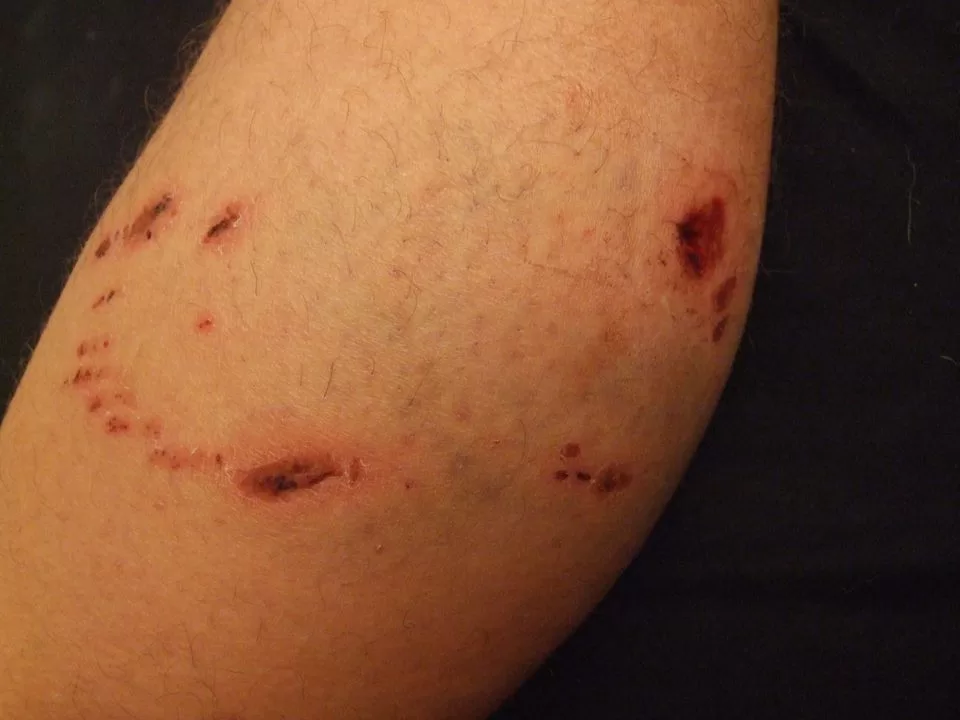
Animal and human bites can occur unexpectedly, making it essential to understand the associated risks and first aid procedures to ensure health and safety. Whether it’s a playful nip from a dog or a human bite during an altercation, these incidents can lead to serious complications, including infections. Recognizing the symptoms of infections and the bite infection risks is crucial for timely intervention. This article will explore the necessary steps for animal bite treatment, highlighting the importance of proper care and when to seek medical help. By being informed, you can effectively respond to bites and minimize the potential for serious health issues.
When we discuss bites, we often refer to injuries caused by the teeth of either animals or humans. These injuries can manifest in various forms, from scratches and puncture wounds to more severe lacerations. Understanding the implications of such injuries, including the potential for infection and the necessary first aid measures, is vital. Whether it’s the playful bite of a pet or a more aggressive encounter with a human, being aware of the appropriate responses and treatments can greatly reduce the risks involved. This content will delve into the nuances of bites, including common symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Understanding the Risks of Animal and Human Bites
Animal and human bites can introduce harmful bacteria into the body, leading to various infections. For instance, when an animal bites, it may carry pathogens in its saliva, which can infect the wound. Common bacteria associated with animal bites include *Pasteurella* and *Staphylococcus aureus*. Similarly, human bites can transmit potentially dangerous bloodborne viruses, such as HIV and Hepatitis B and C, which elevate the infection risks significantly. Awareness of these risks is crucial, especially for individuals who interact frequently with animals or are in environments where human altercations might occur.
In addition to immediate infection risks, bites can lead to complications that require medical intervention. Symptoms like swelling, redness, and discharge signal that a bite may be becoming infected. The severity of the bite, whether animal or human, can escalate depending on the location, depth, and the health status of the individual bitten. Therefore, understanding the potential consequences of bites and the importance of seeking timely medical advice is essential to prevent severe health issues.
Identifying Symptoms of Bite Infections
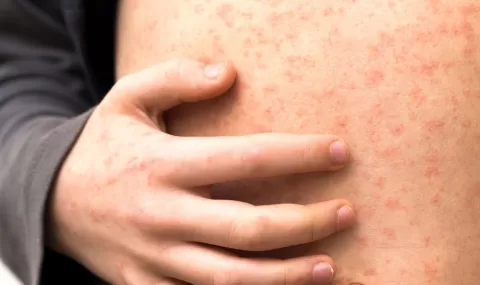
Recognizing the symptoms of infections following a bite is crucial for effective treatment. Common indicators include localized pain, swelling, redness around the bite site, and the presence of pus or unusual discharge. These symptoms may develop within hours or days after the bite occurs, highlighting the importance of monitoring the wound closely. If any of these symptoms worsen or persist, it is vital to seek immediate medical attention to avoid serious complications.
