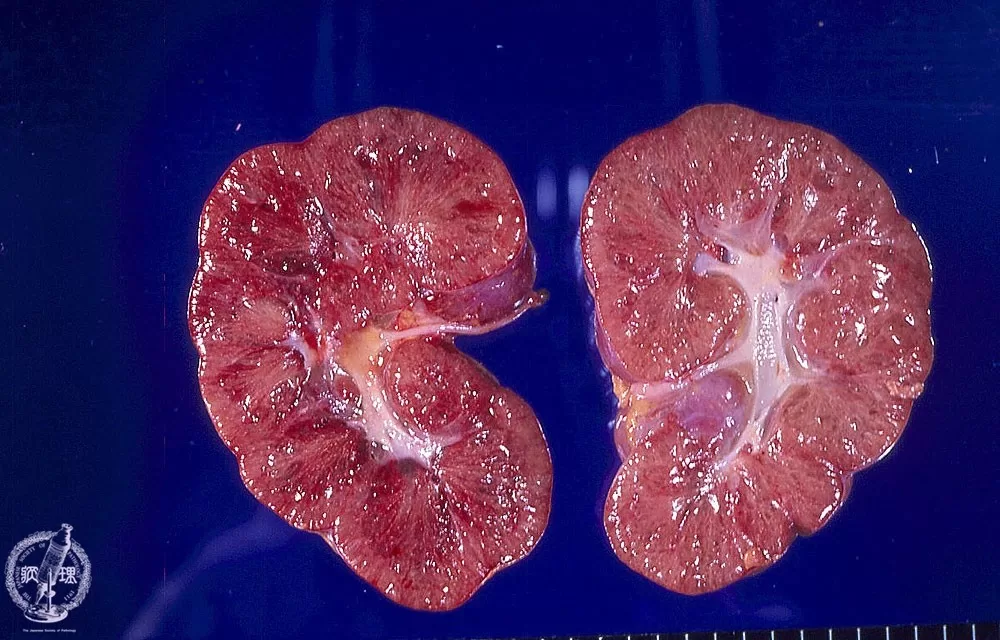
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that significantly impacts kidney and liver function, characterized by the cystic dilation of renal tubules and biliary ducts. This condition arises due to mutations in the **PKHD1 gene**, which play a crucial role in kidney disease diagnosis and understanding. With a prevalence of approximately 1 in 20,000 births, ARPKD often presents early in life, making timely detection vital for effective management. Symptoms may vary, but they typically include enlarged kidneys leading to hypertension and potential liver complications. By raising awareness about ARPKD and its implications, we can enhance early intervention strategies and improve outcomes for those affected by this challenging genetic disorder.
Often referred to as ARPKD, Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease is a serious condition that primarily affects renal and hepatic systems. This genetic disorder leads to the formation of numerous cysts within the kidneys, which can cause significant health challenges from infancy. The underlying cause of ARPKD is linked to mutations in the PKHD1 gene, which are critical for proper kidney function and overall health. Understanding the complexities of this condition is essential for healthcare providers, as it presents unique diagnostic and management challenges compared to other forms of polycystic kidney disease (PKD). By exploring the nuances of ARPKD, we can better equip families and medical professionals with the knowledge needed for effective care.
Understanding the Genetic Basis of ARPKD
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is primarily caused by mutations in the PKHD1 gene, which plays a crucial role in the development of the kidneys and liver. This genetic disorder leads to the abnormal formation of renal tubules and biliary ducts, resulting in the characteristic cystic dilation observed in affected individuals. The inheritance pattern of ARPKD is autosomal recessive, meaning that a child must inherit two copies of the mutated gene, one from each parent, to manifest the disease. Understanding the genetic underpinnings of ARPKD is vital for accurate diagnosis and genetic counseling.
Recent developments in genetic testing have made it easier to identify mutations in the PKHD1 gene, allowing for early diagnosis of ARPKD. This is particularly important as early detection can lead to better management of the disease and its complications. Understanding the genetic basis of this condition can also aid in differentiating it from other forms of polycystic kidney disease, such as Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD), which is associated with different genetic mutations and has a different clinical presentation.
Symptoms and Complications of ARPKD
The symptoms of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) can vary widely, but they often manifest soon after birth. Common renal complications include significantly enlarged kidneys, which may lead to hypertension and renal insufficiency. Additionally, many infants with ARPKD also experience hepatic complications such as congenital hepatic fibrosis, which can severely impact liver function. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for initiating timely interventions that can improve patient outcomes.
