce the recurrence of bacterial vaginosis (BV), it is imperative to adopt evidence-based strategies that address both partners in a relationship. The trial showing the benefits of coupled treatment not only emphasizes the importance of treating the infected individual but also the need for ensuring their male partners undergo a full course of antibiotics. This strategic approach targets the potential reservoirs of infection and minimizes the risk of reinfection, which is particularly high among women with regular partners.
In conjunction with male partner treatments, healthcare providers should encourage women to engage in discussions about BV with their partners. This outreach can help demystify the condition, alleviate stigma, and promote healthy practices that contribute to the maintenance of the vaginal microbiome. Furthermore, supporting women with education on prevention strategies, including lifestyle changes and the proper use of antibiotics, is essential in combating the high incidence of BV recurrence.
The Impact of Antibiotic Treatment on the Vaginal Microbiome
Antibiotics play a crucial role in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis (BV) by targeting the harmful bacteria disrupting the vaginal microbiome. However, the use of antibiotics is a double-edged sword—while they are effective against pathogens, they can also inadvertently affect the beneficial bacteria necessary for maintaining a healthy vaginal environment. This alteration in the vaginal microbiome raises concerns regarding prolonged or repeated antibiotic usage, potentially leading to a greater risk of recurrence of BV.
Understanding the complex dynamics of the vaginal microbiome is vital in shaping treatment protocols for BV. Emerging research not only focuses on antibiotic treatment but also explores other interventions that might help support the return of healthy flora after a BV episode. Approaches such as probiotics or dietary modifications may provide additional layers of protection against recurrence, showcasing the need for personalized treatment regimes that respect the delicate balance of vaginal health.
Changing Perspectives on Bacterial Vaginosis as a Sexually Transmitted Infection
The recent findings from clinical trials have prompted a reevaluation of bacterial vaginosis (BV) as a potential sexually transmitted infection (STI). As research indicates that reinfection from male partners significantly contributes to BV recurrence, healthcare professionals are encouraged to consider the implications of these findings when diagnosing and treating women with the condition. This shift challenges longstanding assumptions about BV and opens the door for more inclusive treatment strategies that focus on both partners.
By acknowledging BV as a potential STI, clinicians can enhance communication with patients about sexual health and the importance of treating male partners. This educational strategy is essential in promoting a shared responsibility for prevention and treatment. Ensuring that male partners are treated and educated about the possible implications of BV can drastically affect overall treatment success and diminish the shame and stigma often associated with the condition.
Challenges in Bacterial Vaginosis Treatment and Management
Despite the promising results from recent studies, there are still significant challenges in the treatment and management of bacterial vaginosis (BV). One major hurdle is the increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistance, which can limit the effectiveness of standard treatments. As BV often recurs, developing new treatment modalities and preventive measures becomes crucial in the face of evolving bacterial populations. Mental health considerations are also critical for patients dealing with recurrent infections, as they can lead to distress, anxiety, and impact personal relationships.
Another challenge lies in patient education and compliance. Women must understand the importance of consistent treatment and follow-up care, which can be hindered by misconceptions about BV. Clinicians should prioritize clear communication regarding the disease process, treatment regimens, and the role of male partners. A collaborative model of care that engages both partners can mitigate some of these challenges, leading to improved outcomes and better long-term management of BV.
The Importance of Comprehensive Education on Bacterial Vaginosis
Providing comprehensive education on bacterial vaginosis (BV) is vital for both prevention and improvement of treatment outcomes. Patients, particularly women, need to be informed about the causes, symptoms, and potential complications associated with BV. Programs that incorporate education about the vaginal microbiome, hygiene practices, and the significance of partner treatment can empower individuals to take charge of their reproductive health and seek timely medical assistance.
Moreover, educating male partners about their role in BV transmission can encourage more proactive involvement in the treatment process. Open discussions about sexual health, understanding how BV may affect both partners, and the necessity of following through with recommended treatments can create a supportive environment that fosters better health outcomes. Ultimately, patient education is a cornerstone in the battle against bacterial vaginosis and its recurrent nature.
Future Directions in Bacterial Vaginosis Research
As the understanding of bacterial vaginosis (BV) continues to evolve, there is a growing need for further research in this area. Future studies should focus on exploring the specific bacteria responsible for BV and how they interact within the vaginal microbiome. This research could lead to more targeted therapies that go beyond standard antibiotic treatment, potentially incorporating probiotics or other microbiome-supporting interventions.
Additionally, expanding the scope of research to include diverse populations can provide valuable insights into racial and ethnic disparities associated with BV. Understanding how these differences manifest in treatment response and recurrence rates can help tailor interventions to various demographic groups. The ongoing collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and public health experts is essential for driving forward innovative solutions that improve the lives of those affected by bacterial vaginosis.