In some cases, systemic symptoms may also arise, such as fever, chills, or general malaise, indicating that the infection may be spreading beyond the local area. Early intervention is key to managing infections effectively; untreated infections can lead to more severe complications, such as abscess formation or systemic infections. Being aware of these symptoms enables prompt action, ensuring that appropriate treatments, such as antibiotics, are administered as soon as possible.
Effective First Aid Steps for Bites
When dealing with animal and human bites, immediate first aid is critical to reducing infection risks and facilitating recovery. The first step is to clean the bite thoroughly with soap and water for at least 5 to 10 minutes, which helps remove dirt and bacteria from the wound. Following cleaning, applying gentle pressure with a clean cloth or bandage can control bleeding, ensuring that the area is stabilized before further treatment.
After initial cleaning and bleeding control, applying an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment can further help to prevent infection. Covering the wound with a sterile bandage is also essential to protect it from dirt and bacteria. It’s crucial to monitor the bite over the next few days for any signs of infection, such as increased swelling, redness, or discharge. If these symptoms appear, consulting with a healthcare professional is necessary for further evaluation and possible treatment.
Special Considerations for Animal and Human Bites
Different types of bites require specific considerations for effective treatment. For instance, if bitten by a wild animal, there is a significant risk of rabies, a potentially fatal disease. Immediate medical evaluation is crucial in such cases, as post-exposure prophylaxis can prevent the onset of rabies if administered promptly. Understanding the type of animal involved in the bite can help healthcare providers assess the risk and determine the appropriate course of action.
On the other hand, human bites often present a unique set of challenges due to the bacteria found in human saliva, which can lead to serious infections. Bites in areas such as the hands or fingers are especially concerning, as they may affect joints and tendons. Medical professionals typically recommend that anyone sustaining a human bite seeks immediate medical attention to assess the wound properly and to consider the need for a tetanus shot or further treatment.
Preventing Bites Through Awareness and Education
Prevention is a key aspect of managing the risks associated with animal and human bites. Educating individuals about the behaviors of animals, especially those that may display signs of aggression or illness, can significantly reduce bite incidents. When children interact with unfamiliar animals, supervision and guidance are crucial to prevent unexpected bites. Furthermore, educating communities about safe practices and potential dangers of human altercations can also help in minimizing risks.
Moreover, educational programs aimed at healthcare providers are essential for improving first aid responses to bite incidents. Training medical students and professionals on recognizing bite risks and managing them effectively can lead to better patient outcomes. Such initiatives can enhance the overall knowledge base regarding bite management, ensuring that communities are better prepared to handle such incidents and reduce the incidence of infections stemming from bites.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the first aid steps for animal and human bites?
For animal and human bites, immediate first aid is crucial. Start by cleaning the bite with soap and water for 5 to 10 minutes to remove bacteria. Apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth to control bleeding. After cleaning, use an antibiotic ointment and cover the wound with a sterile bandage. If the bite is from an unknown animal or shows signs of infection, seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications.
What symptoms indicate an infection from animal and human bites?
Symptoms of infection from animal and human bites can include increasing pain, redness, swelling, warmth around the bite area, and the presence of pus or discharge. If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical care as untreated infections can lead to serious health issues.
What are the risks associated with animal and human bite infections?
Both animal and human bite infections carry significant risks. Animal bites can introduce bacteria like *Pasteurella*, leading to severe infections, while human bites pose a higher risk for bloodborne viruses such as HIV and Hepatitis. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are essential to mitigate these risks.
When should I seek medical attention after an animal or human bite?
You should seek medical attention after an animal or human bite if the wound is deep, bleeding excessively, or shows signs of infection (such as increased redness, swelling, or pus). Additionally, if bitten by a wild animal or if the bite is from a person who appears sick, immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
What vaccination may be required after an animal bite?
After an animal bite, particularly from a wild or unknown animal, a rabies vaccination may be necessary to prevent this potentially fatal disease. Healthcare providers will assess rabies risk based on the type of animal and the bite circumstances, advising appropriate vaccinations if indicated.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of a Bite | A bite is the act of seizing something with the teeth, which can occur from animals or humans. |
| Risks of Bites | Infection risks from bacteria in saliva, potential transmission of bloodborne viruses from human bites. |
| Symptoms to Monitor | Localized pain, redness, swelling, discharge or pus. |
| First Aid Steps | 1. Clean the bite with soap and water. 2. Control bleeding. 3. Apply antibiotic ointment. 4. Seek medical assistance if necessary. 5. Monitor for infection. |
| High-Risk Factors | Unprovoked animals, illness signs in animals, children with unfamiliar animals, confrontational situations. |
| Educational Efforts | Medical training programs are incorporating bite care education to enhance response skills. |
Summary
Animal and human bites can lead to serious health issues if not addressed promptly and properly. Understanding the risks associated with these bites, including the potential for infections and the need for immediate first aid, is essential for everyone. Following proper first aid procedures—such as cleaning the wound, controlling bleeding, and monitoring for signs of infection—can significantly mitigate risks. Additionally, being aware of high-risk situations and the importance of medical consultations when necessary can prevent complications. Stay informed about animal and human bites to ensure safety and effective management of bite incidents.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.