Furthermore, respiratory issues can arise due to kidney enlargement, which may compress the lungs, potentially leading to respiratory distress. The variability in symptoms necessitates comprehensive monitoring of affected infants, particularly during the perinatal period. Healthcare professionals should maintain a high index of suspicion, especially in cases with a family history of genetic disorders related to kidney disease, to ensure timely management and appropriate care.
Advancements in ARPKD Diagnosis
Recent advancements in diagnostic imaging have significantly improved the identification of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD). Ultrasound remains the most common diagnostic tool, revealing characteristic findings such as enlarged kidneys filled with multiple small cysts. These echogenic kidneys serve as key diagnostic markers for healthcare providers. Radiological-pathologic correlations are being emphasized in recent studies, enhancing the accuracy of ARPKD diagnosis and enabling clinicians to make informed decisions regarding patient management.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into diagnostic processes has shown promising results in improving the identification of ARPKD. AI technologies can analyze imaging data more efficiently, aiding in the detection of subtle anomalies that may be overlooked by traditional methods. The use of AI in diagnosing ARPKD highlights the potential for technological advancements to enhance clinical awareness and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Management and Treatment Options for ARPKD
While there is currently no cure for Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD), management strategies focus on alleviating symptoms and addressing complications. This often involves careful monitoring of kidney function and managing associated conditions such as hypertension. Medication may be prescribed to control high blood pressure, which is commonly observed in ARPKD patients. Additionally, nutritional support plays a critical role in managing complications related to liver function.
Regular follow-ups with ultrasound imaging are essential for assessing kidney function over time and for making necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Supportive care is crucial for improving the quality of life for individuals with ARPKD, and families should be educated about the importance of early intervention and regular medical check-ups to manage this genetic disorder effectively.
Comparing ARPKD with Other Forms of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Understanding the distinctions between Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) and other forms of polycystic kidney disease, particularly Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD), is essential for appropriate patient care. While both conditions involve the formation of cysts in the kidneys, they differ in their genetic causes, age of onset, and clinical manifestations. ARPKD typically presents in infancy or early childhood, whereas ADPKD often develops symptoms much later in life, usually between the ages of 30 and 50.
The genetic mutations involved also vary; ARPKD is caused by mutations in the PKHD1 gene, while ADPKD is associated with mutations in the PKD1 or PKD2 genes. Recognizing these differences ensures that patients receive tailored interventions and management strategies appropriate to their specific type of polycystic kidney disease. Awareness of these distinctions is key for healthcare providers in delivering effective care and counseling to affected families.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)?
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by cystic dilation of renal tubules and biliary ducts. This condition is linked to mutations in the PKHD1 gene and can lead to significant kidney and liver complications, often manifesting in infants.
What causes Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)?
ARPKD is caused by mutations in the PKHD1 gene, which affects the normal development of renal tubules and biliary ducts. This genetic disorder results in enlarged kidneys filled with cysts, leading to various complications, including hypertension and liver dysfunction.
How is Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests, primarily ultrasound. Ultrasound reveals enlarged, echogenic kidneys, which are key indicators of ARPKD, especially in infants with a family history of polycystic kidney disease.
What are the symptoms of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)?
Symptoms of ARPKD can include significantly enlarged kidneys, hypertension, renal insufficiency, and complications like congenital hepatic fibrosis. Many infants with ARPKD may show symptoms early in life, requiring careful monitoring and intervention.
What treatment options are available for Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Currently, there is no cure for Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD). Treatment focuses on managing complications, such as controlling hypertension, providing nutritional support, and regular monitoring of kidney function through ultrasound imaging.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the kidneys and liver. |
| Genetic Basis | ARPKD is caused by mutations in the PKHD1 gene. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms include enlarged kidneys, hypertension, renal insufficiency, and respiratory distress. |
| Diagnostic Tools | Ultrasound is the primary diagnostic tool for identifying ARPKD, revealing echogenic kidneys. |
| Recent Developments | Advancements in AI and imaging techniques are improving diagnosis and awareness of ARPKD. |
| Management Strategies | Management includes controlling hypertension, providing nutritional support, and regular monitoring. |
| Comparison with Other PKDs | ARPKD is distinct from Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) which presents later in life. |
Summary
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a critical genetic condition that requires thorough understanding and early intervention. This rare disorder, primarily impacting the kidneys and liver, underscores the importance of recognizing symptoms and utilizing advanced diagnostic techniques. With the recent advancements in imaging and artificial intelligence, healthcare providers are now better equipped to detect ARPKD early, which is essential for managing the associated complications effectively. Continued research and awareness are vital for improving outcomes for affected individuals, making it imperative for caregivers and medical professionals to stay informed about this condition.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.