Integrating Feedback from Patients in Bacterial Vaginosis Management
Incorporating patient feedback into the management strategies for bacterial vaginosis (BV) is crucial for developing effective treatment protocols. Patients often have unique insights into their experiences with the infection, which can shed light on the practicalities of treatment adherence and the real-world effectiveness of prescribed regimens. Continuous feedback allows healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans based on patient preferences and experiences, leading to improved satisfaction and outcomes.
Moreover, involving patients in discussions about their treatment can foster a greater sense of agency and partnership in their healthcare journey. Encouraging patients to share their concerns, preferences, and lifestyle factors can help providers tailor interventions to meet individual needs effectively. This collaborative approach ultimately enhances the management of BV and can lead to the development of more effective therapeutic strategies that prioritize patient perspectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most effective treatment for bacterial vaginosis?
The most effective treatment for bacterial vaginosis (BV) typically involves antibiotic treatment, such as metronidazole or clindamycin. These antibiotics help restore the balance of bacteria in the vaginal microbiome. In recent studies, adding treatment for male partners has shown to significantly reduce the recurrence of BV.
How does male partner treatment affect bacterial vaginosis recurrence?
Research indicates that male partner treatment with antibiotics can significantly reduce the recurrence of bacterial vaginosis in women. In a study, women whose partners received both topical and oral antibiotics experienced a 63% lower risk of BV recurrence compared to those whose partners did not receive treatment.
What are the implications of treating male partners in bacterial vaginosis cases?
Treating male partners in cases of bacterial vaginosis is crucial because it addresses potential reinfection. The recent trial highlighted that treating male partners can reduce BV recurrence significantly, suggesting that sexual transmission plays a role in BV and that it should be treated as a sexually transmitted infection.
How can I prevent recurrence of bacterial vaginosis after treatment?
To prevent recurrence of bacterial vaginosis after antibiotic treatment, it is essential to discuss possible treatments for male partners with your healthcare provider. Additionally, maintaining a healthy vaginal microbiome, avoiding douching, and practicing safe sex can help minimize the chances of future infections.
What are the symptoms of bacterial vaginosis and when should I seek treatment?
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis include abnormal vaginal discharge, a strong fishy odor, and discomfort during urination or intercourse. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek treatment promptly, as ignoring them can lead to complications and recurring infections.
What are the side effects of antibiotic treatment for bacterial vaginosis?
Antibiotic treatment for bacterial vaginosis may cause side effects such as nausea, headaches, and a metallic taste, particularly in male partners receiving topical and oral antibiotics. It is essential to discuss these potential side effects with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
How does the vaginal microbiome relate to bacterial vaginosis treatment?
The vaginal microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining vaginal health. Disruption of this balance often leads to bacterial vaginosis. Antibiotic treatment aims to restore this balance, and incorporating male partner treatment may further enhance the restoration of a healthy vaginal microbiome and reduce recurrence.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can aid in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as reducing sugar intake, avoiding douching, using condoms during intercourse, and maintaining good hygiene can aid in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Discussing the potential treatment of male partners can also be an effective strategy in preventing recurrence.
What research supports the treatment of male partners for bacterial vaginosis?
Recent studies, including a randomized trial, suggest that treating male partners with antibiotics alongside women significantly lowers the recurrence rate of bacterial vaginosis. The findings indicate that sexual transmission may contribute to BV recurrence, warranting a shift in treatment paradigms.
Can bacterial vaginosis be considered a sexually transmitted infection?
Yes, recent evidence supports the notion that bacterial vaginosis can be considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI) since male partners may harbor bacteria associated with BV and contribute to its recurrence in women. This perspective underscores the importance of partner treatment in managing BV effectively.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Results | Adding antibiotic treatment for male partners cuts bacterial vaginosis recurrence by 50%. |
| Recurrence Rates | 35% recurrence in partner-treatment group vs 63% in control group. |
| Study Design | Randomized controlled trial with 164 couples; one group received male partner treatment, the other did not. |
| Antibiotics Used | Women received first-line antibiotics; male partners received oral metronidazole and topical clindamycin. |
| Study Conclusion | Male partner treatment is a promising strategy for preventing BV recurrence. |
| Implications for Future Treatment | Treatment of male partners shifts the paradigm in managing bacterial vaginosis. |
Summary
Bacterial vaginosis treatment can significantly benefit from including male partners in the treatment regimen. A recent trial has shown that addressing the male factor in BV management reduced the infection’s recurrence in women. This model of care opens new doors for improving women’s health by considering sexual transmission as an integral part of bacterial vaginosis treatment.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.